Renal Tubular Transport #10. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Potassium Transport 2 (Paracellular Transport)
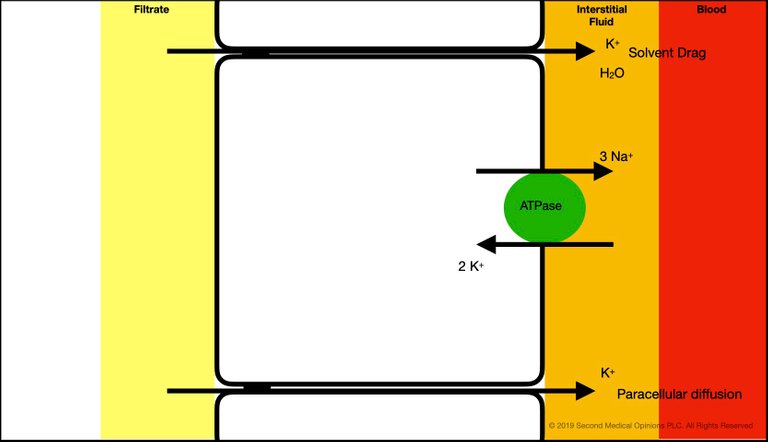
Here, I show the paracellular movement of potassium in the proximal tubule. Up to 65% of the potassium is reabsorbed at this level. The paracellular movement of potassium could be through solvent drag (the majority), which follows the movement of sodium and water. There is another mechanism that uses a change in transepithelial voltage (paracellular diffusion) to favor the reabsorption of potassium around (not through) the tubular cells.
Renal Tubular Transport #1. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 1
Renal Tubular Transport #2. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 2
Renal Tubular Transport #3. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 3
Renal Tubular Transport #4. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 4
Renal Tubular Transport #5. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 5
Renal Tubular Transport #6. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 6
Renal Tubular Transport #7. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 7
Renal Tubular Transport #8. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Sodium Transport 8
Renal Tubular Transport #9. S1 Segment, Proximal Tubule. Potassium Transport 1
0
0
0.000
0 comments