Demystifying the Black hole
Albert Einstein's theory of relativity in simple terms states that "space and time are two aspects of spacetime. Spacetime is curved when there is matter, energy, and momentum resulting in what we perceive as gravity". The links by these forces are explained through Albert Einstein's field equations. Through this theory, Albert was able to forecast the existence of black holes.
In order to understand what a black hole is, I will adopt the defintion of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. According to the body;
A black hole is a place in space where gravity pulls so much that even light can not get out. The gravity is so strong because matter has been squeezed into a tiny space. This can happen when a star is dying.
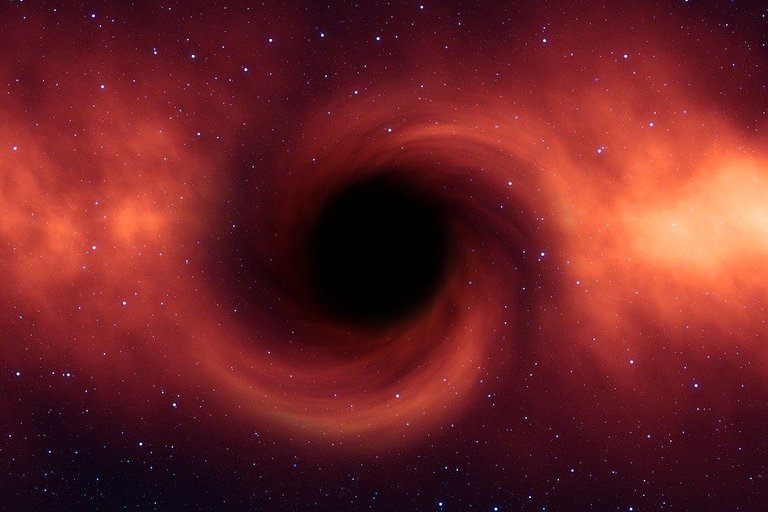

The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can deform spacetime to form a black hole. Despite Einstein's theorizing in 1916, it took over a century before the first-ever recorded image of the black hole was captured, this was done in 2019 and it was the culmination of 2 years worth of work from over 200 scientists. Below are some questions that would help you understand what Blackholes are
Why are they called Black?
Black holes can not be seen because of how far away they are and because gravity pulls all of the light into the middle of the black hole Owing to black holes and how they affect stars and gas around them, scientists can tell if they are around a black hole. They are able to tell this by using telescopes and satellites in space to see the high-energy light, a light that cannot be seen with human eyes. This light is as a result of a fusion between a black hole and a star, at that point in time scientists are able to know the colour.
Why do Blackholes happen?
Black holes come to being when a massive star dies. While the star is dying, its nuclear fuel is exhausted, its core collapses to the densest state of matter imaginable, a hundred times denser than an atomic nucleus. It is so dense that protons, neutrons, and electrons are no longer discrete particles. Since Blackholes can be found when they orbit a normal star, that means they are dark. The properties of the normal star allow scientists to infer the properties of its dark companion, a black hole. It should be noted that it is not every time a star dies that it collapses into a black hole.
Can the black hole swallow the Earth?
The thought of a bottomless devourer of stars is not one that is going to sit pretty with many people. Not to worry, black holes are not the end of the world nor the universe. This can be linked with the fact that the Earth and order planets are in a constant orbit state and if any of them was replaced with a black hole, they would all just keep orbiting. Leaving the only way for it to be swallowed to the Earth's mistake in coming across a black hole and that is never going to happen. In other words, the gravitational pull of a black hole is not stronger than that of a star of the same mass. The only massive black hole in our galaxy, the milky way galaxy, is light-years away.
Any significant structure in a black hole?
The most significant structure in a black hole would be the event horizon, and it represents a barrier that even light cannot get out of. If one happens to be around the edge of a black hole, time dilation and relativistic effects would kick in. For someone who was observing you get eaten by a black hole, they would not notice much because time would appear to be slowing down for you. You on the other hand would not see anything until gravity has finally dealt with you.
Why are we not able to actually see inside a black hole?
Black holes are regions in space where matter becomes so closely packed that nothing is allowed to escape due to the influence of gravity. Black holes use a gargantuan amount of energy to pull any object that comes too close to them, even time and light are not spared. All laws of physics break down at the edge after time comes to a stop here. Though it is unsafe for humans or anything in the universe to be close to a dark matter, Karl Schwarzchild still provides a useful distance from the center of the black hole that anyone should not want to go beyond, he does this through the Schwarzchild radius.
This radius marks the boundary where the speed required to escape the influence of the gravitational pull of a black hole is equal to the speed of light. Beyond this point, matter and light are useless and trapped. This is why no one knows what the inside of a black hole looks like
Can black holes get smaller?
Yes. Blac kholes can get smaller. Stephen Hawking proposed the "Hawking Radiation". It meant that alongside getting bigger because they were eating material, black holes could also slowly shrink because they are losing small doses of energy called "Hawking radiation."
This Hawking radiation occurs because empty space is not empty in whatsoever way. Empty space is a sea of particles continually coming in and out of creation. Hawking showed that if a pair of these empty particles is created near a black hole, there is a high probability that one of them will be sucked into the black hole before it is destroyed. In a scenario like this, the other free pair will escape into space, the energy for this comes from the black hole. Here, the black hole gradually loses its energy and mass.
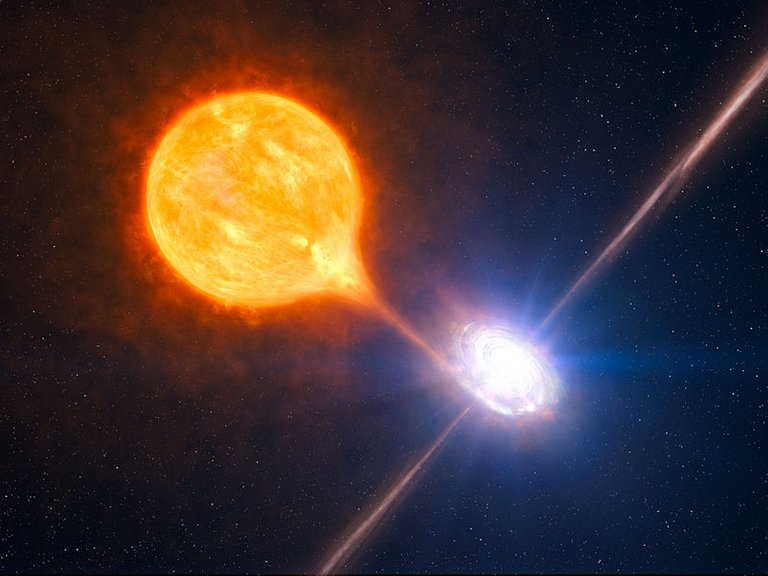
Theoretically speaking, black holes will evaporate through Hawking radiation. However, it would take much longer than the age of the universe for most black holes to significantly evaporate. Black holes, even the ones around the mass of the Sun, will be very much around for a long time.
Black holes are a fascinating discovery of space science, even right from when they were mere postulations by Einstein and other scientists, they have always been intriguing. Seeing that the subject of black holes was confusing for a number of people, these questions were poised at demystifying most confusions around black holes.
Congratulations @aamin! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Your next target is to reach 15000 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPSupport the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider supporting our funding proposal, approving our witness (@stem.witness) or delegating to the @stemsocial account (for some ROI).
Please consider using the STEMsocial app app and including @stemsocial as a beneficiary to get a stronger support.