Renal Tubular Transport #14. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Glucose Transport 1
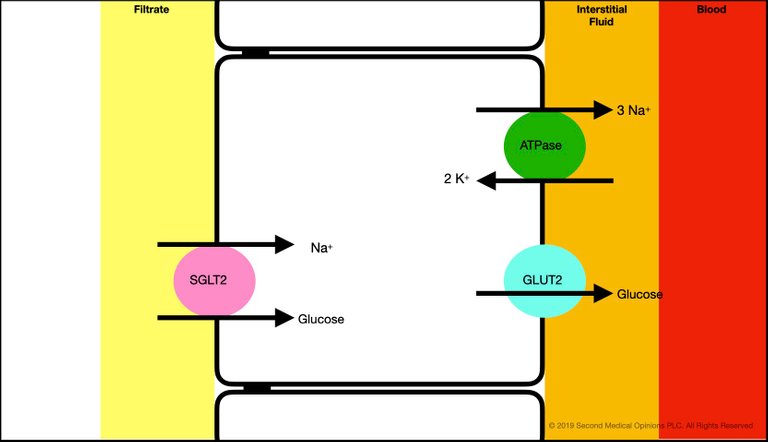
In this post, I show that the glucose reabsorption in the S1 segment of the proximal tubule occurs when glucose enters the S1 tubular cell from the fltrate via the SLGT2 (sodium/glucose cotransporter). Glucose then leaves the tubular cell and it moves from the intracellular space to the interstitial space by facilitated diffusion using the solute transporter GLUT2.
Renal Tubular Transport #1. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 1
Renal Tubular Transport #2. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 2
Renal Tubular Transport #3. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 3
Renal Tubular Transport #4. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 4
Renal Tubular Transport #5. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 5
Renal Tubular Transport #6. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 6
Renal Tubular Transport #7. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 7
Renal Tubular Transport #8. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 8
Renal Tubular Transport #9. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Potassium Transport 1
Renal Tubular Transport #10. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Potassium Transport 2
Renal Tubular Transport #11. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Calcium Transport 1
Renal Tubular Transport #12. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Water Transport 1
Renal Tubular Transport #13. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Magnesium Transport 1
0
0
0.000
0 comments