How Was the Antimatter Counterpart of the Electron Discovered?
In 1932 Carl Anderson discovered the positron, which is the antiparticle of the electron. Carl Anderson built a cloud chamber, his goal was to know the composition of cosmic rays (Cosmic rays are high-energy radiation that can produce secondary particles when they meet the earth's atmosphere). So Anderson placed a magnet, to know the charge of particles that passes in, and he placed a lead plate to slow down the particle that passes through, so he was able to take a photograph of the tracks taken by cosmic ray particles. The curve of the trajectory indicated that the particle was positively charged, but it was less massive than a proton, it is positively charged but it cannot be a proton, so what is that particle? Physicists thought they discovered a new particle, a positively charged electron, and gave it the name "positron" (for positive electron). When Anderson realized that the positron is the same as an electron but with opposite charge, he knew it was an antiparticle, which Paul Dirac had predicted in 1931.
The positron was the first experimental evidence of the existence of antimatter, and later on, Carl Anderson won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1936 for his discovery.
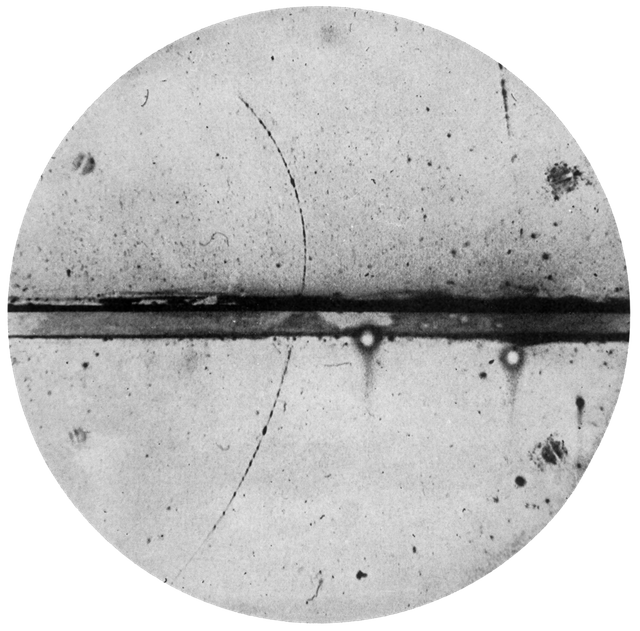
This is the cloud chamber photograph by Carl Anderson of the first positron ever detected.
Image credit
Reference: Biographical Memoirs: Volume 73 (1998), chapter: Carl David Anderson BY WILLIAM H. PICKERING.
Congratulations @universe.laws! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
Your next target is to reach 600 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPSupport the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!