Today's Human Body Molecule #13: Angiotensin II
Molecular weight: 1046
Formula: C50H71N13O12
Angiotensin II is an 8 amino acid peptide formed after the cleaving of 2 amino acids from angiotensin I by the angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) which exists mainly in the lungs. Angiotensin II is a powerful vasoconstrictor and promotes the secretion of vasopressin in the CNS and aldosterone in the adrenal gland. In addition, it increases the activity of the NHE3 exchanger in the proximal tubule. It acts as a hormone. It actes through 2 receptors, the AT1 and AT2. AT1 mediates most of the effects mentioned above
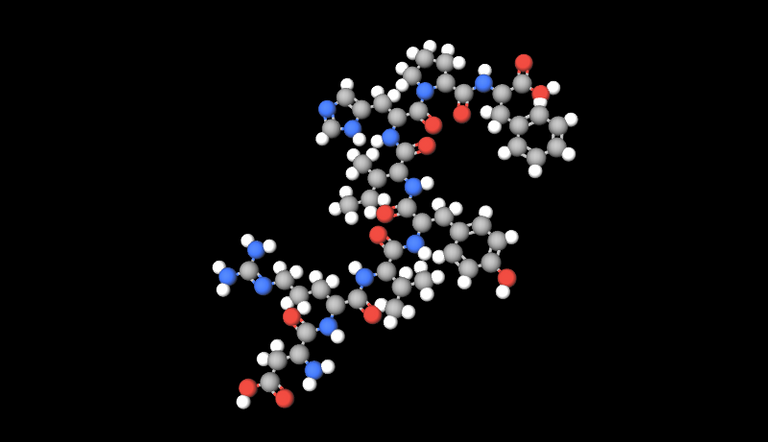
Picture created with molview.org
Gray=Carbon, Red=Oxygen, White=Hydrogen, Blue=Nitrogen
References
Wikipedia contributors. "Angiotensin". Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. Accessed February 14, 2020. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angiotensin
Previous Posts in this Series
Today's Human Body Molecule #1: Urea
Today's Human Body Molecule #2: Creatinine
Today's Human Body Molecule #3: Carbon dioxide
Today's Human Body Molecule #4: Glucose
Today's Human Body Molecule #5: Adrenaline
Today's Human Body Molecule #6: Noradrenaline
Today's Human Body Molecule #7: Dopamine
Today's Human Body Molecule #8: Bicarbonate
Today's Human Body Molecule #9: Adenosine
Today's Human Body Molecule #10: Acetylcholine
Today's Human Body Molecule #11: Serotonin
Today's Human Body Molecule #12: Aldosterone
0
0
0.000
0 comments