Renal Tubular Transport #8. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 8 (Sodium/Amino Acid Transport)
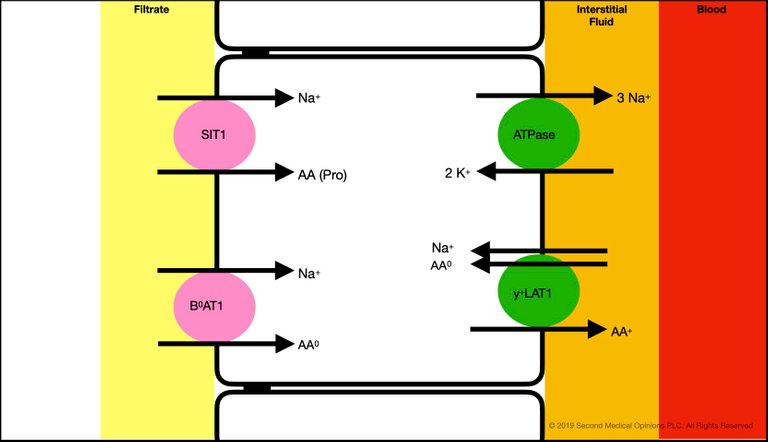
Most of amino acid reabsorption occurs in the proximal tubule. Amino acids are divided into basic (cationic), neutral, and acidic (anionic). The sodium coupled transporters are mentioned in this post and more transporters will be mentioned when the amino acid transport is presented in detail in a future post
Here, we show the following, present in the apical membrane of the S1 segment of the proximal tubule.
- The SIT1 cotransporter, which transports a molecule of proline together with a sodium ion from the tubular filtrate to the intracellular space
- The B0AT1 cotransporter, which transports a molecule of neutral aminoacid together with a sodium ion from the tubular filtrate to the intracellular space
Also, the following, present in the basolaterall membrane of the S1 segment of the proximal tubule.
- The Na+/K+ ATPase
- The y+LAT1 antiporter (exchanger) which brings into the proximal cell an ion of sodium and a molecule of neutral amino acid and releases into the interstitial space a molecule of cationic (basic) amino acid
Renal Tubular Transport #1. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 1
Renal Tubular Transport #2. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 2
Renal Tubular Transport #3. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 3
Renal Tubular Transport #4. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 4
Renal Tubular Transport #5. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 5
Renal Tubular Transport #6. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 6
Renal Tubular Transport #7. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 7
0
0
0.000
0 comments