Polarization of a dielectric
Introduction
In the previous publication I shared the capacity of a capacitor, which will be the quotient between the absolute value of the charge of an armature and the potential difference between the two, also the unit of capacity is cardio, and then enter in terms of the association in parallel, where it shows us that all the armatures of the same sign are united at the same point and with the difference in potential, now it is called insulators or dielectric to those substances that are not conductive, since it is evident that while the loads remain in the same area of the body, where they have been produced, as in the case of glass material, there are pillars and nonpolar ones. The most unique thing about this, dear reader, is the case of a material contains polar molecules, they will normally be in a random orientation when it does not have an applied electric field, they are taken into account, it considers that an electric field is applied, it will polarize the material, which stimulates the dipole moments of polar molecules, it is easy to experience that when introducing a dielectric between the armatures of a capacitor the potential difference decreases, but it is considered that the charge remains constant: Co = Q / V1 - V2.
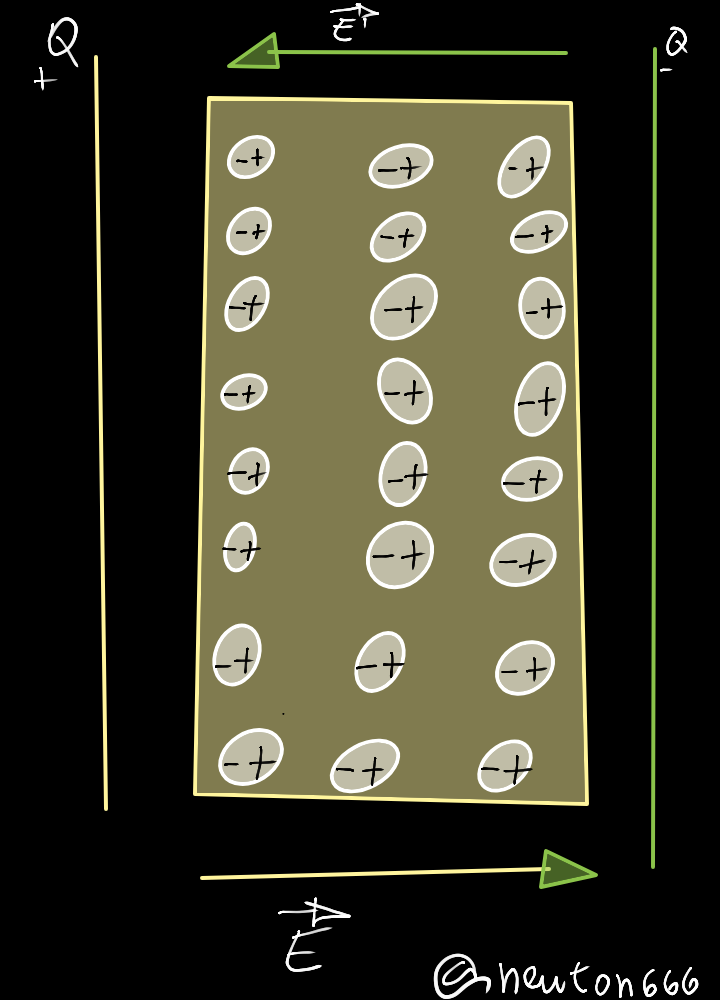
In the case of the capacitor, an electric field Eo appears, directed from the positive to the negative armature, but if a dielectric is introduced between it, it is the vector field that expresses the density of the permanent or induced dipole electric moments in a dielectric material, since the polarization vector, this is defined as the dipole moment per unit volume, but if you introduce a dielectric between it, the field polarizes its molecules, it directs the negative charge towards the positive plate and vice versa. Besides, we also have the reference to the electric field lines for two point charges of equal magnitude, but with opposite signs they are known as electric dipoles, where it shows us a system of two charges of opposite sign and equal magnitude close to each other, it is very different For what happens in conductive materials, electrons are not free in insulators.
When the polarization of the molecules is found, it creates an electric field E, with the direction opposite to the initial one, where we have Eo - E, it is clear that it will be less than the initial one, now for the case of the difference of potential we have V'1 - V'2, since it says, dear reader, that the capacity in Co will be the capacity of the same dielectric to the client of this which we have C / Co, this will be the result of the dielectric constant in E. It is also applied in two spherical capacitors joined by a conductive wire, where it is associated in parallel, due to its potential difference after the union occurs, it is common for both capacitors, this is due to the electric flow through a closed surface it is proportional to the net charge contained within it.
[1]- General Physics by Santiago Burbano, 2003.
