GLAUCOMA; THE IRREVERSIBLE CAUSE OF BLINDNESS.
According to this study, diagnosis is usually delayed because it may be asymptomatic until a relatively late stage. A general understanding of the disease pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment may help eye physicians in referring high-risk patients for complete ophthalmologic examination and in more actively participating in the care of patients affected by this condition.
Glaucoma is an eye condition that leads to irreversible blindness.
Glaucoma is a chronic, progressive optic neuropathy caused by a group of ocular conditions which lead to damage of the optic nerve with loss of visual function.
It is characterized by:
- Optic neuropathy,
- Specific pattern of visual field defect.,
- Raised intra-ocular pressure (IOP).
Damage to optic nerve is an irreversible process which makes glaucoma an irreversible cause of blindness.
Hypotony; <10mmHg
Normal IOP; 10-21mmHg
Suspicious case; 20-25mmHg
Glaucoma; >25mmHg
A study done in 2014, showed the global prevalence of glaucoma for population aged 40-80 years to be 3.54%. The prevalence of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma is highest in Africa, and the prevalence of Primary Angle Close Glaucoma is highest in Asia.
The pathology of glaucoma revolves around the aqueous humor dynamics. The principal ocular structures concerned with it are; the PARS PLICATA part of the ciliary body, ANGLE OF ANTERIOR CHAMBER, and the AQUEOUS OUTFLOW SYSTEM.
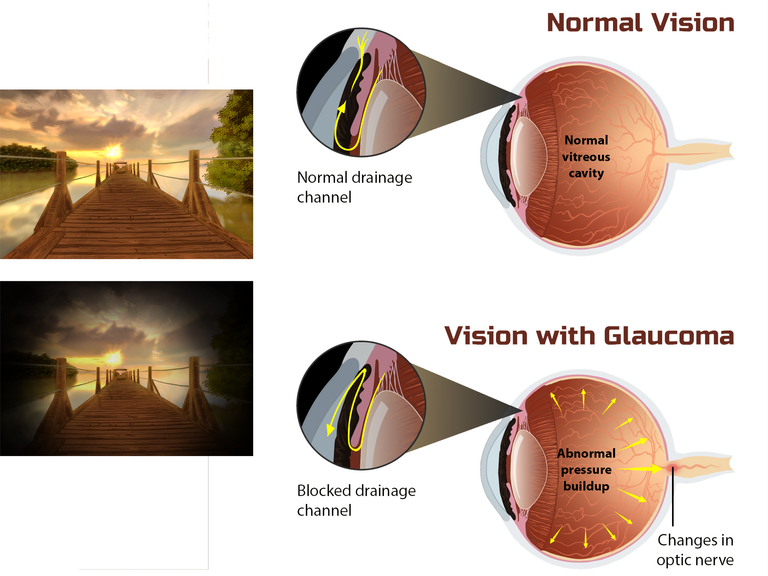
By MyUpchar - File:Depiction_of_vision_for_a_Glaucoma_patient.png, CC BY-SA 4.0
CILIARY BODY; this is the main site of aqueous production and it consists of 4 layers, (ciliary muscle, stroma, ciliary processes and epithelium) and 2 parts, (pars plicata, and pars plana). The pars plicata secretes aqueous humor.
ANGLE OF ANTERIOR CHAMBER; plays an important role in the process of aqueous drainage. The angle width is different for individuals and plays a vital role in the pathology of different types of glaucoma. Clinically the various angle structures can be seen during a gonioscopic examination.
AQUEOUS OUTFLOW SYSTEM; It includes the trabecular meshwork(sieve-like structure that filters aqueous humor into the canal of Schlemm.), canal of Schlemm, aqueous veins(These are about 25-35 in number. They leave the canal of Schlemm at oblique angles to terminate into episcleral veins.) and the episcleral veins.
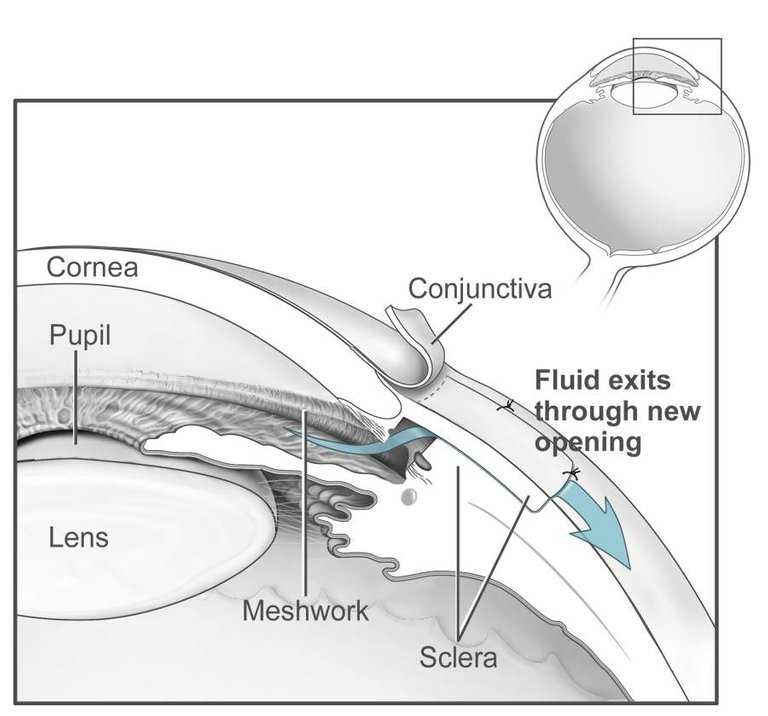
By National Eye Institute, National Institutes of Health - Public Domain
The factors which maintain the normal IOP are the formation of the aqueous humor using secretion and ultrafiltration processes, the outflow of the aqueous humor via the angle of anterior chamber and uveoscleral outflow routes, and the pressure in the episcleral veins.
The most important factor which causes rise of IOP is obstruction to the drainage of the aqueous humor through the angle of the anterior chamber and at the pupil.
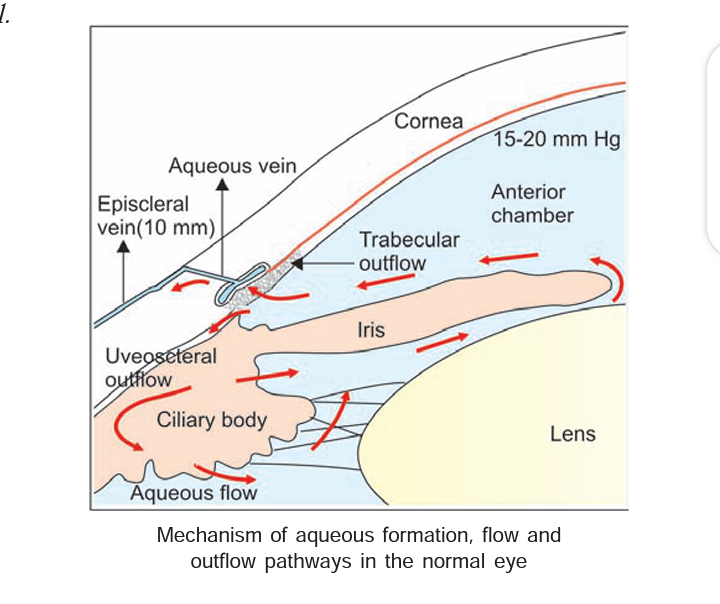
Elevated IOP in glaucoma results from increased resistance within the aqueous drainage system.
Retinal ganglion cell death due to compromise of the microvasculature with resultant ischaemia in optic nerve head, and mechanical damage due to raised IOP.
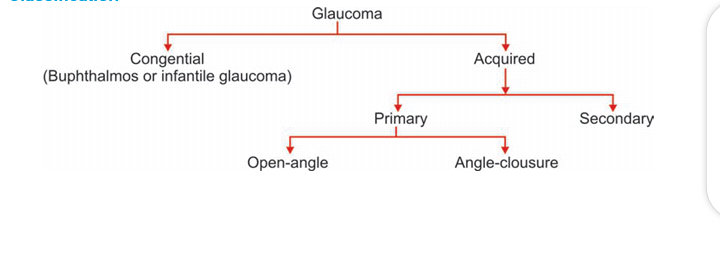
The classification of glaucoma is as seen in the picture below.
Secondary glaucoma could be due to trauma, steroid, tumor, e.t.c.
Primary open angle glaucoma is mostly seen.
Other Factors that could predispose one to glaucoma are; myopia, disc haemorrhage, increased cup/disc ratio, age, race, family history e.t.c.
This condion is commonly asymptomatic and detected incidentally. For those who have symptoms, they could present with mild headache, eye pain, minimal blurring of vision, frequent changes in presbyopic spectacles.
On examination, conjunctiva, cornea and anterior chamber depth may be normal with decrease in vision, open angles on gonioscopy, raised or normal IOP, Central cornea thickness e.t.c.

By The original image is in the public domain; it was originally released by the NIH. Effect of Glaucoma. Public Domain
Some of the assessments done includes gonioscopy, fundoscopy, perimetry, optical coherence tomography, slit lamp biomicroscopy.
The management could be medical or surgical.
MEDICAL TREATMENT; prostaglandin analogue; preparation using latanoprost, tarvoprost and bimatoprost; miotics (such as pilocarpine); sympathomimetic (such as epinephrine); systemic carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (such as methazolamide, acetazolamide) e.t.c.
These help increase the uveoscleral outflow of aqueous and decrease episcleral venous pressure.
SURGICAL TREATMENT; Argon laser trabeculoplasty, trabeculotomy, minimally invasive glaucoma surgery, glaucoma drainage devices.
In most cases, glaucoma is a chronic condition that requires lifelong management Currently available treatments cannot reverse glaucomatous damage to the visual system; however, early diagnosis and treatment can prevent progression of the disease.
Regular eye check up is adviced and a proper eye hygiene,such as good illumination while reading, reduced screen time e.t.c
Congratulations @beulah4real! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s):
Your next target is to reach 300 comments.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOP