Invertebrates feeding adaptation to their environment
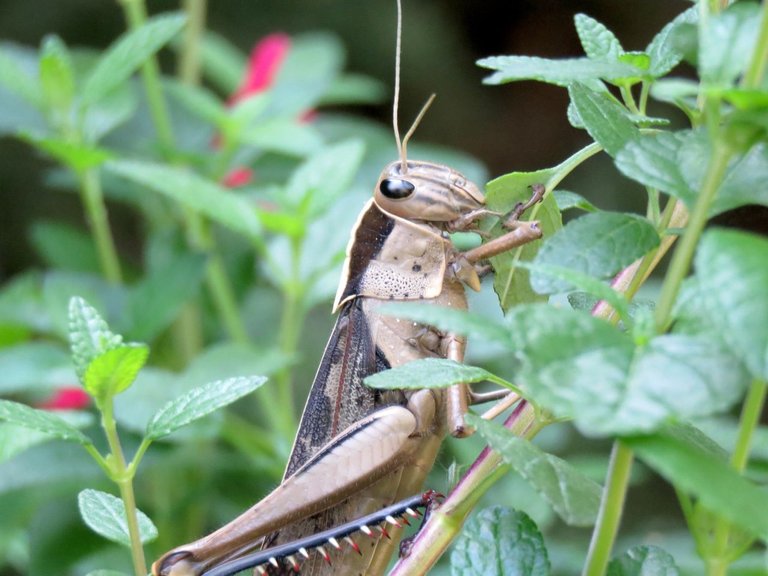

A grasshopper feeding on plants
Source:Pixabay
Feeding is another attribute of dwelling organisms. All residing organisms ought to feed to develop, reproduce, and to remain alive. Many invertebrate organisms have to evolve modified feeding mechanisms that resource them to devour or feed on their environment.
Knowing that distinct organisms live at a specific phase of the ecosystems, this may additionally be in waters, on land, or inner host. Organisms ought to boost suitable feeding modifications for them to adapt successfully to their environments. In this article, I'll like us to have a look at the modifications and mechanisms of feeding in some invertebrate animals.
From research, I have stated that there are several feeding mechanisms show off by an invertebrate.
Feeding in invertebrate organisms
Invertebrate like Amoeba which lives in moist surroundings and has a holozoic mode of nutrition possesses no mouth section for feeding however shows what is referred to as the phagocytosis mechanism.
Amoeba injects different microorganisms like diatoms, bacteria, flagellates, and so on as food via extending its pseudopodium closer to these microorganisms.
Whenever Amoeba comes throughout its food, it extends its pseudopodium and gradually engulfs the meals alongside with a drop of water into the body of the animal.
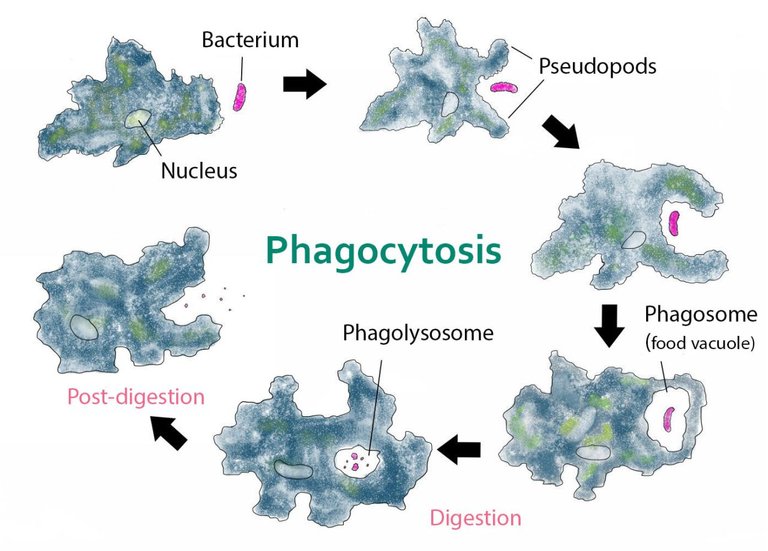
Source:Wikipedia, author: Kate Taylor, CC0 1.0
When the meals are injected into its vacuole where digestion takes place, protozoan developed inside the food vacuole secretes digestive enzymes that will act on the food. From the food vacuole, the digested food is diffused into the protoplasm for assimilation whilst the undigested ones are expelled away from the vacuole.
On the order hand, Paramecium lives in aquatic surroundings and suggests a holozoic mode of a diet too. It feeds mostly on yeast and different organic natural substances. Paramecium feeds by beating its cilia ( a skinny hair like that surrounds its whole-body) in opposition to the water current. The movement of the water swept meals particles into the gullet of this organism.
These particles which ought to be yeast are moved to the food vacuole positioned at the gullet posterior. During the digestion of the food, the endoplasm produces enzymes that aids digestion in the food vacuole.
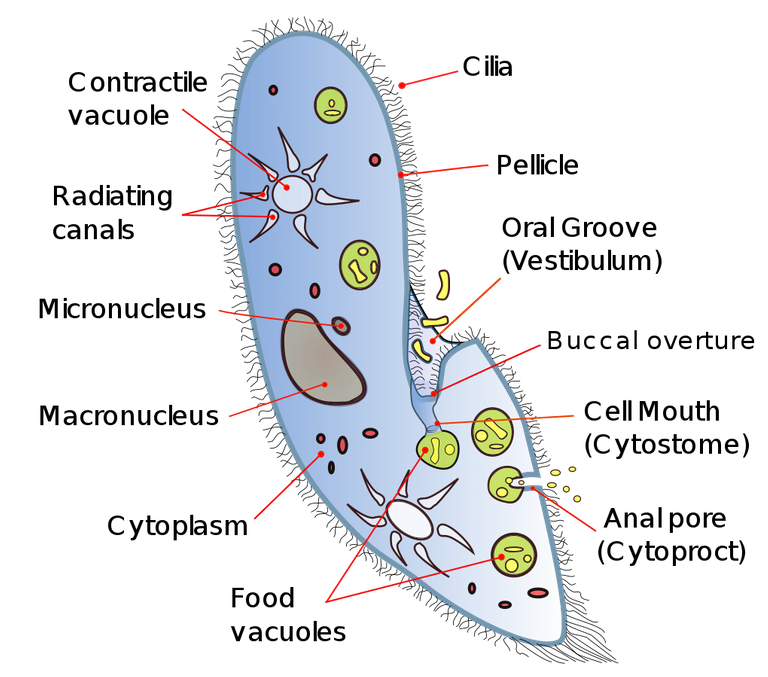
A diagram of Paramecium caudatum, with cell structures labeled.
Source:Wikipedia, Author:Deuterostome, CC BY-SA 4.0
The undigested food is being excreted as waste products with the aid of the anal pore. In this way, Paramecium digest, absorb, and assimilate its food.
Organisms like tapeworm carry out absorbing mechanisms. Tapeworm is recognized as an endoparasite that lives and feeds from the interior of its host. It has no mouth and possesses no alimentary canal however can take in digested food from the gut of its host that is the man.
The feeding mechanisms of the tapeworm are achieved because its structure is much less complicated in modification. The physique of the tapeworm is modified and adapted for feeding as follows:
The hooks and suckers on its head assist the organism to mounted itself to the intestine of the host to avoid dislodgement. Enzymes from the host can now not digest tapeworms due to the thick cuticle received on its body.
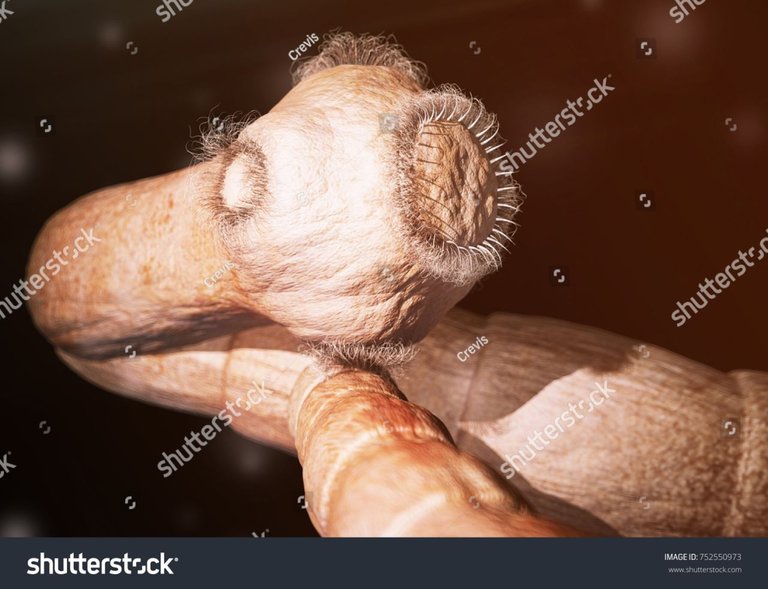

A photo of a tapeworm showing the hooks and sucker on its head
Photo By Crevis on Shutterstock
Since tapeworm has a flat body, food is immediately absorbed from the host into its body besides the need for an alimentary canal because the flat body surface of the tapeworm gives a massive floor location for the absorption of already digested food. So the whole physique floor is used additionally for the absorption of food.
Organisms that show off biting and chewing mechanisms e.g. Grasshoppers and cockroaches possess mouthparts modified and adapted for biting or chewing their food. This kind of animal browses sparkling depart of plants typically as their diet. So to live efficiently in their superior tropical environment, they possess mouthparts that encompass the labrum or upper lip which help to hold food from falling off the mouth. The mandibles which are heavy, toothed, and jaw-like structure used for cuttings and chewing food materials.
The grasshoppers additionally have a pair of maxillae which is a biting blade. The work assigned to the maxillae is the breaking down of the food in which the mandibles have chewed into smaller particles. The lower lip acknowledged as the labium prevents the wastage of meals from the mouth.
Go out and look for a common biting and chewing organism like the grasshopper, then carefully learn about its mouth part. Believe me, you will be amazed by way of what you will see!
Animals like the mosquito, butterfly, and housefly show other types of feeding mechanisms referred to as sucking mechanisms. These are the three famous tiny organisms that showcase sucking mechanism and they have developed a different considerable modification of mouthparts adapted for feeding on meals through the mechanism of sucking.
Describing the feeding mosquito which lives primarily on fluid substance possesses a piercing mouthpart known as the proboscis used for sucking the blood of man, animals, and liquid chemical substances from plants. From expects observation, the mouthparts altogether form a robust sharp stylet succesful of penetrating the physique of animals and plants.
Inside the mouth of a mosquito is located the saliva that prevents the clotting of blood while it is being sucked in. Another interesting personality of a mosquito labium is that it easily folds back to allow the stylet to function its work of penetration of the body to suck fluids.
Nectar feeding insects like a butterfly that feeds on a flower has mouthparts modified for sucking the fluid.
By the use of its long coiled proboscis, the animal is capable of sucking the nectar of flowers. Other mouthparts of the insects like the labrum, mandibles, and palp are non-functioning due to the type of meals taken by the insect. The lengthy proboscis is folded again below its head when no longer in use.
In the case of the housefly, it has enlarged labella which are sucking structures for liquid food. The insect is succesful in feeding on strong substances by secreting its saliva on the solid food to convert it to a liquid form.
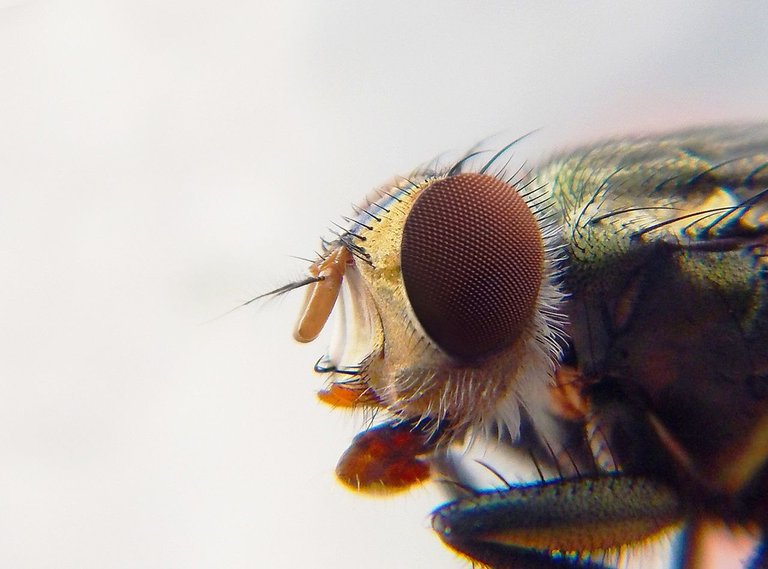

Photo of a housefly
Image credit
Again, another section of its mouth referred to as the sponging and the labella can suck fluid. The labella have dined channels that useful resource the speedy absorption of liquid meals into the mouth.
References
•ESSENTIAL BIOLOGY FOR SENIOR SECONDARY SCHOOLS by M.C. MICHAEL ISBN 978-8089-36-4
•Unicellular organisms
•Mouthpart conduit sizes of fluid-feeding insects determine the ability to feed from pores
•Insect mouthparts
•EVOLUTIONARY ADAPTATIONS OF FEEDING IN INSECTS
https://twitter.com/Jsalvage2/status/1324503396339077121
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider supporting our funding proposal, approving our witness (@stem.witness) or delegating to the @stemsocial account (for some ROI).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support. Using the STEMsocial app could yield even more supporti next time.