Funciones seccionadas o escalonadas//Sectioned or staggered functions
Las funciones seccionadas son aquellas que están compuestas por funciones individuales/Sectioned functions are those that are made up of individual functions.
La siguiente función representa a una función individual
This is a function represents an individual:
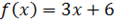
Cuando se agrupan varias funciones individuales en una sola función da como resultado una función seccionada.
When multiple individual functions are grouped into a single function it results in a sectioned function.
Consideremos las siguientes funciones individuales/Let us consider the following individual functions
f(x)= -3 si x ≤ 0 y f(x)= x+1 si x > 0
Ambas funciones pueden ser integradas en una sola función así:/Both functions can be integrated into a single function like this:
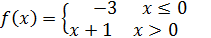
Observe que este tipo de función toma diferentes formas dependiendo de la ubicación de los valores de x en su dominio./Note that this type of function takes different forms depending on the location of the x-values in its domain.
Veamos el Dominio de esta función/Let's see the Domain of this function
Observe que los valores de x están determinados por dos intervalos, el primero de ellos consta de todos los valores de x que se encuentran a la izquierda de 0, incluyendo al 0, es decir (-∞,0]; y el segundo, consta de todos los valores de x que se encuentran a la derecha de 0 es decir (0,+∞) . De la unión de estos dos intervalos resulta el Dominio de f, el cual corresponde al Conjunto de los Núneros Reales R.
En base a esta informacíón podemos desarrollar la siguiente actividad:
Note that the values of x are determined by two intervals, the first of which consists of all the values of x that are to the left of 0, including 0, that is (-∞, 0]; and the second, consists of of all the values of x that are to the right of 0 that is (0, + ∞). From the union of these two intervals the Domain of f results, which corresponds to the Set of Real Numbers R.
Based on this information we can develop the following activity:
Halle: /Find:
f(-2), f(-1), f(-0,5), f(-0,25), f(0), f(0,25), f(0,5), f(1) y f(2)
Desarrollo/Developing
Para obtener f(-2) debemos ubicar x=-2 en uno de los dos intervalos del domino de f, en tal caso -2 está ubicado en (-∞,0] consecuentemente f(-2)=-3 (recuerde que f se define como -3 en este intervalo). Bajo el mismo razonamiento se sigue con las demás igualdades, por ejemplo f(0.25)= 0.25+1= 1.25 (ya que 0.25 está en el intervalo ( 0,+∞).
Un ejemplo emblemático de este tipo de función es la función Valor Absoluto.
To obtain f (-2) we must locate x = -2 in one of the two intervals of the domain of f, in which case -2 is located in (-∞, 0] consequently f (-2) = - 3 (remember that f is defined as -3 in this interval.) Under the same reasoning, the other equalities are followed, for example f (0.25) = 0.25 + 1 = 1.25 (since 0.25 is in the interval (0, + ∞).
An emblematic example of this type of function is the Absolute Value function
Función Valor Absoluto/Absolute Value Function
La función valor absoluto se define de la siguiente manera:/The absolute value function is defined as follows:
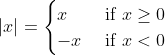
La forma elemental de su gráfica corresponde a una "V", pero en la práctica esto puede variar de acuerdo a la forma en que se nos presente la función en combinación algebraica con otras funciones, lo cual es el caso del ejemplo planteado en la función correspondiente a la próxima actividad.
The elementary form of its graph corresponds to a "V", but in practice this may vary according to the way in which the function is presented in algebraic combination with other functions, which is the case of the example presented in the function corresponding to the next activity.
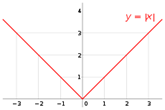
En ella se observa que el dominio de esta función corresponde a los números reales R; y el recorrido, a los números reales positivos más el 0, esto es: R+U {0}.
In it it is observed that the domain of this function corresponds to the real numbers R; and the path, to the positive real numbers plus 0, that is: R + U {0}.
Actividad:/Activity:
Con ayuda de https://www.desmos.com/calculator/ueqnbdgdch?lang=es, graficar e identificar el dominio y recorrido de las siguientes funciones seccionadas:
With the help of https://www.desmos.com/calculator/ueqnbdgdch?lang=es, graph and identify the domain and path of the following sectioned functions:
1) 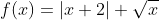
2) 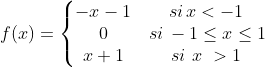
Referencia Bibliográfica/Bibliographic Reference
TAN, SOO (2005). MATEMÁTICA PARA ADMINISTRACIÓN Y ECONOMÍA. 3º EDICIÓN. CENGAGE LEARNINGEDITORES./TAN, SOO (2005). MATH FOR ADMINISTRATION AND ECONOMICS. 3rd EDITION. CENGAGE LEARNINGEDITORES.
Créditos/Credits
1 Para el trazado de las gráficas:/For plotting the graphs:
https://www.desmos.com/calculator/ueqnbdgdch?lang=es
2 Para la construcción de las ecuaciones:/For the construction of the equations:
https://latex.codecogs.com/eqneditor/editor.php?lang=es-es
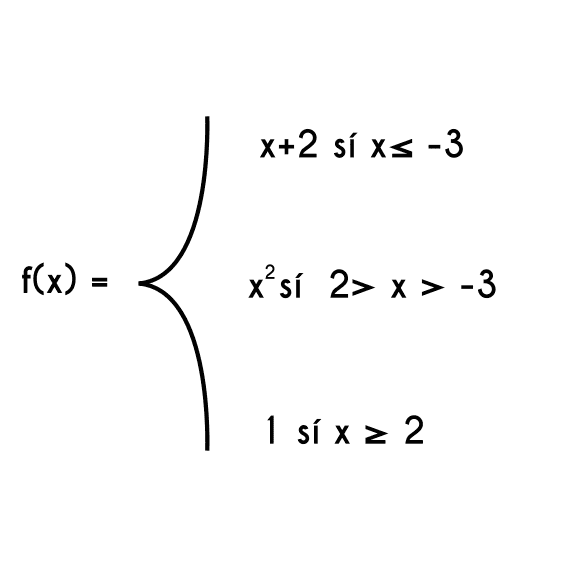
I've known it as piecewise functions. Maybe it is a North American thing to call it piecewise functions versus staggered/sectioned functions. Same idea.
That LaTeX codecogs website at the end looks interesting. I use Quicklatex.com for my Latex and math rendering in my posts.