What is nuclear fission and how energy is generated through it?
Nuclear fission is the process of splitting the nucleus of an atom into two or more smaller nuclei. This process releases a large amount of energy, which can be harnessed for a variety of purposes, including the generation of electricity.
The process of nuclear fission was first discovered in the late 1930s by scientists working in Germany and the United States. It was later developed into a practical technology during World War II as part of the Manhattan Project, a secret US government program to build the first atomic bomb.
Nuclear fission is a type of nuclear reaction that occurs when the nucleus of an atom is split into two or more smaller nuclei, releasing a large amount of energy in the process. The energy released in nuclear fission comes from the binding energy that holds the nucleus of an atom together. When the nucleus is split, some of this binding energy is released, and this energy is what powers the fission process.
There are several different types of nuclear fission reactions, but they all involve the same basic process. When a nucleus is struck by a neutron, it can either absorb the neutron or it can be split into two or more smaller nuclei. If the nucleus absorbs the neutron, it becomes unstable and can then split into smaller nuclei. The smaller nuclei that are produced in a nuclear fission reaction are called fission products.
The energy released in a nuclear fission reaction is very large. In fact, it is millions of times greater than the energy released in a chemical reaction such as the burning of coal or oil. This makes nuclear fission a very attractive source of energy, as it has the potential to produce a large amount of electricity with a relatively small amount of fuel.
However, there are also some significant drawbacks to nuclear fission as a source of energy. One of the biggest concerns is the production of radioactive waste, which is a byproduct of the fission process. Radioactive waste can be harmful to people and the environment, and it can remain radioactive for thousands of years. Additionally, there is the risk of a nuclear accident, such as the one that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi power plant in Japan in 2011.
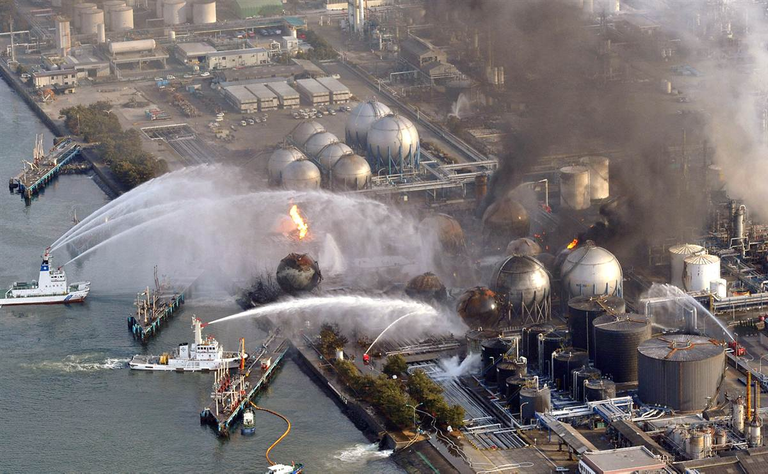

The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident was a catastrophic failure that occurred in Japan in 2011. The accident was caused by a powerful earthquake and a subsequent tsunami, which damaged the power plant and caused a series of nuclear meltdowns.
Despite these risks, many countries around the world continue to rely on nuclear fission as a source of electricity. It is a complex and controversial technology, but it remains an important part of the global energy mix.
Nuclear energy currently accounts for about 10% of the world's total electricity production. Some countries, such as France and Belgium, generate more than 50% of their electricity from nuclear energy, while others, such as Germany and Switzerland, have decided to phase out nuclear power entirely.
There are several reasons why some countries rely heavily on nuclear energy. One reason is that nuclear power plants can generate a large amount of electricity using a relatively small amount of fuel. This makes nuclear energy a cost-effective source of electricity in some cases. Additionally, nuclear power plants do not produce greenhouse gases or other air pollutants, which makes them an attractive option for countries that are looking to reduce their carbon emissions.