A COMMON CONDITION IN AGING MEN; BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH)
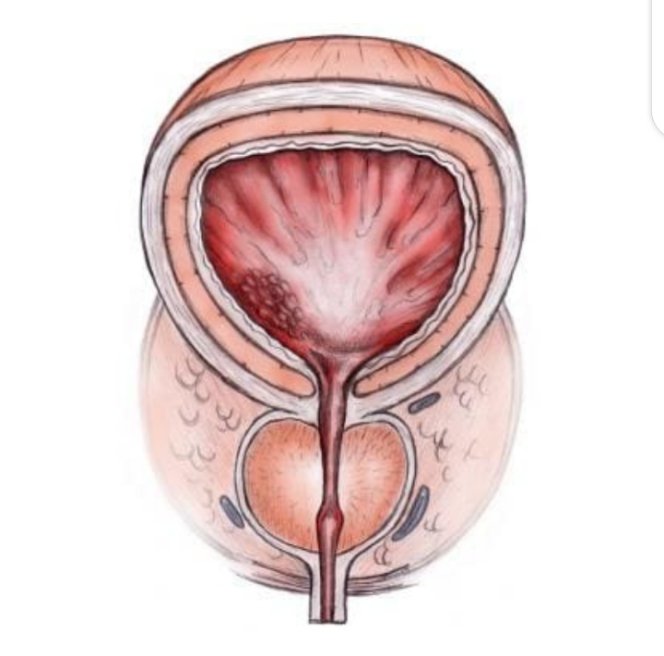
Anatomy of a normal prostate
The Prostate forms part of the male reproductive system. It is situated anterior to the rectum and just below the bladder. It is walnut shaped. It has the outer layer of tissue called capsule that enclosed the zones within. These zones include, the peripheral, central, anterior fibromuscular stroma and transition zones.
Having discussed the anatomy of the prostate briefly, we'll be diving into our topic for today.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia a.k.a BPH is a histologic diagnosis. There is an enlarged Prostate due to cellular proliferation.
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a common condition in aging men that is frequently associated with troublesome lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).
Prostatic enlargement depends on the potent androgen dihydrotestosterone (DHT). In the prostate gland, type II 5-alpha-reductase metabolizes circulating testosterone into DHT, which works locally, not systemically. DHT binds to androgen receptors in the cell nuclei, potentially resulting in BPH.
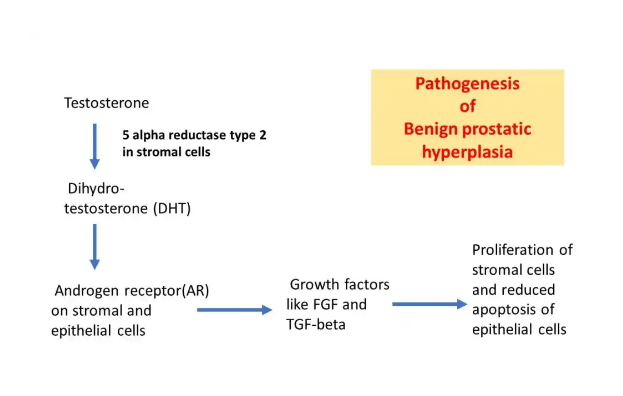
Pathophysiology
However, the fact that serum testosterone levels decrease with age, yet the development of BPH increases, suggests that other agents play an etiologic role. Possible factors include the metabolic syndrome, hyperinsulinemia, norepinephrine, angiotensin II, and insulin-like growth factors.
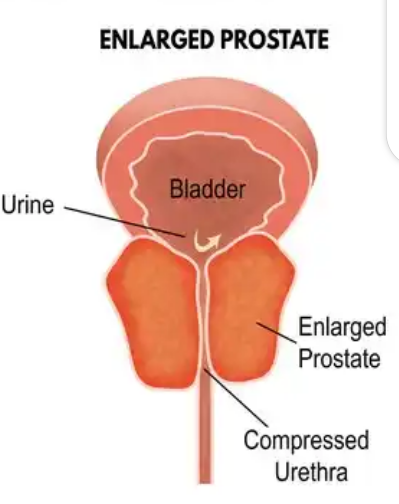
The theory behind BPH is that, as the prostate enlarges, the surrounding capsule prevents it from radially expanding, this results in urethral compression. However, obstruction-induced bladder dysfunction contributes significantly to LUTS. The bladder wall becomes thickened, trabeculated, and irritable when it is forced to hypertrophy and increase its own contractile force.
This increased sensitivity (detrusor overactivity), even with small volumes of urine in the bladder, is believed to contribute to urinary frequency and LUTS such as Urinary frequency, Urinary urgency, Nocturia, Hesitancy, Incomplete bladder emptying, Straining, Decreased force of stream, Dribbling.
The bladder may gradually weaken and lose the ability to empty completely, leading to increased residual urine volume and, possibly, acute or chronic urinary retention.
The size of your prostate doesn't necessarily determine the severity of your symptoms. Some men with only slightly enlarged prostates can have significant symptoms, while other men with very enlarged prostates can have only minor urinary symptoms.
In some men, symptoms eventually stabilize and might even improve over time.
Risk factors for prostate gland enlargement include:Aging, family history, diabetes and heart disease, lifestyle.
Complications of an enlarged prostate can include:Sudden inability to urinate (urinary retention), urinary tract infection, bladder stones, bladder damage and kidney damage.
The American Urological Association [AUA] has issued a guideline on the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia [BPH]. The guideline includes an algorithm for the diagnosis and basic treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS).
The digital rectal examination (DRE) is an integral part of the evaluation in men with presumed BPH. With the DRE, the examiner can assess prostate size and contour, evaluate for nodules, and detect areas suggestive of malignancy. The other means of assess the patients include: Abdominopelvic ultrasound scan (size of Prostate, volume of urine after voiding, bladder wall thickness); Trans Rectal Ultrasound scan of Prostate, TRUSS(echo pattern); Prostatic Specific Antigen PSA, Prostatic biopsy, (transrectal, transperineal trucut, transurethral resection); kidney function test; complete blood count e.t.c.
BPH is an important disease, and as the pathogenesis is not fully understood it impacts the effectiveness of medical therapies.
The International Prostate Symptom Score, IPSS, is used to assess the severity where total score is 35.
Mild is Scored 1 to 7, moderate is scored 8 to 19 and severe is scored greater than or equal to 20.
Management depends on severity and includes;
- Watchful waiting/active surveillance.
- Medical therapy.
- Minimally invasive procedures.
- Surgery.
Watchful waiting involves regular follow up with assessment of IPSS, Digital rectal examination, peak flow rate, PSA, Abdominal USS with post void urine volume recorded.
Medical therapy is aimed at dynamic/static obstruction.
A. Alpha adrenergic blockers e.g doxazosin, terrazosin, tamsulosine.
B. Androgen suppressant e.g finesteride, episteride, glutamine.
C. Others e.g aromatase inhibitors, phytotherapy.
Some of the drugs can be given as combination therapy.
Minimally invasive procedures are indicated for patients with IPSS 8-19/severe symptoms but not fit for major surgery.
A. High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound, HIFU.
B. Transurethral vaporization of Prostate.
C. Transurethral laser therapy. e.t.c
Surgical management such as transurethral incision of the prostate; transurethral resection of the prostate, TURP, Open prostatectomy.
In conclusion, BPH is a common condition as men get older. An enlarged prostate gland can cause uncomfortable urinary symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. It can also cause bladder, urinary tract or kidney problems. If you're having urinary problems, discuss them with your doctor. Even if you don't find urinary symptoms bothersome, it's important to identify or rule out any underlying causes. Untreated, urinary problems might lead to obstruction of the urinary tract.
If you're unable to pass any urine, seek immediate medical attention.
REFERENCE
Medscape
Mayoclinic
HTTP is in use instead of HTTPS and no protocol redirection is in place. Be careful and do not enter sensitive information in this website as your data won't be encrypted.
It's also a good habit to always HOVER LINKS to see the preview in the bottom-left corner of your browser.
@cryptoshots.nft 🔫
P2E 3D game @ Hive
Congratulations @beulah4real! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s):
Your next target is to reach 500 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out the last post from @hivebuzz: