Today's Human Body Molecule #7: Dopamine
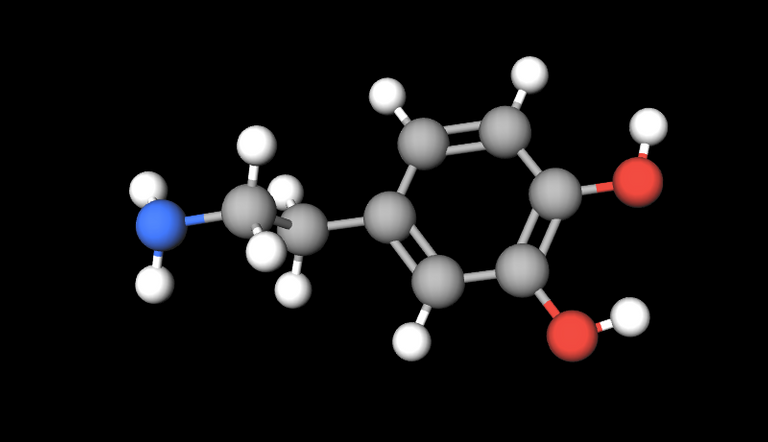
Molecular weight: 153
Formula: C8H11NO2
Dopamine is a molecule which functions as a hormone and neurotransmitter as adrenaline or noradrenaline. It belongs to the family of the cathecolamines and is structurally similar to adrenaline and noradrenaline, having as precursos the aminoacids phenylalanine and tyrosine. Its actions are mediated by D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5 receptors. In addition, it has actions in alpha (α) and beta (β) adrenergic receptors.
As a hormone, mainly as a paracrine messenger it has actions in the vascular system, the kidney, the pancreas, the heart, ans the immune system. As a neurotransmitter it is the main mediator of the reward-motivated response and its deficiency in the substantia nigra (area in the midbrain that produces dopamine ) causes Parkinson's disease.
Dopamine is used to treat some types of shock due its actions in alpha (α) and beta (β) adrenergic receptors.
According to the Bible, What is the proper way of teaching children about the Church??
Comment what you understand of our Youtube Video to receive our full votes. We have 30,000 #SteemPower. It's our little way to Thank you, our beloved friend.
Check our Discord Chat
Follow my Steemit account on https://www.steemit.com/@hiroyamagishi