Artificial intelligence to discover new gravitational lenses
Source
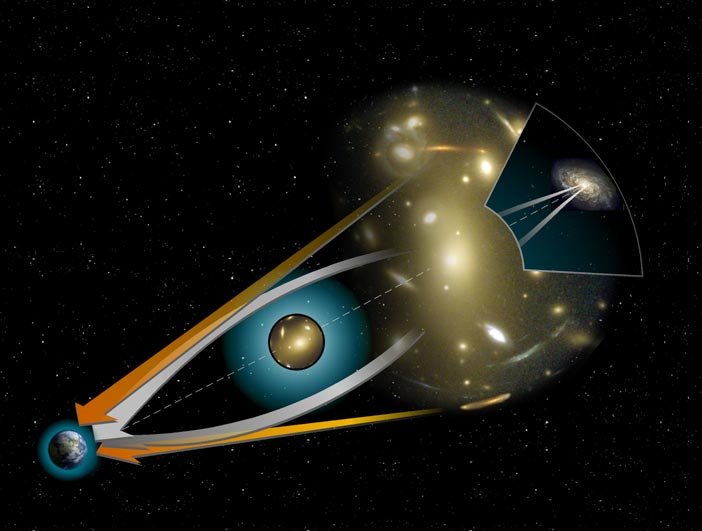
In astrophysics a gravitational lens is formed when light from distant and bright objects curves around a massive object, located between the emitting and receiving objects, allowing us to see objects that should be hidden.
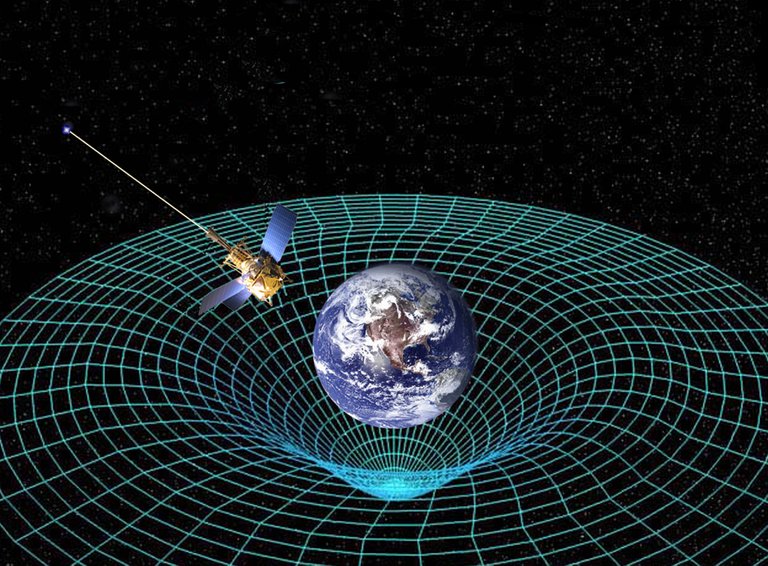
This phenomenon is one of the predictions that arises from Einstein's Theory of General Relativity and was first verified in 1919 by Arthur Eddington, comparing the position of some stars during an eclipse of the sun and at night.
The objects that make up these lenses are usually galaxy clusters that, due to their large mass, greatly curve space-time, producing an effect similar to that of a gigantic magnifying glass.
Source
Despite the hard work of identifying these types of phenomena by manually scanning the data obtained by telescopes, hundreds of these strong gravitational lenses have now been identified.
From now on, thanks to artificial intelligence, many more lenses can be located just by searching among the existing images taken by the telescopes.
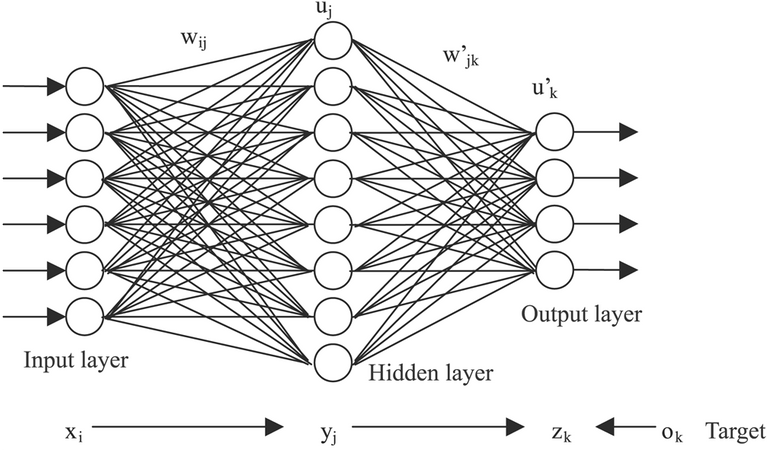
A group of scientists at the University of San Francisco developed a neural network that they trained with data from 432 known gravitational lenses and more than 9,000 non-lens cases.
Source
From here, new data can be given to the neural network, which will be proposing candidate cases that are later verified by specialized scientists.
In the end, artificial intelligence is sneaking into our lives, for increasingly diverse uses.
More information:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitational_lens
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/05/200514143600.htm


Versión en español