Stratigraphy and Absolute Dating, Homeschooling Blog, Grade &
Stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is the method of reading (putting in order) layers of rocks in sequence. Layers of rocks are called strata. Scientists use stratigraphy to provided relative ages for fossils and geological phenomena.
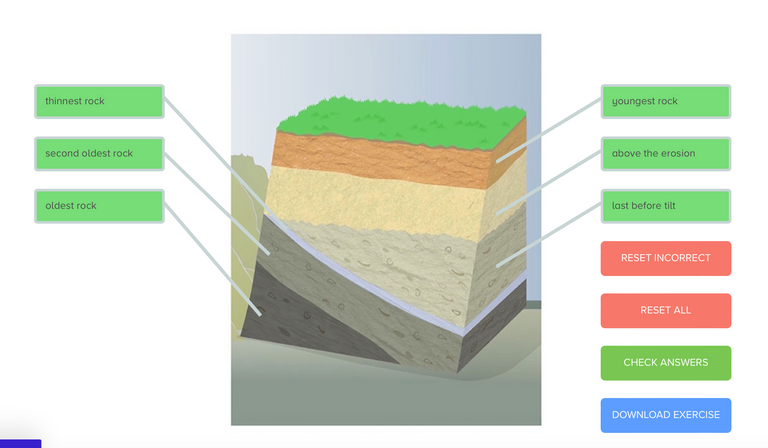
When determining the relative age of different rocks, geologists assume when studying strata in sedimentary rock that the bottom layers are older than those on top. This is called the Law of Superposition. This tells us which organisms found in the fossil record are older than others.
Radioactive Dating
There are two ways the geologists determine the absolute age of fossils or rocks. The first is based on the Law of Superposition. Certain fossils are known to be found only in a certain time period. However radiometric methods are more accurate for absolute aging. Measuring radioactive isotopes with their known half-life, how long it takes half of a sample to change into its non-radioactive isotope, we can determine the absolute age of sample. The ratio of the non radioactive isotope to the radioactive isotope tells us how old the sample is because radioactive decay is a constant process; it occurs at a steady rate.
When a sample does not contain radioactive material, a combination of stratigraphy and radioactive dating can be used. Related strata is radioactive dated instead and an age range is given to the sample. Sedimentary rock is often low in radioactive material. Igneous and metamorphic have more. The aging of rocks is complicated by
Igneous intrusions.