Electro-pneumatic Basics: Time-dependent control with Logic Controller.
1. Introduction
The concept of independent control was already discussed in the previous blogs. In this blog, we focus on creating a circuit that enables time-dependent response of a system using the logic controller. We create a logic controller that resonates the operation of a automatic washing with timer.
In the automatic washing system, a container is submerge to the bath within10 seconds before the next cycle proceeds. We initialized the washing process by pressing the start button while pressing the stop button terminate the process. The cylinder that holds the container does not retracts when the stop button is pressed simultaneously with a running timer. This ensures the washing is done prior to cutting off the process. In the next section, we present the circuit and the logic controller for the process at hand.
2. Circuit and Simulation
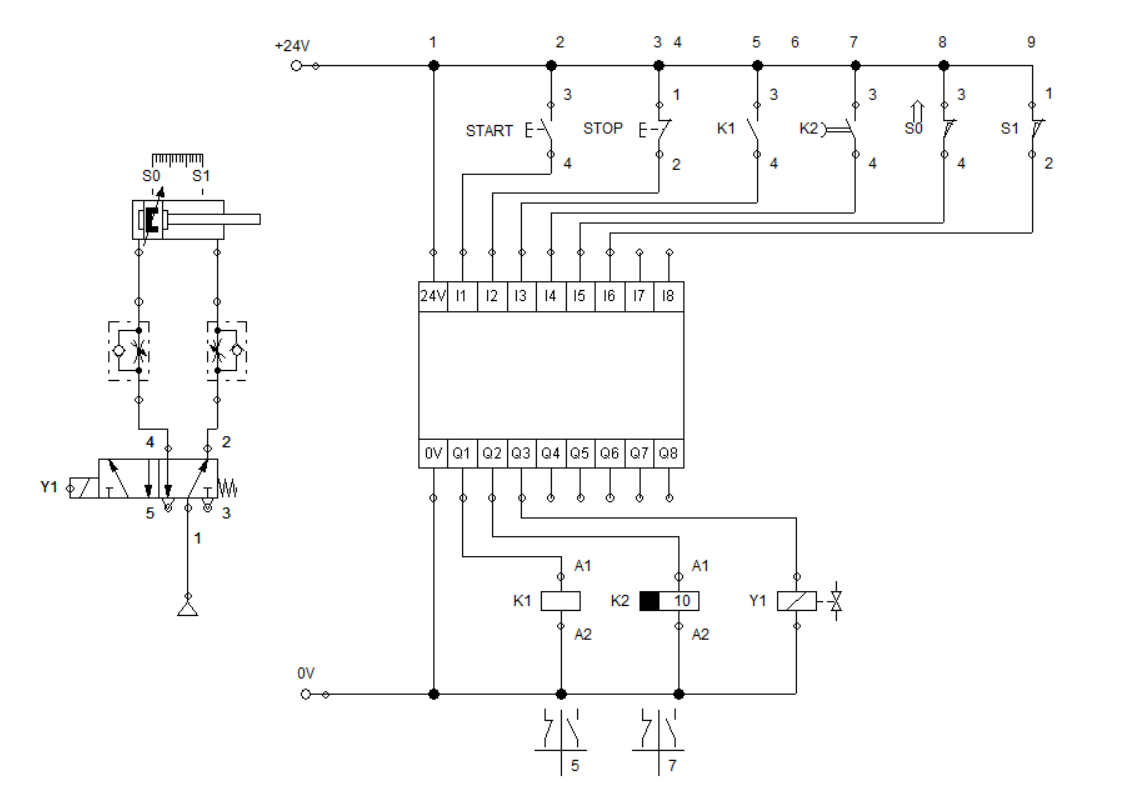
Figure 1: Automating with Timer using Logic Controller
Similar to the previous blog on logic controllers, we start setting up the pneumatic circuit and input and output devices to the logic module. The pneumatic circuit consist of a double acting cylinder (fulfil the washing motion), single solenoid 5/2 way directional control valve ( actuates the cylinder) and a one-way flow control valve ( controls the speed of the cylinder). There are two push button, two contacts, two sensors. The output connected to the logic module are a regular relay, timer relay, and a solenoid valve. The placement of the input and output is shown in Figure 1.
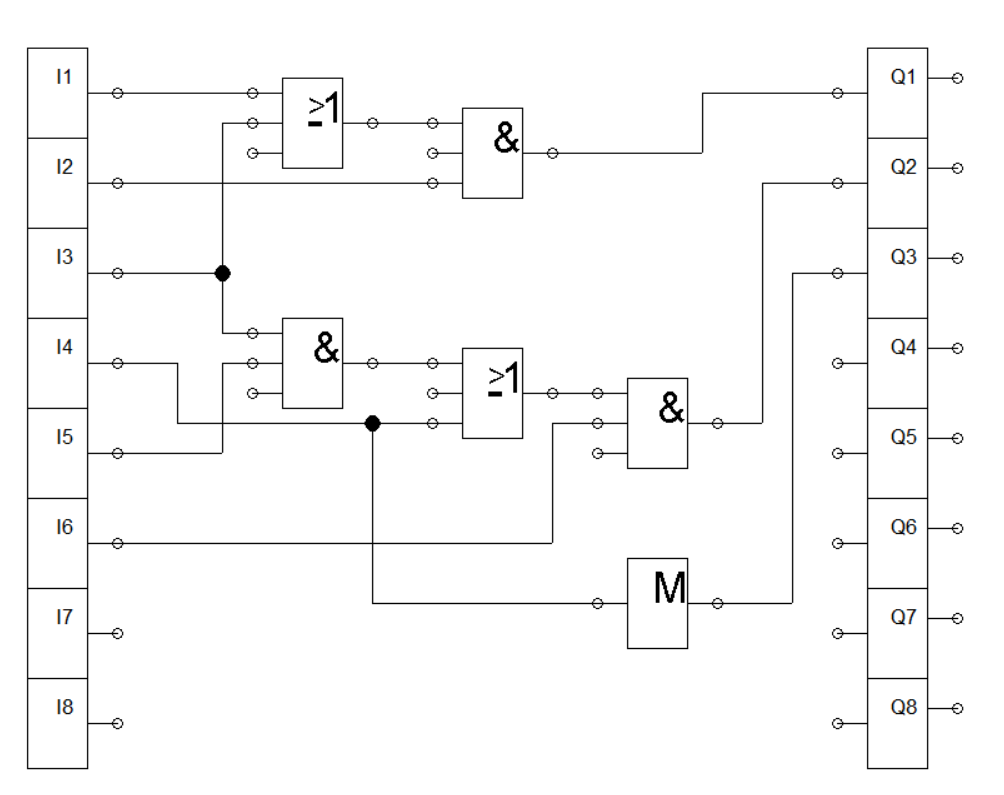
Figure 2: Logic Circuit
In Figure 2, we feed the start button and the contact K1 to an AND gate and the result is connected to an OR gate together with stop button. The first ladder enables the relay K1 to activate when we press the start button. Activating K1 enables timer relay K2 to activate. Once K2 is activated, solenoid Y1 actuates the 5/2 way DCV and the cylinder extends to start the washing process.
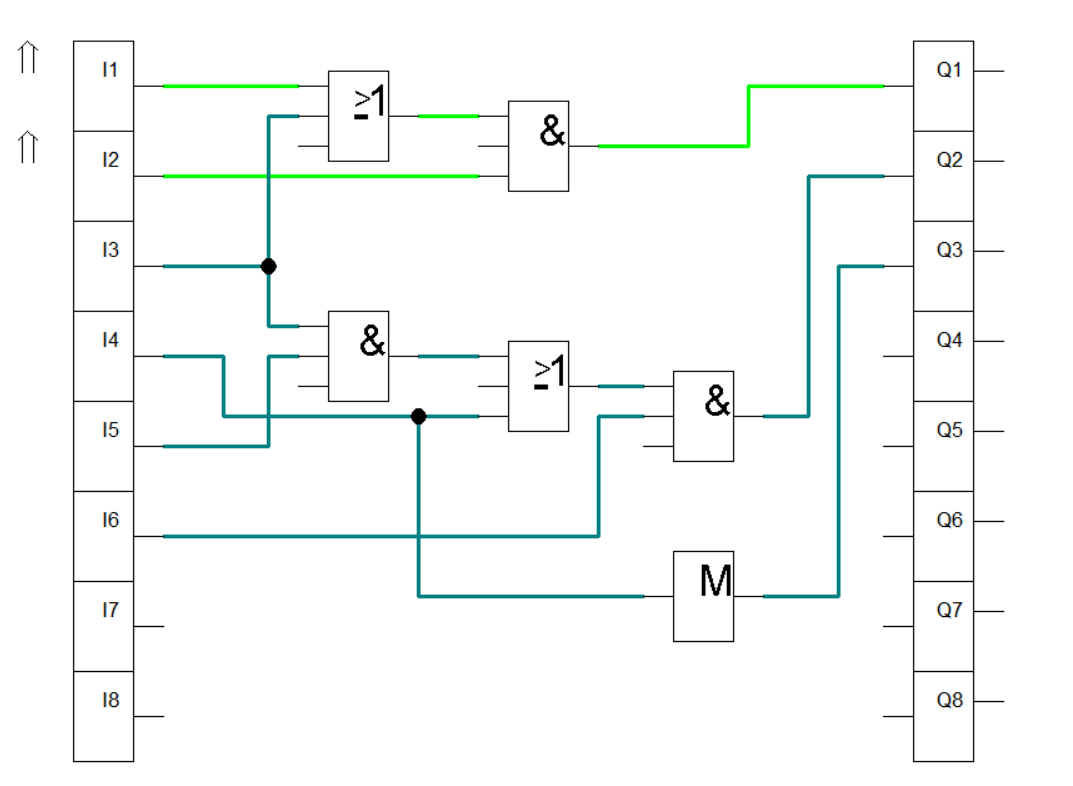
Figure 2: Activating K1
For activating K2, we connect K1 and S0 to AND gate. Afterwards, connect the output of the AND gate to an OR gate together with K2. K2 allows the relay K2 to sustain activation. The combination is then feed to an AND gate together with S1. For solenoid Y1, a buffer with K2 as the input enables the solenoid activation. The logic simulations is shown in the figures.
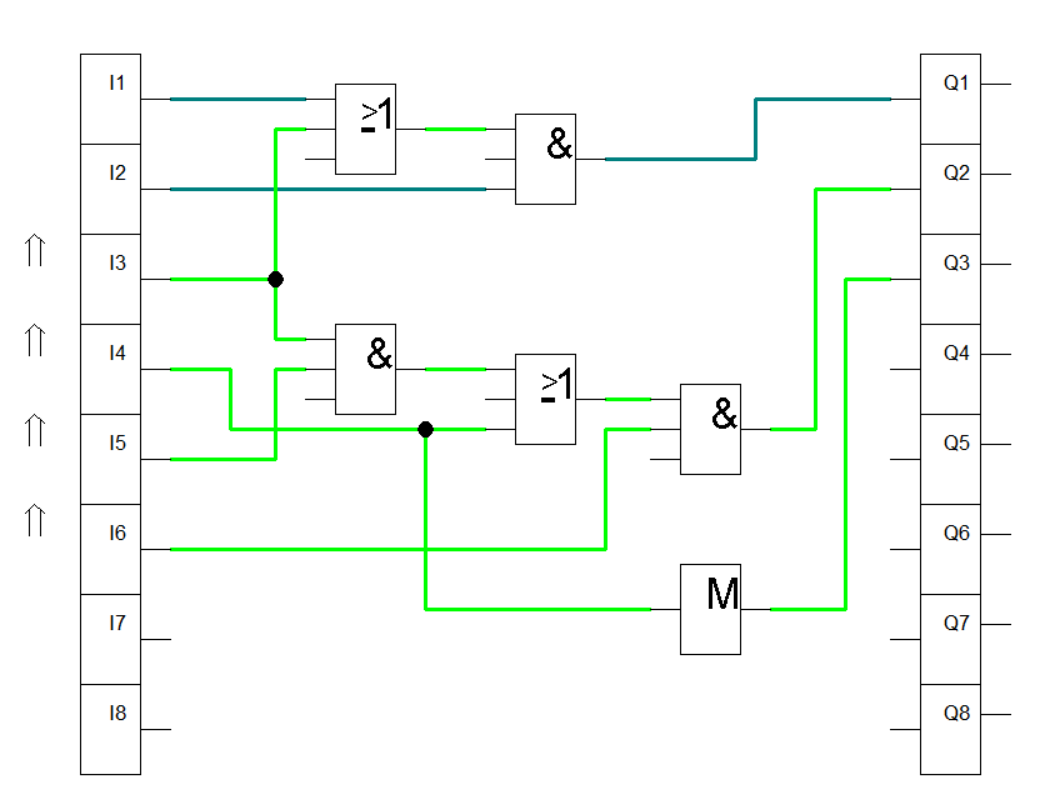
Figure 3: Activating K2 and Y1
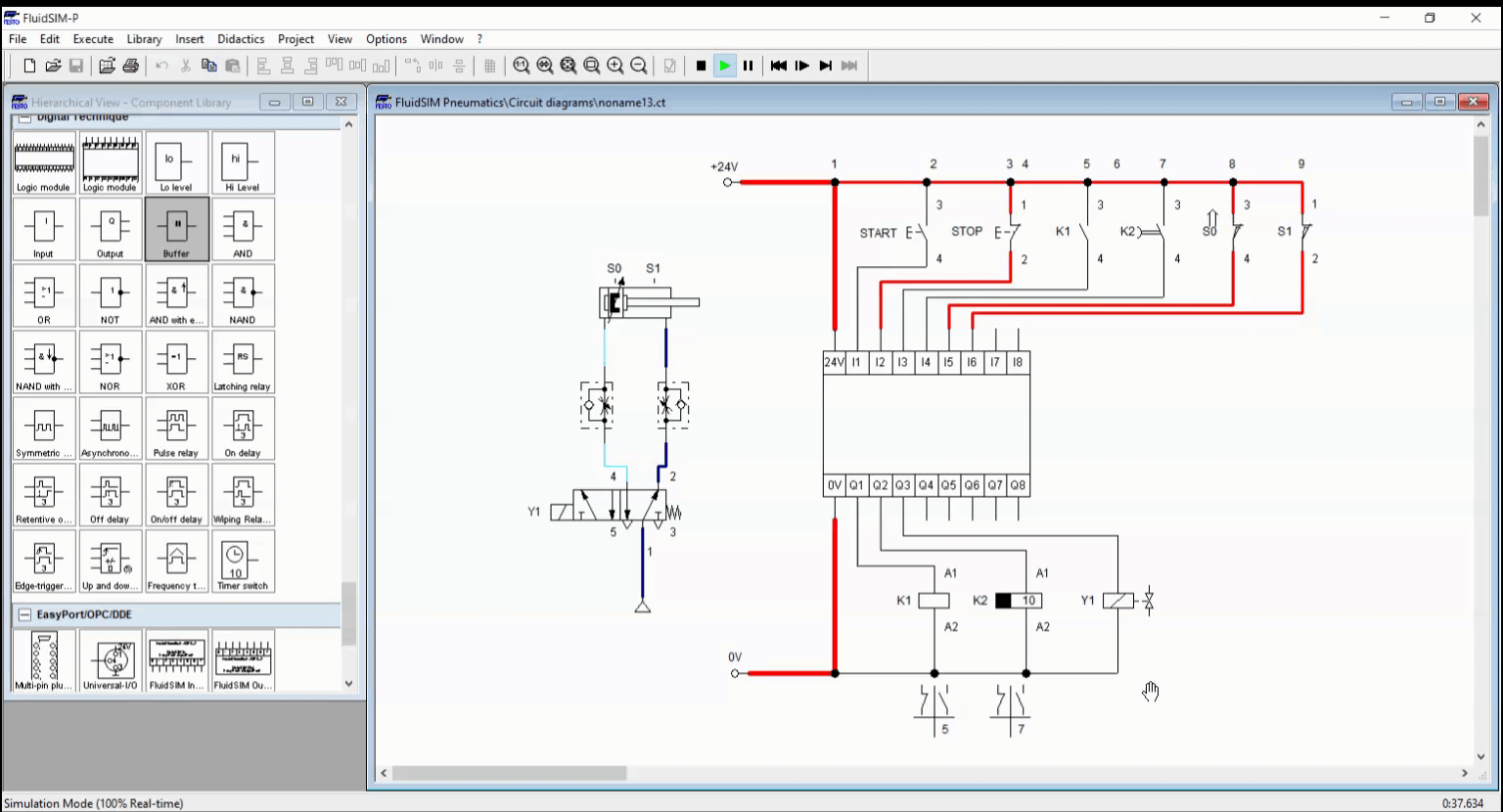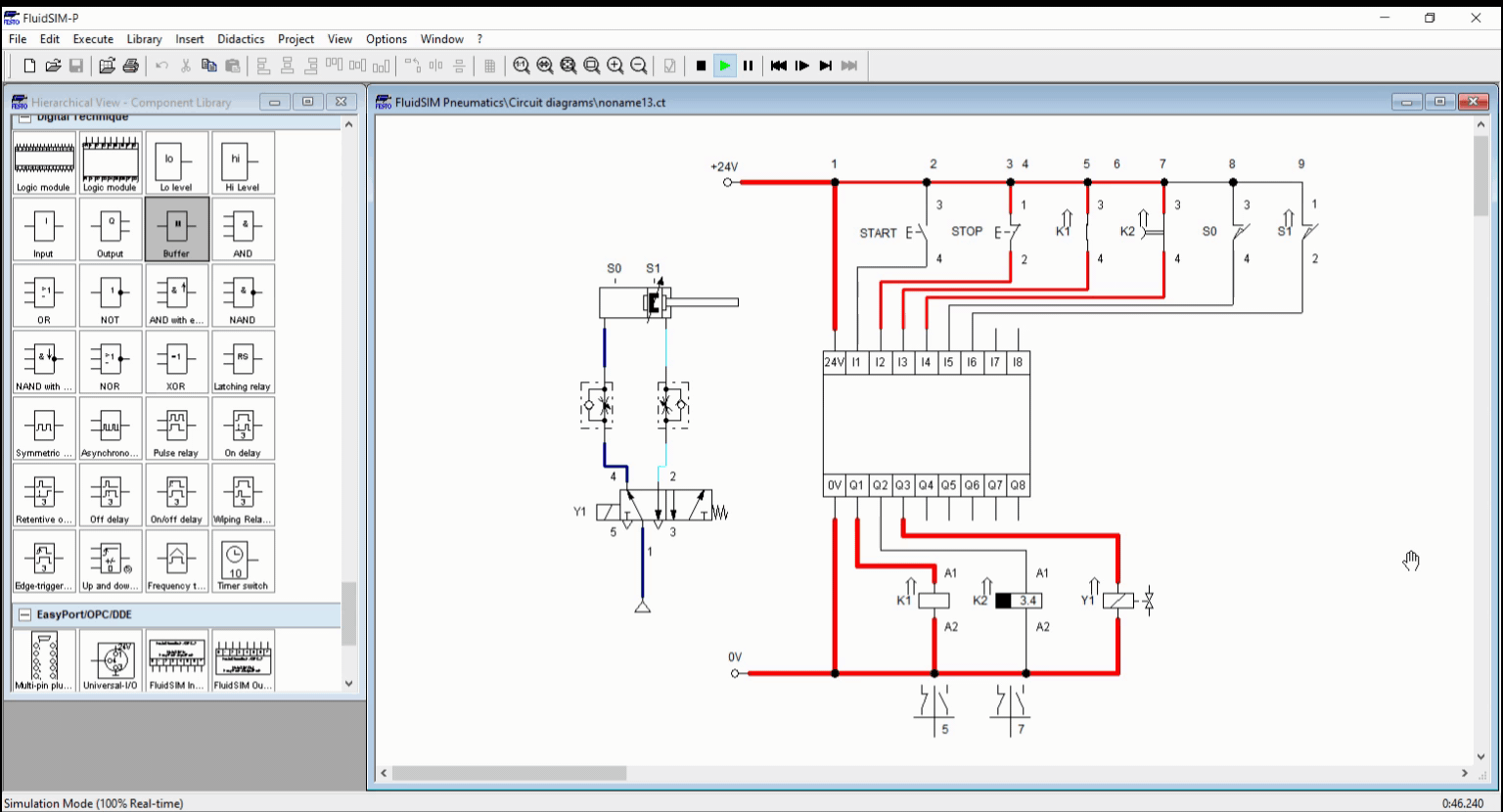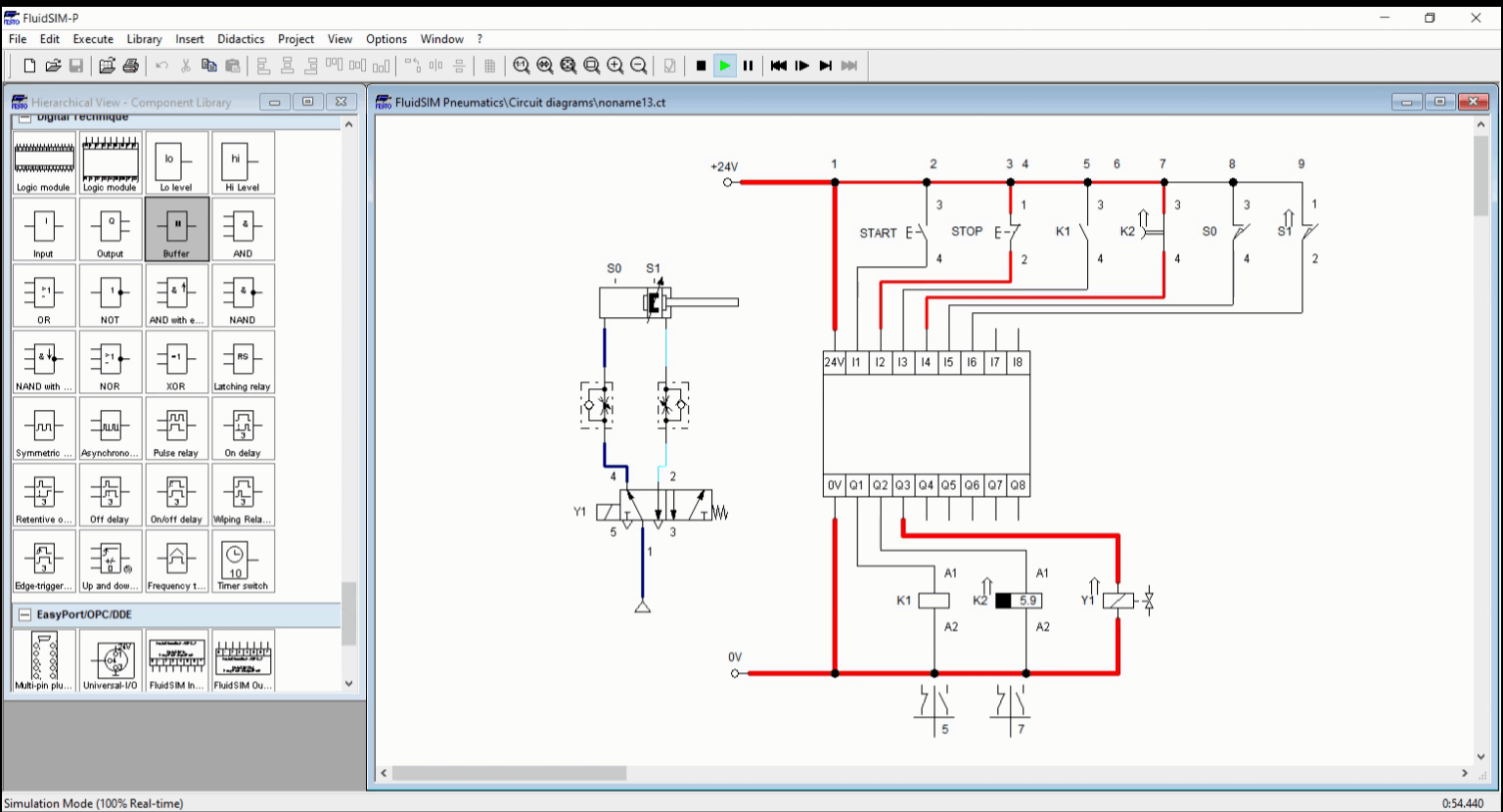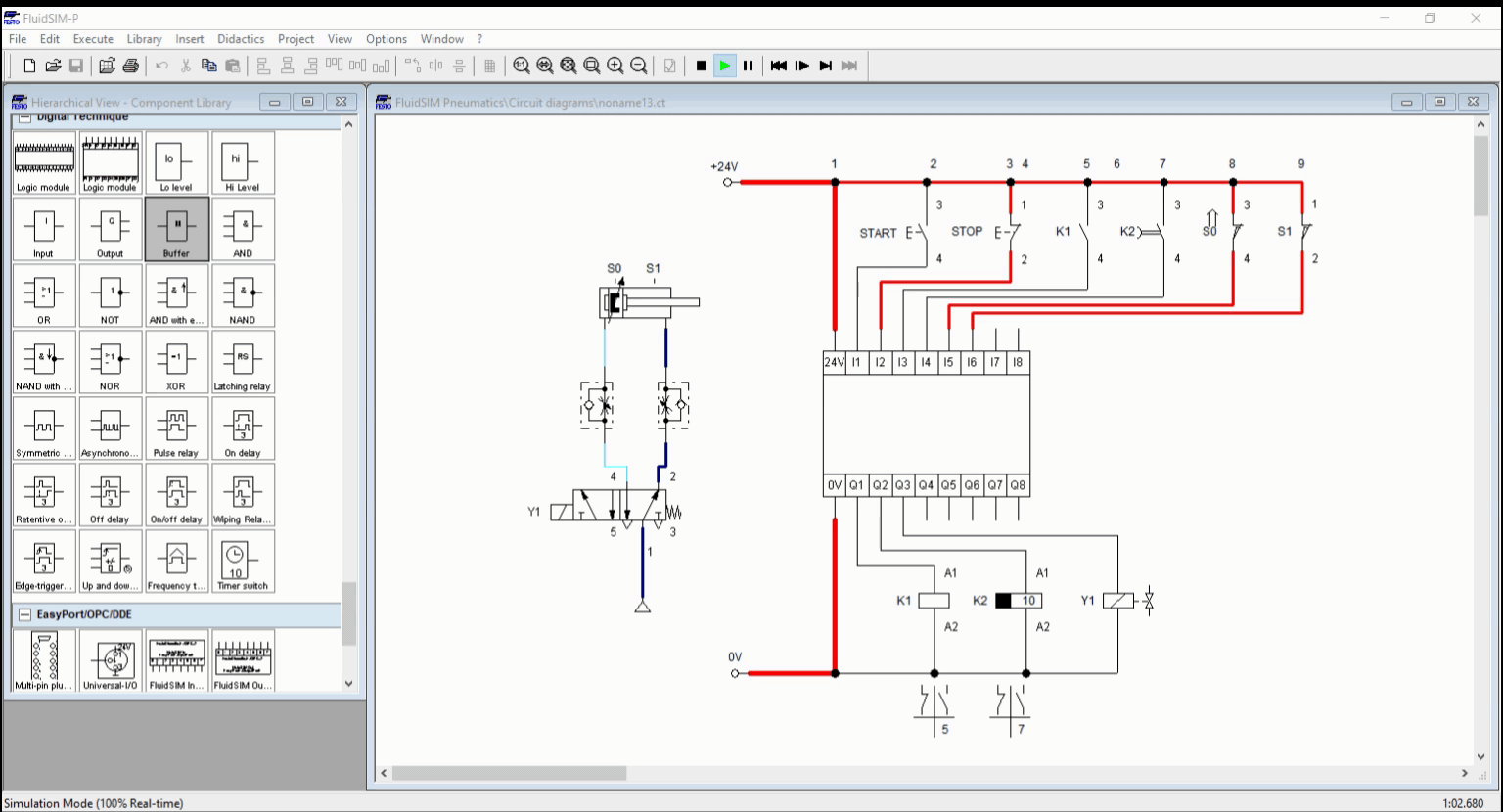
Figure 4: Full Simulation
3. Conclusion
We created a basic automation circuit with time-dependent control, shown in Figure 1. We created a circuit for an automatic washing system with timer using the logic controller. The logic controller coordinates the response of the cylinder with respect to the timer. The timer holds a process to a specific time interval and terminate after the time expires. The process in this blog is continuous unless manually terminated through a stop button.
4. References
[1] Pneumatic Basic Level. online access
[2] Pneumatic Advanced Level. online access
[3] Electro-pneumatic Basic Level. online access
[4] Electro-pneumatic Advance Level. online access
[5] Programmable Logic Controller Basic Level. online access
(Note: All images and diagram in the text are drawn by the author (@juecoree) except those with separate citation.)
If your are Interested in pneumatic and electro-pneumatic system, you can read:
1. Pneumatic Basics: Direct Control
2. Pneumatic Basics: Indirect Control
3. Pneumatic Basics: AND and OR Logic
4. Pneumatic Basics: Memory Circuit and Speed Control
5. Pneumatic Basics: Dependent control
6. Pneumatic Basics: Multiple Actuators
7. Electro-pneumatic Basic: AND and OR Logic
8. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Interlocking, Latching and XOR logic
9. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Distribution of Workpiece
10. Electro-pneumatic Basic: Ejecting a workpiece
11. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Basic Automation
12. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Automation with Counter
12. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Automating with Timer
13. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Cementing Press (Time Dependent Control)
14. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Embossing Device
15. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Bending Device
16. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Introduction to Logic Module
17. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Automating with Logic Controller
18. Electro-pneumatic Basics: Logic Controller for Multiple Actuators
Posted with STEMGeeks