Essentials basic of the function of the straight line // Analytical Geometry
Introduction
In this opportunity I share of basic and academic form on the content of the function of the straight line, which is a part of the analytical geometry, dese his considerations and for which it is a linear function.
Basic Essentials
This linear function that it is a part of the equation of the straight line, is considered inside the set of functions of real variable because they are defined by the set of real numbers: f = A-R, AcR.
The escuacion of the straight line is defined by the equation and =mx+b, where m represents the slope, x is the dependent term and b is the independent term, also where it goes to cut the above mentioned straight line, but that must be known about this equation, the following thing, this straight line obtained by the equation previously renowned can be represented in a plane it is, which is in turn can relate use of the system of Cartesian axes, determined by the function of the variable already defined for this case of function of real variable, that must satisfy each and everyone of the points that constitute the above mentioned line.
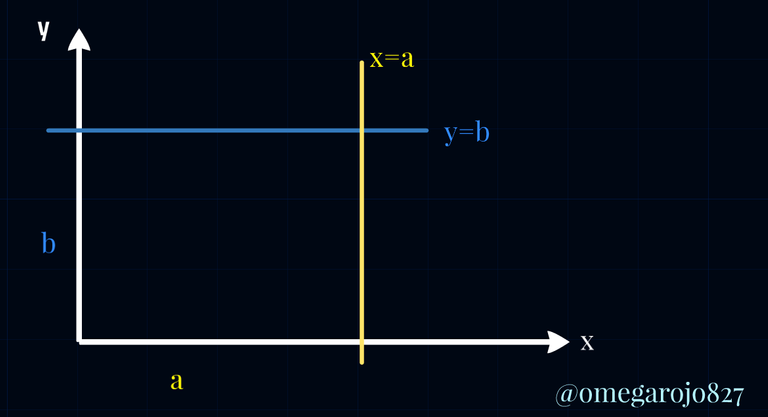
In the siguente example we can observe that doing a line in parallel happiness, what in case of the distance b and of to, remaining clear that it expires for the values in "x" and in "y" constantly equally to b, where the equation of this straight line parallel is defined for y=b and for x=a, an important fact if the value in b is positive locates the first quadrant of the system coordinated Cartesian, import analysis for yourself it is the following one to chart a straight line as minimum two points are needed.
For the case where the equation of the straight line happens for the origin of the system of coordinated Cartesian, in this situation it is when the equation the term of earring b = 0 and the equation can define it and = mx, where it is assumed that b = 0, having knowledge that with this independent term we know where the straight line happens, we know that, it is said to 0 that it happens for the origin, in such a way that an equation of the first grade is established for two variables.

Continuing in this order of ideas we have now the case of the earring of the straight line, pear to have a better analysis we will use as example the previous equation to continue in tuning with this content, we already have the equation defined for y=mx of the straight line, in such a way that it can it represents from the point of the origin a positive angle, which has sense with regard to the axis of x, where it is possible to take any point of this straight line, the points are marked P (x, y), with the sense of planning linear one for form a triangle rectangle, to be able to define a trigonometric function I enter of her using the angle represented so A = y/x; something that we cannot forget dividing dela definite function dela equation dela straight is y=mx, where m=y/x, but thinking that from the origin we have this raisin left the following thing: so A =m.

For that sele names earring it owes to the following thing, being based on the tangent trigonometric one of the angle of inclination of the straight line of the definite function, thanks to her it is possible to control the biggest or minor inclination with regard to the axis of x, to the moment to give him the values of cross-check of the definite equation, since it has a value of form of coefficient assuming the trigonometrical reasoning of the angle, which goes to be according to x of the equation of y=mx as part of term dependent on this function, recapturing if the case they were for two a straight line parallel it should have the same slope m1 = m2, I hope that this content of analytical geometry should be of his taste in reference dela equation of the straight line.
Bibliographical Consultations
Analytical Flat geometry for Hugo Lázaro Manrique - 1999.
Analytical geometry for Joaquín Ruiz Basto - 2014.

Thanks for your contribution on the equation of the straight line as part of analytical geometry
Thanks for your contribution