Organic pasture management with endogenous resources
The response of pastures to fertilization is expressed in different ways, the most notable effect is the increase in dry matter yield, this response is the one that is generally analyzed to demonstrate the benefits obtained with this agronomic practice, in addition the addition of nutrients also acts on the quality of forage, it is measured by evaluating different parameters such as protein content, minerals or by variations in the digestibility of the pasture; The third effect is manifested in the animal with the increase in meat and milk production, an increase in the carrying capacity, or both, therefore fertilization should improve the profitability of the farm, increasing the producer's income as a reflection of the positive effects on the previous parameters.

Of the nutrients, the most important for the growth and development of forage species are nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K), and with their rational organic or mineral application, considerable increases could be achieved; It has been pointed out that nitrogen fertilization can increase digestibility and crude protein in the plant, as well as stimulate DM production, but this situation is reversed with total carbohydrate levels (TCHO), since it would decrease the cell wall content, according to Buso, Franca, Miyagi, Ferreira and Correa (2016), carbohydrates mainly represent the energy reserves of plants, varying between 50 and 80 %, and are very important for animal feeding, being the main source of energy for rumen microorganisms.
Some researchers such as González and Faría (2008) indicate that the nutritional requirements of species subject to grazing, in which for an animal load of 1 AU/ha, 50 to 60 kg/ha/year of nitrogen, 9 to 12 of phosphorus and 60 to 70 of potassium are required, these levels increase in cut species in which, due to the way they are harvested, no recycling of nutrients is generated due to the absence of interaction with the animal component, the values oscillate between 75-15-100 kg/ha/year of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium respectively. In this case, adopting techniques for the use of excreta and incorporating them into the ecosystem would allow reducing fertilization costs, as well as avoiding the excessive use of synthetic formulas that are detrimental to the soil system.

In this sense, organic agriculture is a clean model of production that involves the use of agricultural techniques based on products of natural origin, free of components that threaten the functional biodiversity of ecosystems, which proposes to avoid and if possible exclude in its entirety the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides in agricultural production, This model in agriculture provides the opportunity to combine traditional knowledge with modern science in order to develop new production technologies and commercial alternatives that allow the generation of income without compromising the resources of the ecosystem.
In addition, in the practice of fertilization, the use of synthetic sources has turned out to be an alternative to improve crop yields, in which the immediate effect generated can be appreciated, guaranteeing the use and conversion by the plant; however, its use depends on the dose, source and the type of soil where it is incorporated. Considering that intensive production models demand an accelerated rhythm, the irrational use of synthetic fertilizers has been promoted, causing an imbalance in the environment, which justifies the high degree of contamination of soils, aquifers, among others, thus compromising the health of the animal and consequently of human beings.

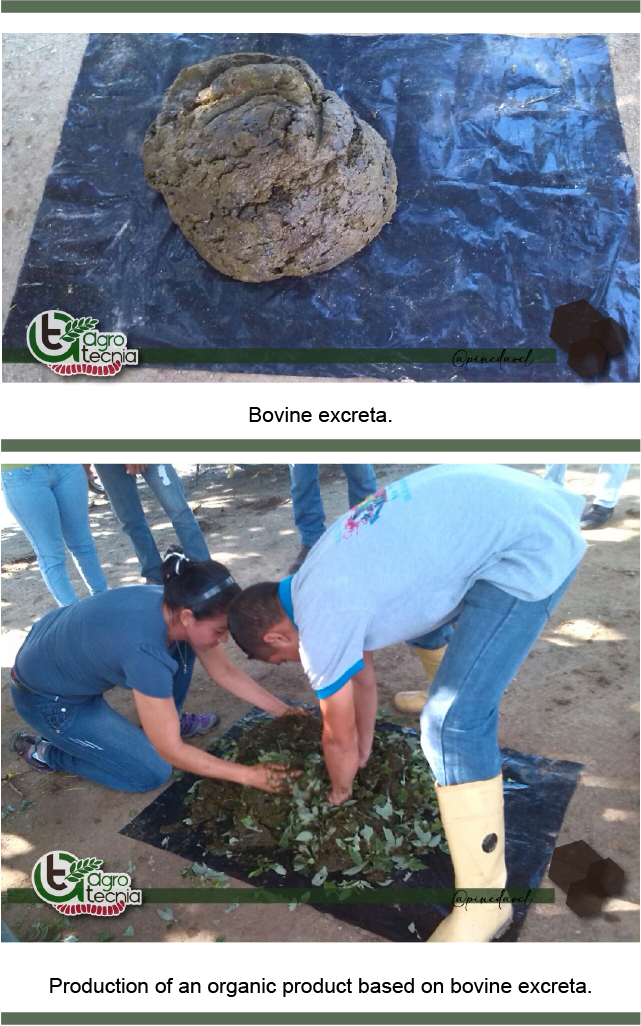
This justifies the importance of resuming agronomic practices that do not threaten the resilience of agroecosystems, the adoption of agroecological alternatives is not an option to develop productive systems, in the agricultural context it is a necessity to protect and prevent their degradation, currently there are several ways to take advantage of local resources that are available on the farms, In the case of livestock, a resource of interest is the use of excreta through fermentation techniques, as well as the application of organic products such as crop residues, worm humus, compost, among others, which make available the nutrients necessary for the growth and development of plants.
Organic fertilizers have a fundamental importance in plant nutrition, since they are a source of microbial life that contributes to improve the biological activity of the soil, allowing the decomposition of organic matter, which through this process releases nutrients that are easily absorbed by plants, which contributes to an optimal development of crops. On the other hand, in addition to increasing the nutritional conditions of the soil, it also improves its physical condition (structure), especially solid fertilizers increase water absorption and maintain soil moisture; this effect can be classified as sustainable, since it maximizes the efficiency of the resource due to its prolonged action, which generates less expense for the use of fertilizers.
In the case of bioproducts that are generated from a biological process, in which bacteria and fungi degrade crop residues, animal excrement and waste, there is a wide range of techniques for their production and application, since they have been classified into three groups: solids such as compost, bocashi, vermicompost; green manures such as crop residues, kudzu, fodder peanuts, centrosema; and liquid fertilizers produced by aerobic fermentation (manure tea, compost, etc.) or anaerobic fermentation (biol), which through microbial activity, the raw material is transformed into carbohydrates, minerals, vitamins, amino acids, organic acids, which in addition to nourishing plants, help restore the physical and chemical properties of the soil.
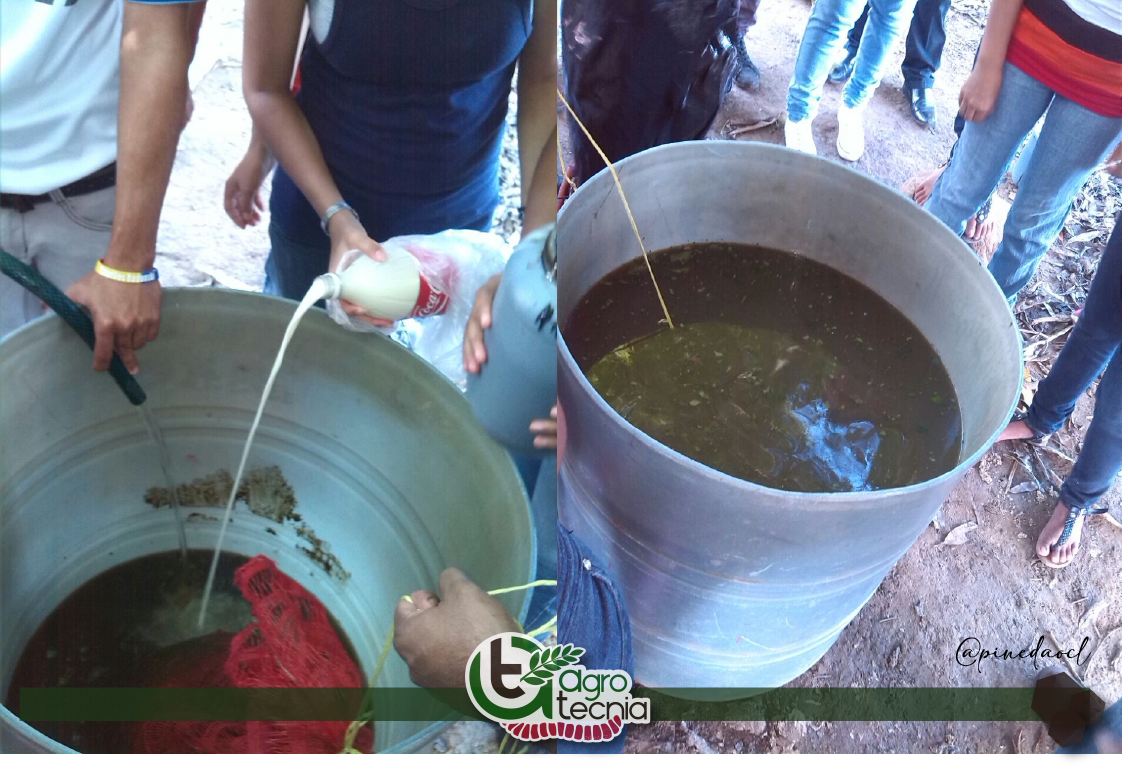

In relation to the above, in the particular case of fertilization of grasses under grazing, one of the techniques of easy application and preparation is the use of liquid fertilizers, as long as the needs of the crop are analyzed. Animal manures can be used to prepare bioproducts such as teas or biol, suitable for application to crops at any stage of growth. The fundamental basis of the preparation is based on releasing the nutrients and other substances from the manure in water, allowing the preparation to ferment aerobically or anaerobically in a container of approximately 200 l.
Therefore, the technology of liquid organic fertilizers based on manure could be an alternative for producers, since they are prepared with animal excrements available in any farm and their use provides the plant and soil with essential nutrients, besides allowing the inoculation of microorganisms that activate the edaphic biota. Likewise, they are bioactivator products that act favoring the recovery of crops under stress conditions, increasing vegetative growth, due to their content of substances that favor plant development and growth .

Buso, W., Franca , A., Miyagi , E., Ferreira , R., & Correa, D. 2016. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on carbohydrate and protein fractions in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) cultivars. Tropical Grasslands, 4, 47-53.
González, B., & Faría, J. 2008. Los pastos y la intensificación racional de la ganadería de Doble Propósito. En C. González, N. Madrid, & E. Soto, Desarrollo sostenible de la ganaderia doble propósito (págs. 335-346). Maracaibo: Fundación GIRARZ.
Orozco, D. 2014. Determinación del rendimiento en Cynodon nlemfuensis y Brachiaria híbrido bajo dos fertilizaciones orgánicas y una convencional en la Hacienda Santa Elisa, Honduras. Trabajo de Diploma (en opción al título de Ingeniero Agrónomo). Zamorano.

0
0
0.000
Thank you for sharing. :)
!1UP
To you for visiting my blog
My pleasure. I learned from it. 🙂
You have received a 1UP from @thecuriousfool!
@stem-curator, @neoxag-curatorAnd they will bring !PIZZA 🍕
Learn more about our delegation service to earn daily rewards. Join the family on Discord.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
Dear @pinedaocl, we need your help!
The Hivebuzz proposal already got important support from the community. However, it lost its funding a few days ago and only needs a few more HP to get funded again.
May we ask you to support it so our team can continue its work this year?
You can do it on Peakd, ecency, Hive.blog or using HiveSigner.
https://peakd.com/me/proposals/199
Your support would be really helpful and you could make a difference.
Thank you!
Thanks for this very nice blog, which I have only found now (cf. the STEMsocial distilled ;) ). I haven't any specific comment this time, and only wanted to let you know that I enjoyed the read.
Cheers!
Thank you very much, I really appreciate your interest in my blog posts, I am currently looking for a methodology that will allow me to publish more often, since work and home responsibilities absorb much of my time.
If you find one, please tell me about it. I am struggling myself to keep a constant rhythm of posting ;)