Renal Tubular Transport #1. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 1 (Sodium/Hydrogen Ion Transport)
(Edited)
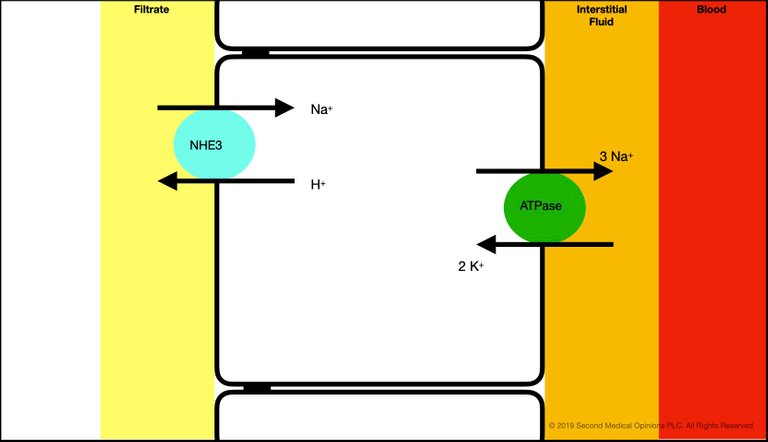
From all the filtered sodium, about 65% is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. The engine of this is the Na/K ATPase at the basolateral membrane of the tubular cell. This is an active transport that requires energy. This ATPase creates the electrochemical gradient that powers the transport through transporters in the apical membrane (where the brush border is), solvent drag and paracellular transport.
Here, we show the following, present in the apical membrane of the S1 segment of the proximal tubule.
- The NHE3 antiporter, which exchanges 1 hydrogen ion for a sodium ion
0
0
0.000
0 comments