Working With Negative Fractional Exponents (Math)
Hello. In this mathematics post, I will go over dealing with negative fractional exponents. Negative exponents can be annoying to deal with along with fractional exponents that may appear in the form of square roots. This algebra concept is needed as a necessary skill for the algebra toolkit in pre-calculus, calculus.
It is assumed that the reader is comfortable with exponent laws, square roots and fractions.
The math text here is rendered with a lot of LaTeX (lay-tech) along with the use of QuickLatex.com

Topics
- Negative Exponents Review
- Fractional Exponents Review
- Dealing With Negative Fractional Exponents
- Practice Problems With Solutions
Negative Exponents Review
Do remember that with negative exponents you do not include negative numbers. The negative exponent actually represents taking the reciprocal (flipping the fraction).
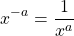
and
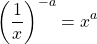
where a is a non-zero number.
If you have a fraction with a negative exponent, you still flip the fraction and apply the (positive) exponent to the numerator and denominator.
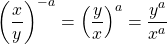
The main reason why answers are written with positive exponents is because of styling and common acceptance.
Example One
Evaluate 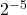 .
.
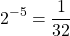
Example Two
Rewrite 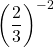 into a fraction with positive exponents.
into a fraction with positive exponents.
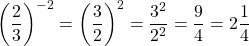
Example Three
Evaluate 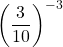 .
.
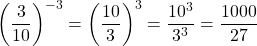
Example Four
Rewrite 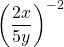 into a fraction with positive exponents.
into a fraction with positive exponents.
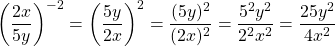

Fractional Exponents Review
It can take some time to get used to the idea of fractional exponents and working with them. A common example that I like to use when I help students with mathematics is the square root. The square root of x for example is actually x raised to the power of one half.
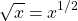
The cubic root has an exponent of one third and can be negative.
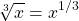
In general, the n-th root can be expressed as 1 divided by n as an exponent. Define n as a whole number.
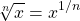
Example 1a
Evaluating 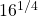 gives 2 as
gives 2 as 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 = 16.
Example 1b
Evaluating 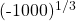 gives -10 as
gives -10 as -10 x -10 x -10 = -1000.
Everything so far in this section dealt with fractional exponents with a numerator of 1. What if we have fractional exponents with numerators greater than one? Let's see some examples.
Example 2a
What is the value of 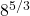 ?
?
When it comes to fractional exponents I like to work with the denominator part of the exponent and take the n-th root first. The third root of 8 is 2. From the two, apply the exponent of five to the two to obtain 32.
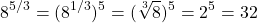
I use the reverse procedure of the power to a power exponent law. Recall that we have:
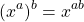
In this example we had:
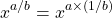
Example 2b
Evaluate 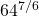 .
.
You could evaluate 64 to the power of 7 first but you could end up with a really large number. Large numbers are annoying to deal with as you have to write more digits and press more buttons on a calculator.
The sixth root of 64 is evaluated first to obtain 2. Then evaluate 2 to the power of 7 which is equal to 128.
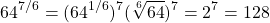

Dealing With Negative Fractional Exponents
So far we have dealt with negative exponents and fractional exponents separately. This section will put it all together.
I generally like to deal with the negative parts from the exponents then deal with the fractional exponents.
Example One
Evaluate 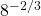 .
.
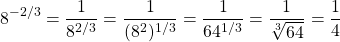
Example Two
What is the numeric value of 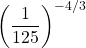 ?
?
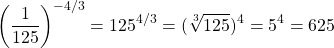
Example Three
Simplify 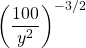 .
.
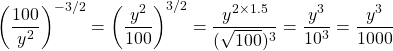
Example Four
Simplify 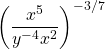 and rewrite this with positive exponents.
and rewrite this with positive exponents.
With this one I simplify the stuff inside the bracket first. Then I apply the negative part of the exponent to obtain 1 divided by the product of x-cubed and y-squared.
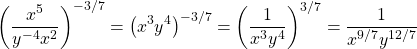

Practice Problems With Solutions
Here are some practice problems for building understanding and to improve algebra speed. Refer to the examples as a guide. For all the questions, simplify the following and express answers with positive exponents.
Question One
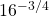
Question Two
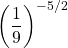
Question Three
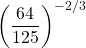
Question Four
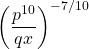
Question Five
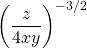
Solutions To Practice Problems
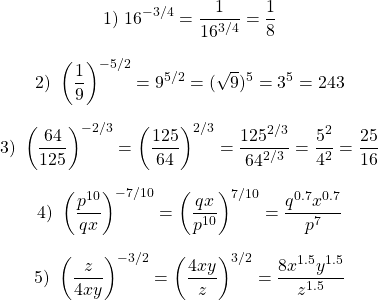
Posted with STEMGeeks