Renal Tubular Transport #7. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 7 (Sodium/Glucose Transport)
(Edited)
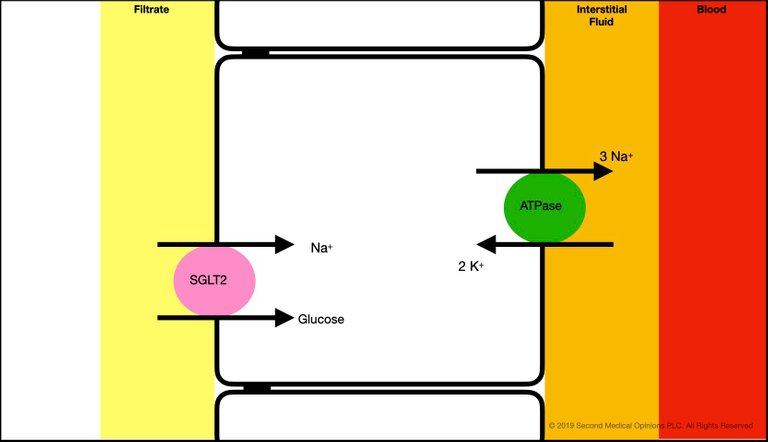
As we I have said before, from all the filtered sodium, about 65% is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. The engine of this is the Na/K ATPase at the basolateral membrane of the tubular cell. This is an active transport that requires energy. This ATPase creates the electrochemical gradient that powers the transport through transporters in the apical membrane (where the brush border is), solvent drag and paracellular transport.
Here, we show the following, present in the apical membrane of the S1 segment of the proximal tubule.
- The SGLT2 cotransporter, which transports a molecule of glucose together with a sodium ion from the tubular filtrate to the intracellular space
Renal Tubular Transport #1. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 1
Renal Tubular Transport #2. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 2
Renal Tubular Transport #3. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 3
Renal Tubular Transport #4. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 4
Renal Tubular Transport #5. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 5
Renal Tubular Transport #6. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 6
0
0
0.000
Hello,
Your post has been manually curated by a @stem.curate curator.
We are dedicated to supporting great content, like yours on the STEMGeeks tribe.
Please join us on discord.