What hallucinations tells us about our brain?
Hey there! Welcome to my new article.
Our brain acts as a command center for our bodies. This 1.5 kg organ which is almost 2% of our body weight contains about 90 billion neurons is one of the most amazing and mysterious organs at the same time. And, if that's not enough, those neurons are connected together by trillions of synapses. well, this vast complexity of the brain is what makes us what we are today. But, this complexity comes with a cost. I mean there are billions of neurons and trillion of connections, what could go wrong? well, the answer is a lot. Anything can go wrong at any point. Each part of the brain has its own function and works in cooperation with one another. If one specific part of the brain is somehow affected, then it might affect other parts too.
Image by August Natterer, Wikimedia, Public domain
Well, there are many things that can happen when something goes wrong in our brain but in this particular article, I will discuss the relation between hallucinations and brain functions.
What really is a hallucination?
In short, hallucination is a perception of false reality in the absence of any type of stimulus, which can not be differentiated from the true reality. It sounds like a science fiction movie, but it's true. A hallucinating person can see things, smell, taste, hear, and even feel things that don't even exist. We all might have experienced any of this at some point in our lives, that doesn't mean there is something wrong with our brain. Let's talk about various forms of hallucinations.
Auditory hallucination: This is the most common one and happens to a lot of people. A person might hear someone talking to them in a neutral, happy, or angry voice, telling them to do certain things or it can be just a simple, tapping, or clicking sound.
Olfactory hallucination: A person can smell something that doesn't exist. Take an example, smelling flowers even if there are no flowers around, or smelling a very unpleasant odor in a very clean environment.
Visual hallucination: This is the most complex and frightening one. A person might see a pattern, lights, object, and even other persons that are not even there. For example, you might see a person talking to someone very convincingly, but the other person doesn't exist.
Gustatory hallucination: This happens to many of us. A person might taste something that he is imagining of. imagine tasting a pizza just by thinking of it LOL.
Tactile hallucinations: A person might feel a sense of touch. example, you might feel something crawling on your hands or legs, but when you look at it, find nothing.
Before we go into the relationship between brain functions and hallucinations we need to have little insight into the anatomy of the brain.
Little insight into the anatomy of the brain
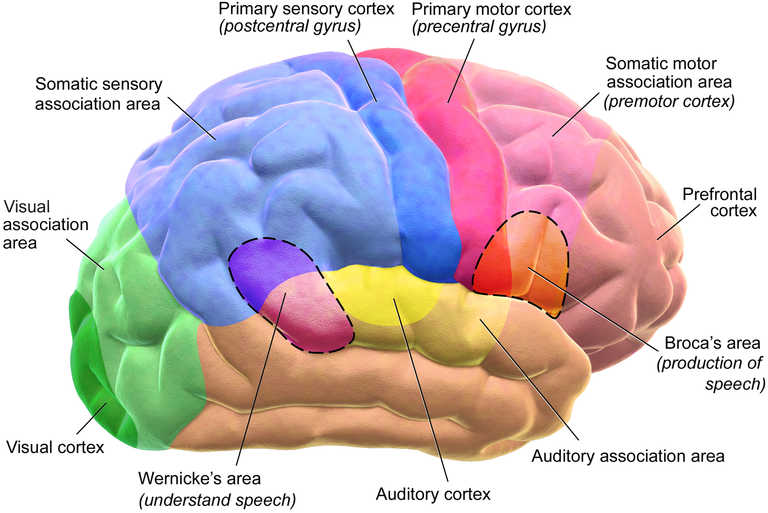
I will keep this part short, providing only the necessary information. Well, the brain is a very complex structure. This approx, 1.5 kg organ has two hemispheres. Right and left. Also known as the right and left cerebrum. brain stem and cerebellum lies under the cerebrum.
The cerebrum's outermost part is known as the cortex. Which can be further divided into the frontal, parietal, temporal, and visual cortex. Each of these cortexes has its own functions. The frontal cortex helps in the thought process, yeah when you are talking to yourself, the frontal cortex is the one replying to you. The temporal cortex helps us with identifying sounds and language. Sounds and language are two different things. Also, the hippocampus and amygdala lie in this cortex which helps us with short term memories and emotions. The parietal lobe helps us with navigation, perception of touch, temperature, and pain. Finally, the visual or occipital cortex helps us processing visual informations.
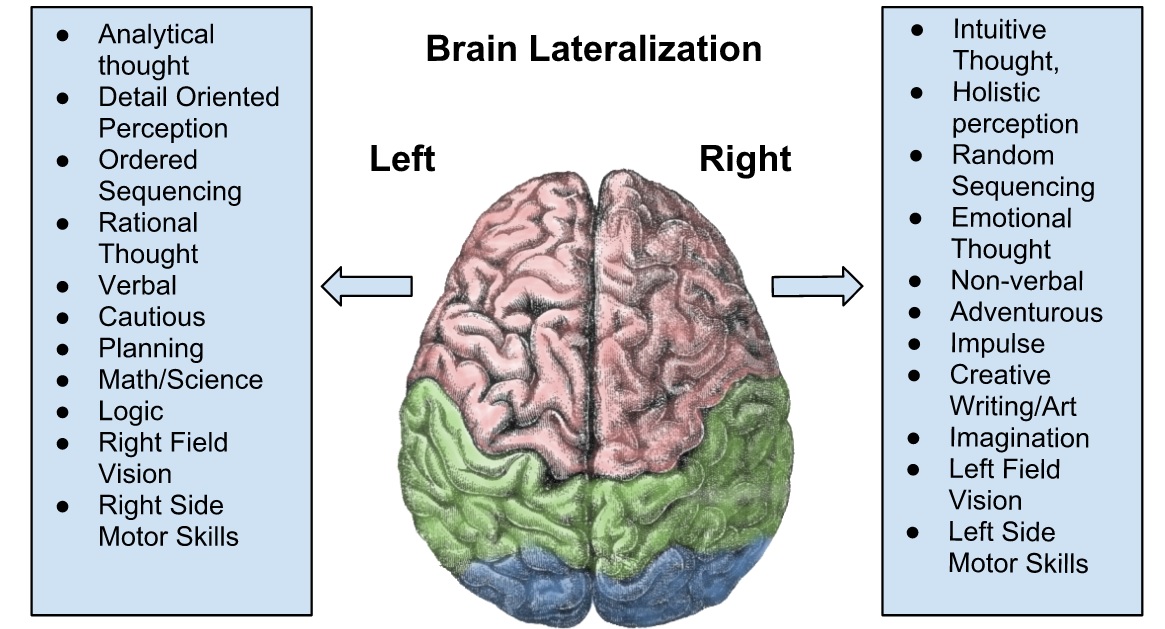
So, both hemispheres of the brain do the same thing?
Well, certainly, both the hemispheres work in coordination with one another, but no, they don't perform the same functions. Both of these hemispheres are connected together by a bundle of fiber in between known as "corpus callosum". This helps in relying on the information to the other side of the brain. These hemispheres control the opposite side of the body. This is the reason behind right-handedness and lefthandedness. In 92% of the population, the left side of the brain is dominant making right-handed and in only about 8% of the population, the right side is dominant, making left-handed.
What really happens in the brain during hallucinations?
there is one major theory that states when something goes wrong in relation to the frontal lobe and the other sensory cortex of the brain, hallucinations are caused. Hallucinations are pretty common though. Take an example, when a person experiences an auditory hallucination as in schizophrenia, there might be overactivity of the auditory cortex in relation to the frontal cortex. This is the sound processing part of the brain. As, a result, random sounds are generated which is perceived as real.
Likewise, patients with Parkinson, have shown an overactive visual cortex which results in random images generation. We don't just see through our eyes, we see through our brain too. This can also happen with the use of psychoactive drugs, which alters the relation between the frontal lobe and the other cortex of the brain.
Cristopher Niell, a neuroscientist conducted an experiment, in which he ingested a mouse with a psychoactive drug to find out the brain activity of the mouse while hallucinating and trust me, the results were surprising.
A hallucinogen named DOI which is very similar to LSD was dosed to mice. Its primary objective was to find out, how would this affect the mice's perception of the surrounding by studying its bran activity. The drug DOI acts by acts by increasing the serotonin activity in the brain. Serotonin is a major neurotransmitter that helps in the feeling of wellbeing and happiness and also plays a major role in vision.
After ingesting the mice with DOI, many pictures were shown to peer images into its brain. At the same time, brain activities were being recorded. They wanted to see, how a hallucinogenic drug and images altered brain activity. They found out that, this process actually decreased the incoming visual information.
The researchers suggested that the visual hallucinations start when we actually over-interpret the decreased or diminished incoming visual information.
Niell said. “We were surprised to find that a hallucinogenic drug instead led to a reduction of activity in the visual cortex.”
He also added visual hallucination might happen because neurons might be firing like crazy to fill in the information gaps. Therefore, this experiment suggested that hallucinations might come from the part of the brain that is trying to fill in the gaps of missing information.
Similarly, a study showed, how high levels of dopamine in schizophrenia patients causes auditory hallucinations. Well, this study also concluded the same thing, which said "Our brain uses past experiences to create new sensory expectations to fill in the gaps when sounds are unclear or diminished". The same as the mice experiment. This taking in information and its processing is so much altered in a schizophrenic patient, that leads to extreme hallucination and a break from reality.
That's it for this article guys. I hope you liked it.
*All the images used are copyright free and are cited with appropriate credits*
References:
[1]https://mayfieldclinic.com/pe-anatbrain.htm
[2]https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324805#Some-surprising-findings
[3]https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hallucination
[4]https://www.uptodate.com/contents/approach-to-the-patient-with-visual-hallucinations
[5]https://www.discovermagazine.com/mind/what-causes-hallucinations-the-brain-may-be-overinterpreting-a-lack-of-info
My previous articles You might be interested in :
[1]An Obstructive Lung Disease - Asthma | All you need to know
Congratulations @idoctor! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your board And compare to others on the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
that was an interesting read !!
@tipu curate 2
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 0/10)
So that means hallucination are the result of diminished activity in some parts of the brain compensated by the actvity of others?
Very interesting!
yes, it might be compensated by other parts of the brain, trying to fill in the gaps creating hallucinations.
Btw, thanks for re-hiving :)
No worries ;-)
Thanks for these information