Disorder of Ovary - Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome | A Deep Analysis
Hey everyone, welcome to my new article. This article will be on the disorder of ovary, specifically "Polycystic Ovarian syndrome" or "PCOS". We are going to discuss its etiological factors, pathologies, clinical features, different investigations, different medical conditions associated with, and its treatment.
Short Introduction
Poly means multiple and cystic means sac or cavity-like structure. So, in short, this is a syndrome of multiple cysts in the ovary. This syndrome was firstly described in 1935 by two scientist Stein and Leventhal. Also, it should be noted that it is the most common endocrinological disorder in a woman in her reproductive age. This syndrome is manifested by Amenorrhea, Hirsutism, and obesity with large cystic ovaries. The prevalence rate is more than 15%.
Etiology
This is a group of disorders characterized by excessive production of androgens mainly by the ovaries although other organs are also involved. Therefore its a multifactorial and polygenic condition. The gene responsible for this condition is CYP11a. This leads to excess production of androgens and androgens biosynthesis pathway. Some insulin receptor gene (19p13.2) might also be involved.
Therefore the diagnosis is based on the following criteria.
- Oligoovultion (decreased ovulation) or anovulation(no ovulation).
- hyper-androgen production
- polycystic ovaries.
Other factors like thyroid dysfunction, hyperprolactinemia, adrenal hyperplasia must be excluded. Infertility women are likely to be affected. Also, about 20% of normal women this syndrome can be seen.
Pathology
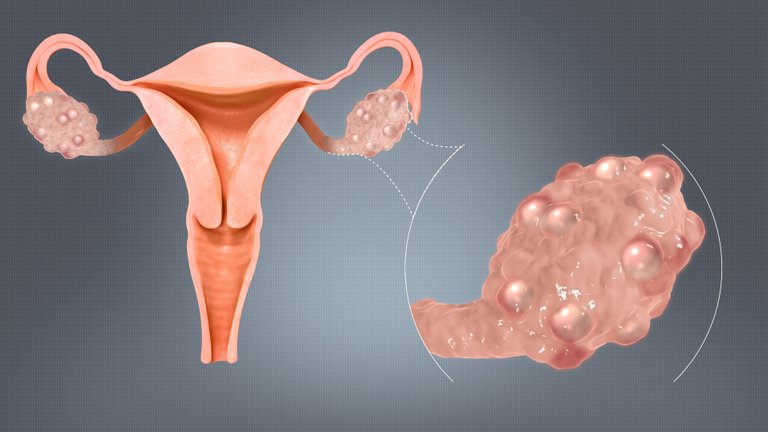
Typically, enlarged ovaries are seen. The volume of the ovary can be somewhere between 10cm3 to 12cm3. The stroma of the ovary is also increased. The capsule is thickened and becomes pearly white in color. Finally, multiple cysts of more than 12 measuring about 2-10 mm in diameter are seen on the ovaries.
Histology
Histology refers to the microscopic study of the cell. So, in this syndrome ovaries are studies microscopically. Under the microscope, thinking of tunica albuginea is seen. Cysts are observed with varying degrees of growth. Theca cells are seen to be enlarging and some level of insulin resistance is seen.
Clinical Features of the patient.
The present complaints to the doctor are abdominal obesity, menstruation abnormalities, presence of hirsutism, acne, and rarely virilism.
Mensuration abnormality might be oligomenorrhea(decreased), amenorrhea(loss), dysfunctional uterine bleeding(heavy or prolonged). hirsutism meaning male features are seen.
Other features are Acanthosis nigricans and HAIR-AN syndrome. acanthosis nigricans is a skin condition characterized by changes in the skin because of insulin resistance. The skin becomes thick and grey-brown pigmented. Commonly seen on the neck, thigh, axilla.
Internal examinations mighty reveal large cystic ovaries which may be hidden due to obesity.
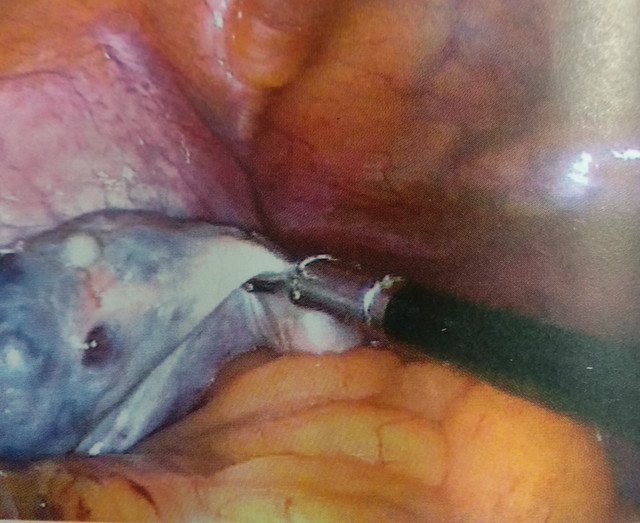
Fig: Polycystic ovaries

Fig: Acanthosis nigricans
Pathophysiology
The exact pathophysiology of Polycystic ovarian syndrome is still not clearly known. But it can be discussed under her following headings.
- Hypothalamic-pituitary compartment abnormality.
- Excess androgen with hirsutism
- anovulation
- Obesity
- Long term findings.
Hypothalamic-pituitary compartment abnormality: There is an increased release of GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) which in turn increases the release of the LH(luteinizing hormone). Increased LH results in an abnormally elevated level of LH. This increases the free Estrogen in the blood. A high level of estrogen inhibits the production of FSH(Follicular stimulation hormone). Therefore LH: FSH ratio is more than 2.
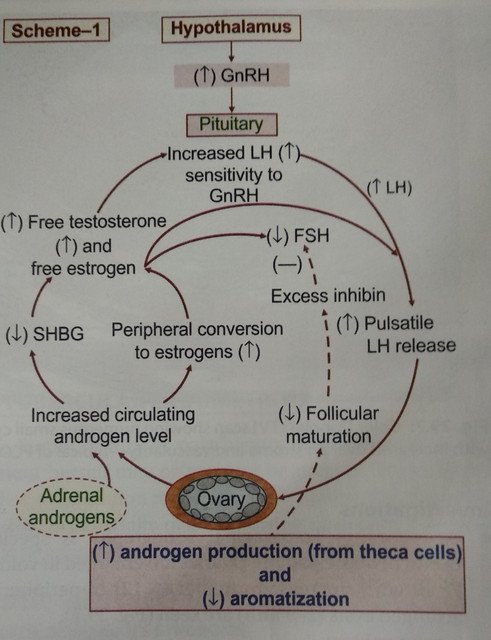
Fig: Pathophysiology of PCOS
Excess Androgen: There is abnormal regulation of enzymes that' regulate androgen formation. The principal sources of androgens are ovaries, adrenal glands. In this case ovaries secrete excess androgen because of elevated LH. LH stimulates ovaries to produce androgens. Also, Adrenal glands are stimulated to produce more androgens is due to stress and other enzyme dysfunctions.
Anovulation: As mentioned above there is Is LH level and low FSH level. FSH is responsible for growth and maturation of ovarian follicle which helps in the menstruation cycle and maintain fertility. Because of low level of FSH, the growth of ovarian follicles is arrested. It only grows to about 2- 9 mm in diameter. Therefore causes anovulation.
Obesity and Resistance to Insulin: Obesity is a very important factor contributing to PCOS. Obesity is associated with the production of androgens and decreased Sex hormone-binding globulin(SHBG). When there is less SHBG, free testosterone and estrogen increase in blood. This contributes to insulin resistance. Therefore, level of insulin also increases in the blood. Although, the exact cause of insulin resistance is still not known.
Investigations for PCOS
Transvaginal Sonography: This investigation is especially useful for obese patients. Enlarged ovaries are seen, more than 10cm3, and peripheral cysts are seen more than 12 in number.

Fig: Color Doppler transvaginal sonography showing numerous small cysts.
Assessment of BMI, Blood pressure, and waist circumference is done: BMI of more than 25kg/m2 and acanthosis nigricans with waist to hip circumference ration > 0.8 is suggestive of PCOS.
Different Serum levels are assessed:
- LH level is elevated with LH: FSH ratio > 2
- Raised estradiol.
- Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) is decreased.
- Excess androgen(male sex hormone)
- Testosterone level > 145 ng/dl
- Raised insulin is seen.
On laparoscopic examination, bilateral enlarged ovaries with multiple cysts are observed.
Management of PCOS
Here, management may vary from patient to patient. This is because the management depends on the factors like presenting symptoms like infertility, obesity, hirsutism, menstrual disorders, or any of those combined symptoms. Ther management is targeted towards correcting the biochemical abnormalities.
First-line management is always "weight reduction". The BMI or body mass index should be less than 25. This in turn improves menstrual disorders, infertility, and insulin resistance, hirsutism, and obesity. Therefore Exercise is found to be a beneficial treatment for PCOS.
Management Protocol if Fertility is not desired by the patient.
Oral contraceptive pills are found to be effective. As, they suppress LH production and improves SHBG which reduces free testosterone. Also, Hirsutism is seen due to inoculation, high androgen. This can be corrected by giving anti-androgens like Cyproterone acetate, spironolactone.
The insulin resistance associated with obesity, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. Metformin is the drug used to increase insulin sensitivity also reduces the weight and risk of diabetes.
Management protocol if Pregnancy is desired.
Generally, these patients are suffering from infertility, so, to make the patient fertile, induction of ovulation should be done. The induction of ovulation is done by using a drug named "Clomiphene Citrate" after correcting other hormonal abnormalities. If this is unresponsive then pure FSH or human menopausal gonadotrophin (HMG) with human chorionic gonadotropin(Hcg) is used.
Surgical treatment
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD) is done for the cases that are unresponsive to medical therapy. In this procedure, the cysts on the surface of the ovary are punctured up to 4 mm deep and then they are vaporized. Several punctures are made in the ovary. This surgery also preserves te fertility.
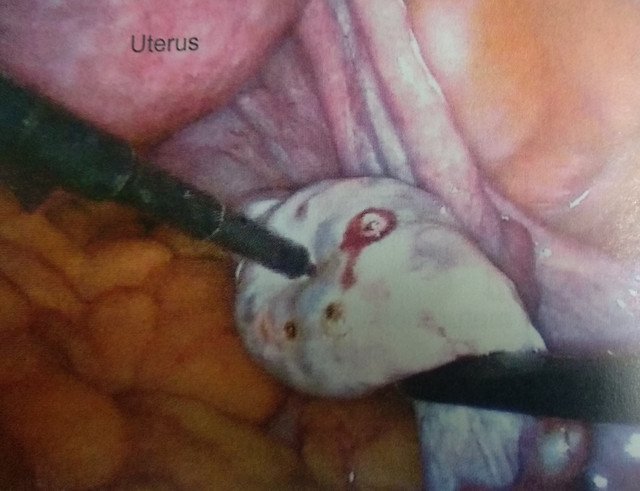
Fig: Surgical drilling of Cysts on Ovary.
You Stayed until the end. Hope you liked the article.
*ALL images used in this article are copyright free. If you have any concerns regarding the images feel free to drop down a comment*.
Refrences:
[1] https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/polycystic-ovary-syndrome-pcos/symptoms/
[2] https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/265309
[3] https://www.aafp.org/afp/2016/0715/p106.html
[4] https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/polycystic-ovary-syndrome
Image sources:
Image I - Credits (Under free to use License)
ALL the other images belong to me @idoctor.
!discovery 40
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our community! hive-193212
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Congratulations @idoctor! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your board And compare to others on the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
Hello @idoctor very well explained this medical pathology...it is understood to perfection, but I have a doubt with some images that you published within the content, I would like to know where the images of "Clinical Features of the patient", "Pathophysiology", "Investigations for PCOS" and finally "Management of PCOS" come from
Thank you for your concern. Actually, I am an intern doctor, and all of the pictures you mentioned are from my own medical notes. They are not downloaded, so I did not cite any link. Should I mention it in my article?
Of course you should mention that the images are of you, so it makes the work of the curators easier :)
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider supporting our funding proposal, approving our witness (@stem.witness) or delegating to the @steemstem account (for some ROI).
Please consider using the STEMsocial app app and including @stemsocial as a beneficiary to get a stronger support.
Nice, I was just looking to study a bit more about this condition and the way you summed up the physiopathology made it very easy to understand, thanks!