How to create Color on film
Hello Hivers, this is the third part of my thesis about the creation of color in audiovisual.
You can find my first and second parts, which are the introduction
The color on B&W film
As its name suggests, those films don't capture colors. They only capture luminance variations. As we saw in the introduction, if a t-shirt is white that's because it reflects all wavelenghts. If it is yellow it's because it absorbs blue and reflects red and green.
After prints and treatment appears in white ( or transparent ) what reflects all wavelenghts and appears in black ( or opaque ) what doesn't reflect any wavelenghts ( or few ) and in more or less dark shades of grey proportionally to the number of wavelenghts reflected for the rest.
Quickly to fix that, appeared the sepias prints.
These prints' goal is to replace the shades of grey with shades of brown. The film stays monochrome but we get some color that warms up the image and gives some comfort to the spectator.
Another technique had been used just since 1985, the cinema's creation's birth date. This technique is the brush painting which we can see on some Méliès' movies.
This technique is pretty simple to realize but really long and tedious to implement. This consists on painting with a brush on the film's positive the object you want to color, frame by frame. And if you want to have several copies of the movie, you need to paint each of them.
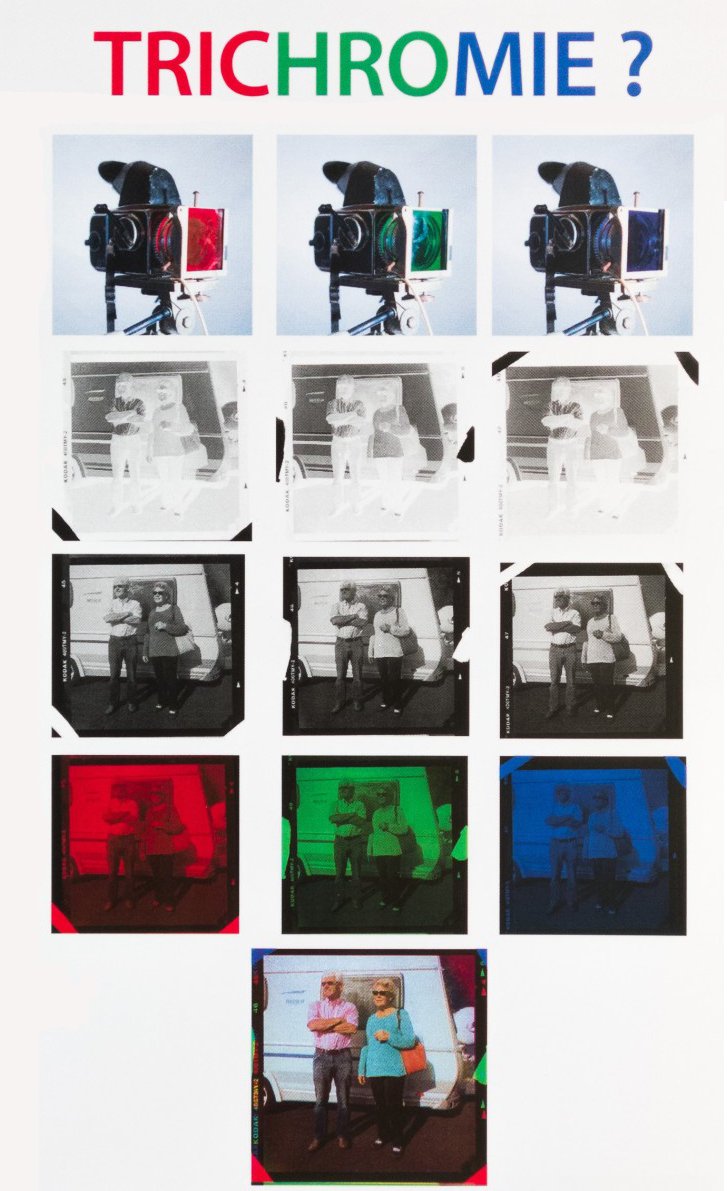


The last way to create Color on black and white film is the Trichotomy :
This process is more expensive, you need to have a camera compatible with prisms to deviate light's colors, colored filters, one for each of the three films to impregnate them with only one hue and three film's storages.
For each frame the camera will deviate the colored lights on three different films, one for the green with a green filter, one for the red with a red filter and the same for the blue one.
In the case you juste want to photograph with a standing subject you can take three pictures with a different filter each time.
On the final picture we can see that the woman's top looks cyan. On the red frame with no filter we can see that here it's dark while it's brighter on the green and blue ones, conversely the skins of the character are bright on the red and dark on the blue and green.
Once the film's have been print, we screen the movie with three projectors, one for each color, with the adequate filter. Thanks to the Additive Synthesis, when overlapping the colored lights, we obtain their mix, here the original color of the subject.
Especially for this exemple,we need to keep in mind that the final color is the result of several steps that all need to be perfect. If on of these step is failed or made with a bad equipment then the final result will be altered.
On color film
The innovation of the color film is that it lets capture red blue and green simultaneous on the same film.
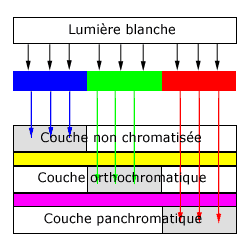
On this color film cross section we can see that three layers are placed to be impressed with only one color for each.
The first layer is sensitive to the blue color and creates yellow crystals if impressed by some blue light. Under it there is yellow filter to prevent blue ray to go further and impress the lower layers.
The second layer is sensitive to blue and green rays and creates magenta crystals when impressed. There is no more blue light so only the green rays impress it. There is a magenta filter underneath it to only allow the red rays to pass through it.
After the magenta filter that cut the green rays, the last layer is sensitive to all colors but only receive red rays. It creates cyan crystals when impressed. With Soustractive Synthesis we can know how objects will appear on negative films.
If we film the three usual exemples de get :
- The red table impress the red sensitive layer and appears cyan on the film.
- The green chair impress the second layer, sensitive to green, and appears magenta on film.
- The magenta cushion impress the blue and red sensitive layers. It will be a mix of yellow and cyan, that will make it appear green.
After the positive print the colors change and become again the real colors. For the projection, only one projector with white light is needed to watch the movie with colors. Once again the quality of the image depends of the quality of the film and the image development. Each manufacturer has their own specificities, Kodak shows a red tint on their film while Fuji has a yellow tint on their own.
The next post will be about color with numeric cameras, it will be way longer, more detailed And will have more mathematics and physics.