Procedure for Performing Endotracheal Tube Intubation
Disclaimer
The purpose of this post is to provide general informational as well as educational information about Endotracheal Intubation. The information contained in this post should be used for educational purposes only. It should in no way serve as a substitute for independent decision making.
Getting over the disclaimer, it is important to know that being able to perform endotracheal intubation requires a practical training by an experienced medical practitioner, just like you cannot learn how to drive a car professionally by reading in books, reading books on Endotracheal Intubation is will only give you the required knowledge but not the practical expertise.
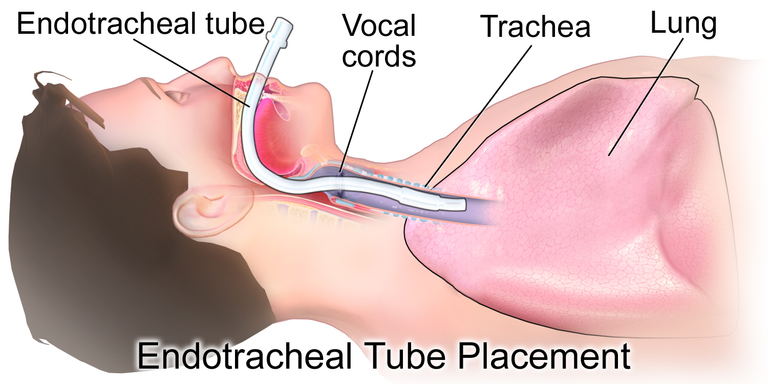
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Endotracheal_Tube
Introduction to Endotracheal Intubation
Endotracheal Intubation is the insertion of a flexible tube basically the endotracheal tube into the vocal cavity, down into the tracheal/wind pipe, in other to provide airway for a patient in need. Intubation is done in patients when the following are noticed; Inability for the patient to ventilate leading to respiratory failure (such as in cases of hypercapnic, or Hypoxic), the inability to protect the airway, conditions that require that the patient be ventilated in order to stabilize the patient. It is important to know that if a patient is still talking properly without difficulty, then the airway is great at the moment. Patients with impaired consciousness (Glasgow coma) lesser than or equal to 8 should be intubated, In cases where the patient's breathing is noisy, or in cases where the patient has injuries in the spine especially the cervical region, then intubating is necessary. Patients with expanding hematoma or emphysema, patients with rapid deteriorating mental health as at the time of bringing them to the Emergency Unit, (cases such as full stroke, brain injury, and overdose) should be intubated. Another reason to intubate patients are in cases where they are required for medical procedures, cases such as surgery, esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), and in cases of bronchoscopy.
Endotracheal Intubation Procedure
Intubation could be done from the mouth (orotracheal) or from the nose (nasotracheal). When intubating, there are different equipments which will be needed to perform an Endotracheal Intubation, depending on the situation. The equipments needed to perform Endotracheal Intubation are oxygen delivery devices, bag valve mask (self-inflating, or flow-inflating), Laryngoscope handle and glide scope, Laryngoscope blade [mac (curved blade), and miller (straight blade)], Endotracheal tube (ETT) of different size, monitoring devices such as colorimetric detector (for detecting CO2) and so on, suction devices including suction catheter, Personal protecting equipments such as gloves, mask, stethoscope, oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway, stylet, ventilator (in case), Bougie, IV pump, and medications. In cases of a crashing patient, it is important to have the crash cart on standby.
There are Medications that will be needed before the intubation, and after the intubation. Before intubation, sedatives are administered. Sedatives such as Etomidate, propofol, midazolam. Paralytics including rocuronium and succinylcholine. Reversal agents such as naloxone, and flumazenil.
Before going on with the Endotracheal Intubation, it is important to Prep the Room in which the intubation is going to take place, If it is possible to empty the stomach, then it is welcomed to prevent aspiration, but in most cases, it isn't possible. It is important to put the bed in the right place, not close to the wall, because when the bed is close to the well, the person intubating won't be able to stay over the head of the patient. Patients are to lie flat, and in cases where they are unrest, sedative can be given to put them in a state of rest. It is important to prep for emergency as well. All these things, including the intubation, would happen as fast as possible, but there isn't a need to worry, because in a standard setting, you wouldn't be the only person doing this. There will be an airway provider (someone who performs the intubation), Nurse, respiratory therapist (if available), In cases where there is difficulty in airway, an otolaryngologist can be present. Identifying the responsibility of each member of the team is very important and will help beat time during intubation. Responsibilities such as handling of Endotracheal tube to the airway provider/intubator, provision of ventilation, and checking patient vitals.
It is important to pick the appropriate type and size of endotracheal tube. When the tube is identified, a stylet should be inserted into the endotracheal tube, not exceeding the end of the tube, or coming out of the Murphy's eye. During the process of intubating, it is important to know that the patient isn't going to be with oxygen, so monitoring the vitals is very important. Ensuring that a pulse oximeter, and blood pressure cuff are placed properly. They should be placed at different extremities. The IV should be working properly to prevent delay or complications. Pre-Oxygenation should be the next step. In most cases, a non-rebreather mask is used. Apneic Oxygenation would be used to deliver oxygen via the nose. Using medications to reduce airway trauma is important, as well as sedatives. The open should be open before inserting the blade, the left hand should be used to insert the blade by holding the laryngoscope, through the right corner of the mouth. The Tongue, is moved to the left to allow for visibility, and for better view of the glottic opening, the laryngoscope is lifted forward and upward in the mouth. The Gums and teeth should be avoided at all cost. Structure that would be seen in the esophagus would be the Epiglottis, the Vallecula, the Aryepiglottic fold, the vocal cord, the Arytenoid cartilage, and the glottis. When the intubator see this structures, it is important to announce to the team, so they can be carried along as you perform the intubation. The aim is to find the Glottic opening of the glottis. Oxygen level should be checked at interval and once the oxygen level drops below 90%, its stats will keep dropping. It is advisable to bag mask again to provide oxygen before continuing with intubation.
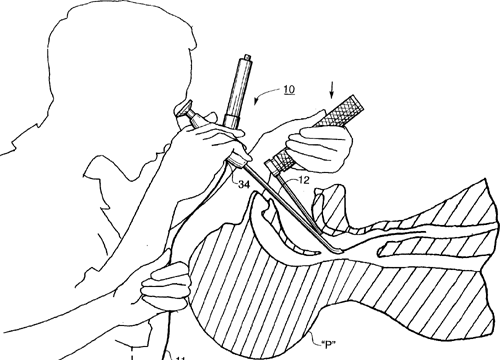
https://picryl.com/amp/media/inserting-an-endotracheal-tube
In cases where there are secretion blocking the glottis, suction should be used to clean the region. Laryngoscopic view should be maintained when the Glottis and the vocal cord are properly seen, and the endotracheal tube should be inserted through the vocal cord, from the right side of the mouth and inserted into the Trachea 3X the diameter of the Endotracheal tube (around 22cm to 24cm). Once the Endotracheal tube is properly inserted into the trachea, the tube should be confirmed it is passing between the cords, and the laryngoscope should be removed, and the endotracheal tube should be held to the hard pallet or towards the upper teeth to help maintain position, after which the stylet is removed from the Endotracheal tube. All stats should be confirmed after the insertion has been done, and the tube should be secured using securing devices, plasters, or tapes depending on what is required by the local health law. X-ray can be taken to identify that the tube is placed in the right position, so the both lungs can recieve oxygen.
Endotracheal Intubation Complications
Complications with intubation could occur due to failed intubation, and this could be as a result of lack of skill, obstruction in the patient's airway, trauma, bleeding, and many more, leading to complications such as wrongfully placing the endotracheal tube in the esophagus of the patient and being unable to perform the intubation properly causing dental trauma, aspiration, airway trauma, anoxic brain injury, tracheostomy, cardiac arrest, Laryngospasm, perforation of the tracheal, dislodged teeth, vocal cord damage, paralysis, infection, pneumonia, and possible mortality. In cases where the intubation is done wrongly, it should be seen as an emergency and removed immediately.
Reference
National Library of Medicine || Endotracheal Tube Intubation Techniques
National Library of Medicine || Intubation Endotracheal Tube Medications
National Library of Medicine || Tracheal Intubation Medications
What is intubation? Types, procedure, side effects, and all else you need to know
Statpearls || Endotracheal Tube
Congratulations @merrymercy! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s):
Your next target is to reach 40 posts.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Check out the last post from @hivebuzz:
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
They once tried intubating an ICU patient in my presence, the gag reflex was terrible enough, even with sedation
I can imagine how you felt. Thanks for reading.
This is a well explained procedure, thanks for sharing this.
Thanks for reading @oluwatobiloba, it is good to have you here.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.