A SIN WE ARE ALL GUILTY OF: ANTIBIOTICS RESISTANCE
 Pixabay
PixabayWhile doing my rural posting, a friend of mine got injured and @babaj went in and got the popular yellow and red capsule. He got Robb and mixed the two together and applied it to the wound. He claimed that his mother used it to treat wounds all the time and the wounds healed properly.
Have you ever wondered about a scenario in which these drugs don't work again because they lose their efficiency?
I am sure your guess is as good as my guess. People will die from small infections and we will be back to the pre-antibiotic era where people died from minor infections.
I will be sharing a live case I was privileged to manage.
She is Mrs. L.M a 30-year-old woman who was in labor for over 24hours and had an emergency cesarean section and delivered a severely asphyxiated male baby who died shortly after birth. She was commenced on antibiotics and had a collection in her abdomen. She also had purulent vaginal discharge and was started on another antibiotic. however, she was not clinically improving. Somehow, the collection spontaneously broke out and 450mls of pus drained out and we decided to take the pus for microscopy and culture. She was totally resistant to all the antibiotics except 1 antibiotic called colistin. This is where I am driving at.
Antibiotic resistance can be very frustrating both to the health giver and the patient.
So what are antibiotics?
Antibiotics are medications that help fight bacteria. However, there is a larger concept, antimicrobials. Antimicrobials are medications that help fight micro-organisms.
The CDC defines "antibiotics as medicines that fight infections caused by bacteria in humans and animals by either killing the bacteria or making it difficult for the bacteria to grow and multiply."
what are bacteria?
They are basically germs that can be found everywhere. They can be found in our environment, in our bodies, on our phones just mention it anywhere.
To have a better understanding of antibiotics resistance we need to know what antibiotics treat. A lot of people use antibiotics for various reasons and have the feeling that the antibiotics worked but in the real sense, the infection just completed its course.
Antibiotics are mainly used to treat infections that are mainly bacterial in origin. Bacterial infections include infections like a sore throat (strep throat), whooping cough, a urinary tract infection, or a sexually transmitted infection.
However, you might come across people who use antibiotics to treat conditions like a common cold, diarrhea, or viral pharyngitis. This is a wrong practice or for a more appropriate word, misuse of antibiotics. A lot of people feel like the antibiotics worked and in the real sense, the condition has completed its course. It is worth noting that antibiotics don't treat viral conditions. Viruses complete their lifecycle and then the infected person gets better.
Are the patient's the only ones guilty of misuse of antibiotics?
The simple answer is a big NO. Patients are guilty, doctors are also guilty big time. Everyone is guilty so don't take it hard on yourself.
So what then is the misuse of antibiotics?
Misuse of antibiotics happens when you fall into one of the following criteria. When a person is prescribed;
- the wrong antibiotic, and this happens when either the doctor or a patent medicine dealer or patient prescribes a drug without having any idea about what antibiotics the bacteria are sensitive to. The resultant effect is clinical deterioration and worsening of symptoms
- the wrong dose of an antibiotic, is mostly the fault of prescribing party and this is one of the major factors that lead to resistance.
- an antibiotic for the wrong length of time; This is in most part the patient's fault as people tend to stop antibiotics when there is symptomatic relief and it ought not to be so. I mean, no one likes drugs, and what is the point of taking drugs when I am feeling better? I am totally guilty of it too... but it ought not to be so.
What is unnecessary antibiotic use?
Sometimes antibiotics are prescribed when they are not needed as I mentioned earlier in cases of all viral infections.
There are some bacterial infections that do not require antibiotics. The body's immune system takes care of them.
When antibiotics are prescribed in the two scenarios stated above, it is called unnecessary antibiotics use of antibiotics.
Both unnecessary use and misuse are major contributors to antibiotics resistance.
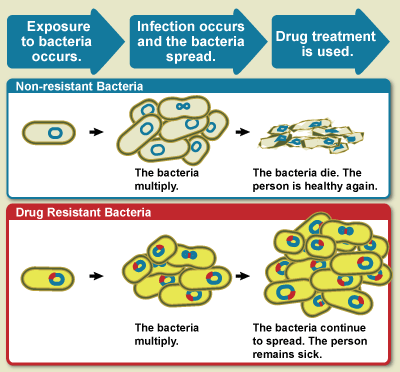
What then is Antibiotics resistance?
By NIAID – NIH - , Public Domain, Wikimedia
Simply put, this is when antibiotics are not able to serve their purpose of killing bacteria or preventing their growth.
It is worth noting that human beings are not the ones that are resistant to antibiotics, it's the bacteria that are resistant and this is where the problem lies.
The problem with resistance lies in the fact that small infections might become fatal and when the particular strain spreads and infects another person, the fight becomes tougher.
What is the magnitude of the problem?
According to the CDC, each year in the U.S., at least 2.8 million people are infected with antibiotic-resistant bacteria or fungi, and more than 35,000 people die as a result. This translates to a mortality rate of 1.25% which means that out of every 100 people who get infected with an antibiotic-resistant bacteria, 1 person dies.
The problem stems from the fact that the numbers are going to rise and if the numbers rise we might go back in time to the pre-antibiotic era where small infections like pneumonia and gonorrhea could kill a patient.
Another problem is that all age groups can be affected and so therefore mortality will affect the children and the elderly more. Those that are chronically ill will also be at risk of death.
There are some countries like my country with poor health guidelines where there is no need for prescription to get antibiotics from a patent drug dealer. These situations will contribute to the increasing number and spread of antibiotic resistance in the world at large.
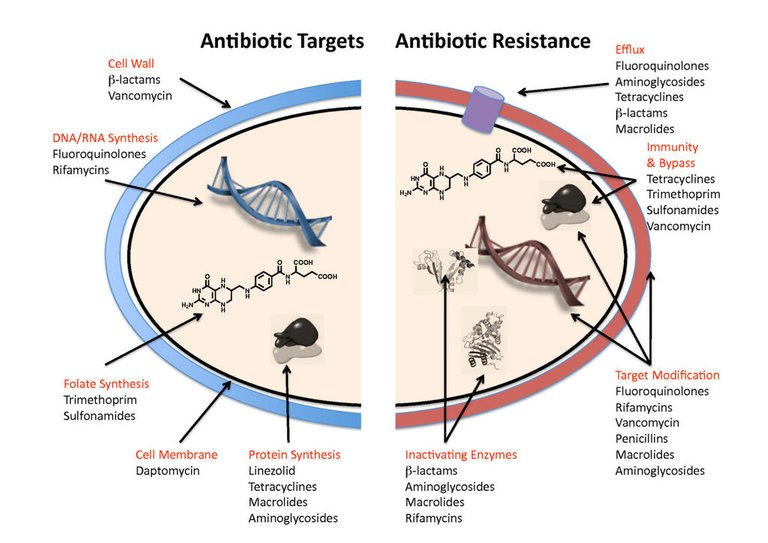
How does antibiotic resistance come about?
By Gerard D Wright - [Biomed central](
 Antibiotic targets and mechanisms of resistance.) See text for details.Wright BMC Biology 2010 8:123 doi:10.1186/1741-7007-8-123Download authors' original image, CC BY 2.0, Wikimedia
Antibiotic targets and mechanisms of resistance.) See text for details.Wright BMC Biology 2010 8:123 doi:10.1186/1741-7007-8-123Download authors' original image, CC BY 2.0, WikimediaHumans have a way of adapting to adverse conditions so do bacteria.
Microorganisms do this by mutation.
Ever seen the movie X-men, they were all products of mutation and they were called mutants. Some of the mutations were advantageous while some were obviously a disadvantage to them.
Mutation in microbiology is just a change in the genetic make-up of an organism. Like I mentioned earlier some of them are protective.
Antibiotics resistance is a protective mutation for the bacteria responsible for preventing it from being killed by antibiotics.
Bacteria have devised different ways of protecting themselves from antibiotics however, some studies have shown that there are 4 mechanisms through which bacteria become resistant to antibiotics. They include;
- drug alteration or inactivation occurs when the bacteria produce substances that change the chemical structure and therefore reduces the effectiveness or totally deactivating the drug. Examples of these substances include beta-lactamases which are responsible for breaking down antibiotics with a beta-lactam ring(penicillin).
- Modification of drug binding site- Some drugs bind to sites on the bacteria called receptors. It's more like a bolt and screw configuration. Each drug has a specific binding site. What happens is this, the bacterium changes the site in which the drug binds to and hence the drug can't fit in and this makes it totally ineffective.
- Reduction in the concentration of the drug intracellularly when drugs eventually get into the bacteria, there is a concentration that is needed for it to kill the bacteria. Bacteria try to find a way of reducing this concentration by either reducing the number of receptors called porins responsible for allowing the passage of antibiotics or increasing the number of pumps that can pump out the antibiotics in the fastest possible time. They either prevent entry or speed up the exit.
- Biofilm formation can be likened to having a protective cover against antibiotics.
In another post, I will be talking about the different mechanism through which antibiotics resistance come about in a detailed manner.
What is the resultant effect of antibiotics resistance?
The bacteria that cause gonorrhea are particularly smart,” Dr. Teodora Wi, medical officer of human reproduction at WHO, said in the report. “Every time we use a new class of antibiotics to treat the infection, the bacteria evolve to resist them.
- One of the major effects of antibiotics resistance is that a growing number of infections – such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, gonorrhea, and salmonellosis – are becoming harder to treat as the antibiotics used to treat them become less effective. I remember my lecturer talking about how his gateman came complaining about gonorrhea-like symptoms and all he had to was give him gentamycin and he became fine. Nowadays, the story is changing.
- The long hospital stays associated with antibiotic resistance can be so bad. This in turn leads to higher medical costs and increased morbidity and mortality. The case I presented above has stayed in the hospital for 40 days and developed depression which necessitated psychiatric evaluation.
How can this disaster be prevented?
I have always believed in the power of educating people as one of the most effective ways to prevent health conditions. So, health education about factors that lead to antibiotics resistance should be done.
Another way of preventing antibiotics resistance is by preventing the misuse and unnecessary use of antibiotics. To further expatiate,
- people should form the habit of only using antibiotics when it is prescribed by a certified health professional
- Individuals should not ask for antibiotics if their health worker does not deem it necessary. A lot of mothers are guilty of this because they want to see results fast.
- Individuals should learn to always follow their health worker’s advice when using antibiotics. Most people are always tempted to use the same prescription when they have the same symptoms. It ought not to be so.
- If infections can be prevented, they should be and this can be done by regular washing of hands, preparing food hygienically following the WHO 5 keys to safer food), avoiding close contact with sick people( what if it's a relative?), practicing safer sex( which includes the use of condoms), and keeping vaccinations up to date(BCG for tuberculosis, PCV for pneumonia, HBV for hepatitis, PENTA for diphtheria, pertussis, tetanus, Haemophilus influenza type B), OPV for polio}.
Policymakers and the government have a huge role to play in preventing antibiotics. Some of the preventive measures include;
- Having a national plan and step-by-step ways to ensure that the plan is executed.
- Improving surveillance of antibiotic-resistant infections by taking statistics and sending them for auditing and also for the purpose of research.
- Policymakers could also help with the funding of projects that are designed to combat antibiotic resistance as it is an urgent public health issue.
- Regulate and promote the appropriate use and disposal of quality medicines.
By CDC - CDC, Public Domain, Wikimedia
Finally, Health professionals have a major role in preventing this disaster and they serve as the main executors of the action plan.
Hand washing, environmental sanitation, and clean instruments are some of the few ways health professionals can help prevent infections. Keeping to the five moments of handwashing will also help prevent the transfer of infection.
- Prescribing and dispensing antibiotics only when they are needed cannot be overemphasized and this prescription should be done based on standard guidelines.
- Antibiotic-resistant infections should be reported to surveillance teams whether they are functional or not.
- Counselling is a continuous process in the management of patients. Talking to patients about how to take antibiotics correctly, antibiotic resistance, and the dangers of misuse will go a long way in preventing misuse and unnecessary use of antibiotics.
I upvoted you, thank you for posting! 👍🏽
Oh man, I have not seen paper culture reports since I was in school.
In my lab, we usually don't report a carbapenem resistant organism (I saw the meropenem was resistant for the E. coli) until we have done repeat testing. Of course, this depends on your protocol and testing method.
But yes, even in my career, I have seen certain organisms becoming more and more resistant.
Oh well, in my centre it happens.
This was like my first in a long time and I was scared because I was attached to the patient so much.
Thank you for stopping by
Good luck, doc.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider supporting our funding proposal, approving our witness (@stem.witness) or delegating to the @stemsocial account (for some ROI).
Please consider using the STEMsocial app app and including @stemsocial as a beneficiary to get a stronger support.
HTTP is in use instead of HTTPS and no protocol redirection is in place. Be careful and do not enter sensitive information in that website as your data won't be encrypted.
It's also a good habit to always hover links before clicking them in order to see the actual link in the bottom-left corner of your browser.