Good morning friends and followers of our community, today we have a post that will reveal some secrets about the stem of the plant, we know from school that plants have the following structures: (leaf, stem and root), the stem being the structure that gives support, size, fixation and conduction to the plant of the nutrients that are absorbed by the soil or by the leaves. But some questions arise! What structures do this conduction work in the stem? Can we see them under a microscope? Well, let's answer all those questions.🧫🧑🏻🎓🔬
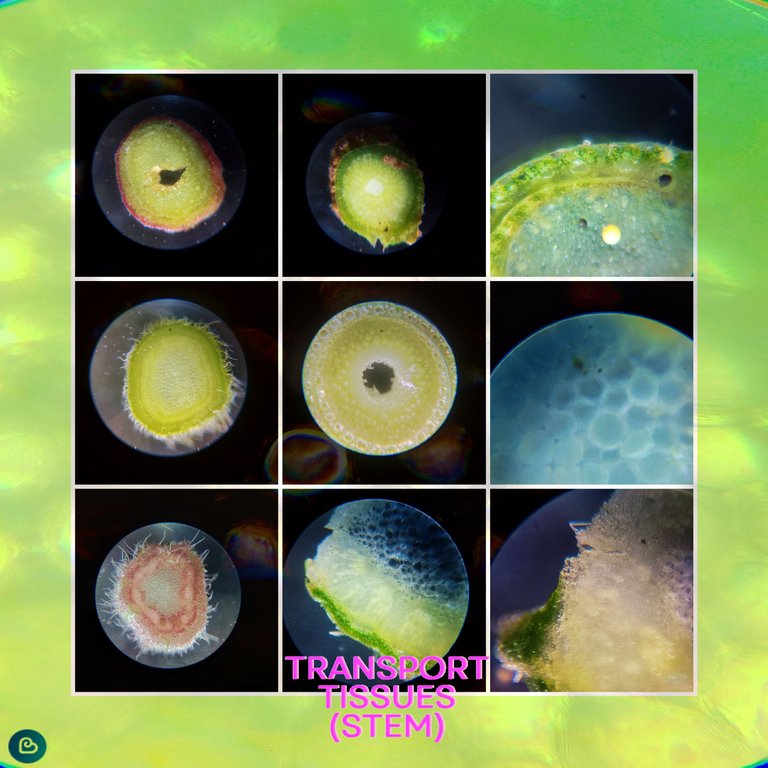
What are herbaceous plants??🧫🔬🫛🌷🌻

To better understand the tissue and structure of the stem, we will work with herbaceous plants, so I went out to collect more than 6 species of herbaceous plants in order to compare the different ways in which the conduction tissue is arranged in the medulla of the stem, but what are herbaceous plants? According to: (www.ecologiaverde.com) "Herbaceous plants are the famous herbs and are spread throughout the world being the most popular, they have a rapid adaptation capacity and are resistant, the difference from "common or woody" plants is that they cannot have bark, that is, that exterior wood covering." Why use several plants? Because within the world of herbaceous plants they are classified into two types according to how the transport tissue is arranged in: (monocotyledons and dicotyledons) and with this we can compare the differences.🫛🧑🏻🎓🔬
https://www.ecologiaverde.com/plantas-herbaceas-caracteristicas-y-ejemplos-1950.html

Characteristic of herbaceous plant🧫🔬🫛🌷🌻

Aqui vemos la foto de un corte transversal de un tallo de una planta herbacea, como puedes ver el color predominante es verde lo que nos dice que hay prescencia de clorofila, sin embargo la principal caracteristica es que no hay madera, no forman esa capa de madera envuelta en la epidermis, y por eso estas plantas no crecen muchos metros como una planta lenosa, sin embargo tome un tallo de una enredadera que si produce madera y la corte para que veas la comparacion, no me centrare mucho en la corteza de madera porque haremos un post de las lenosas, en la proxima fotografia veremos cada estructura.🥬🌻🧪
https://buenosaires.gob.ar/colecciones/herbaceas#:~:text=Las%20plantas%20herb%C3%A1ceas%20se%20distinguen,estepas%20como%20nuestro%20pastizal%20pampeano.

Dicotyledonous stem🧫🔬🫛🌷🌻
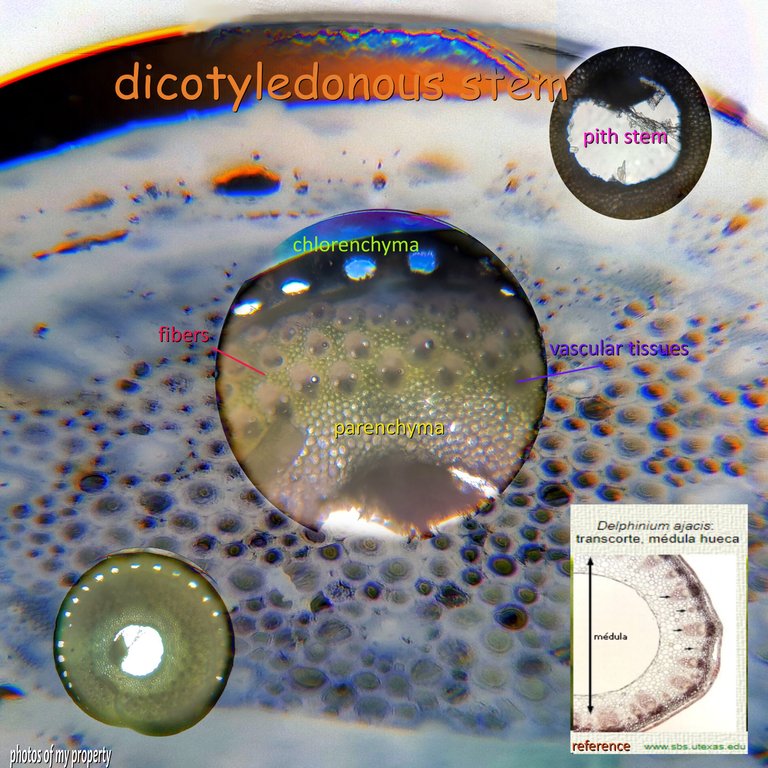
In order to understand the topic we are explaining today we have to differentiate between mono and dicot, it is very simple, one has one "embryo" or seed while the other has 2, but how do we distinguish both in the tissues? Well, dicots have the tissue normally organized towards the outside of the center or the medulla, just as you see in the photo, while monocots have the vascular bundles dispersed throughout the parechyma and even the medulla without a "pattern". We start from the outside in with the chlorenchyma: typical plant tissue where the chloroplast is located, in our case it would be the epidermis, since chlorenchyma is more of a leaf, then we have the parenchyma, which we already defined in the last post, a reserve tissue, with fibers, chloroplasts, starch, etc.🧑🏻🎓🧫🌷
https://blogs.upm.es/innebioveg/tallo-2/

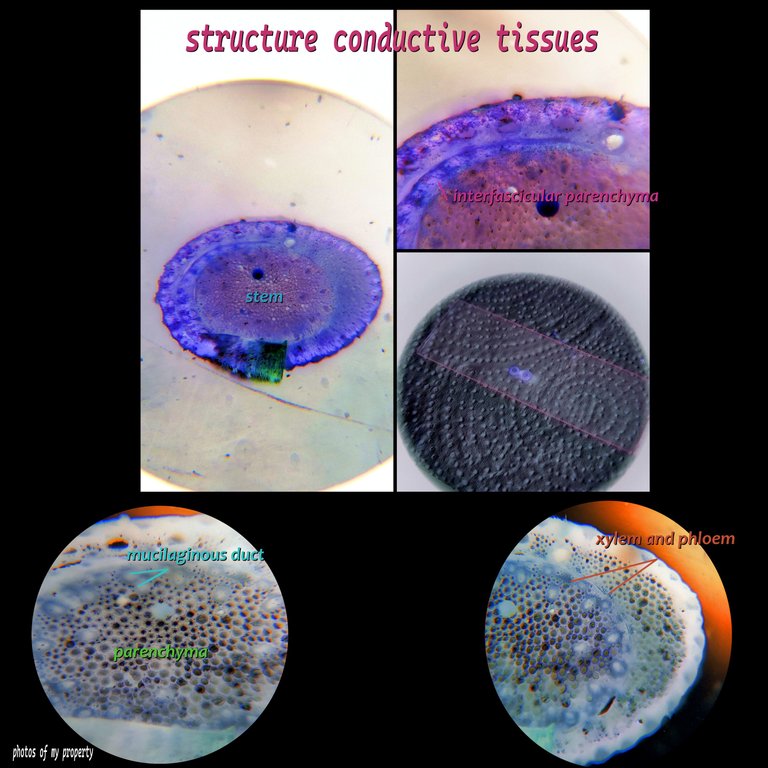
We continue with the structure of the stem and move on to the medulla, which can vary here, for example if you observe the previous plant was hollow, while here it has "fused" with the parenchyma, it serves as support and at the same time as a means of transport and reserve, around the medulla we have the conduction tissues. xylem, phloem, now we will move on to the center of our post which are the vascular bundles where we find the conduction or transport tissues xylem and phloem, always surrounding the bundles and smaller in size.
https://www.biologia.edu.ar/botanica/tema17/17-4Mono.htm

Xylem and Phloem🧫🔬🫛🌷🌻
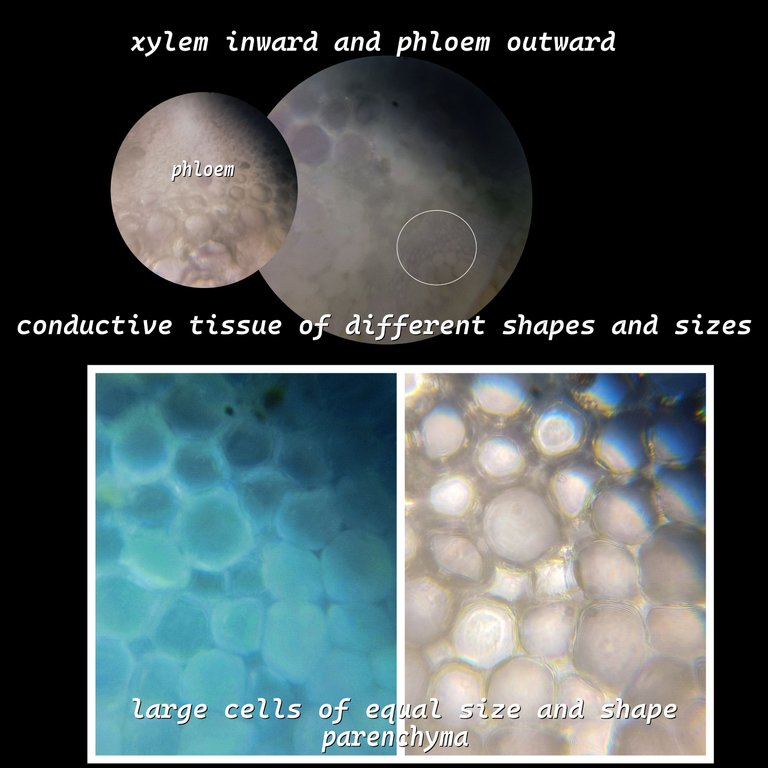
I remember that in botany class the teacher gave us two important pieces of advice: 1) no matter what type of plant, all the structures are the same, the only difference is that in woody plants the tissues are more marked, 2) most of the tissue is parenchyma and they are large cells. Another interesting piece of advice is that we always see the xylem towards the inside of the center of the medulla and the phloem towards the outside. In this photo we see the difference between the parenchyma and the transport tissues. What does the xylem do? Well, it transports substances such as water and minerals, while the phloem transports the substances for photosynthesis. With this we have answered the essential questions about these tissues.🧪🧫
https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tejido_vascular#:~:text=El%20xilema%20es%20una%20estructura,c%C3%A1mbium%20vascular%20y%20el%20fel%C3%B3geno.

Medulla with associated parenchyma🧫🔬🫛🌷🌻
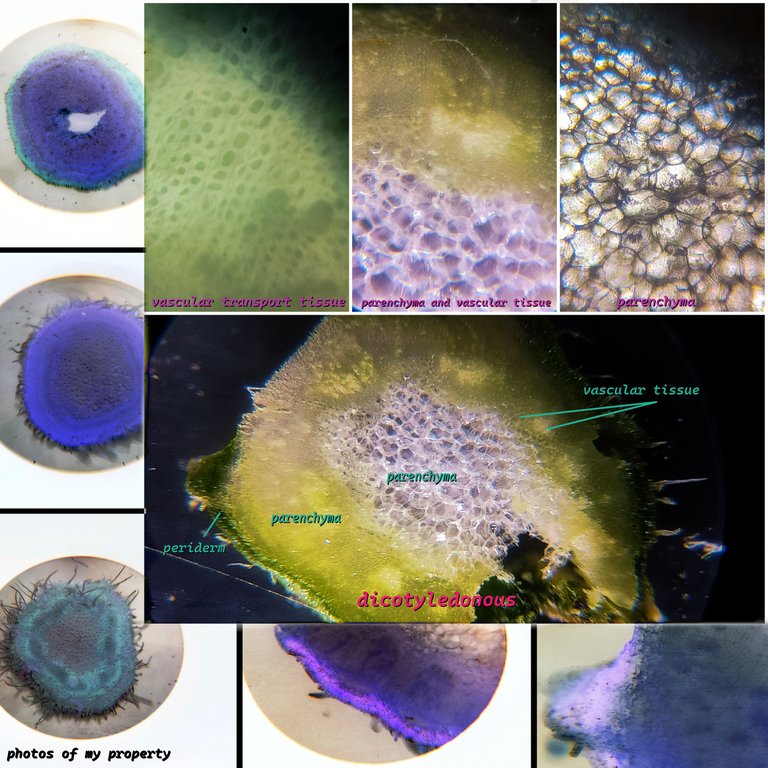
This section is from another vascular plant. Here we see how the medulla is arranged in the center in a different way, that is, it is not hollow, on the contrary, it has a lot of parenchyma. Above we see the differentiation of the xylem and phloem and we see two layers of parenchyma, which the other plant did not have. It is interesting to see it through the microscope because the light easily passes through the tissue in the center. We could say that because it is not hollow, it has more support in the center and this would help it to grow taller.🫛🌎🧑🏻🎓

A cut of Monocotyledon🧫🔬🫛🌷🌻
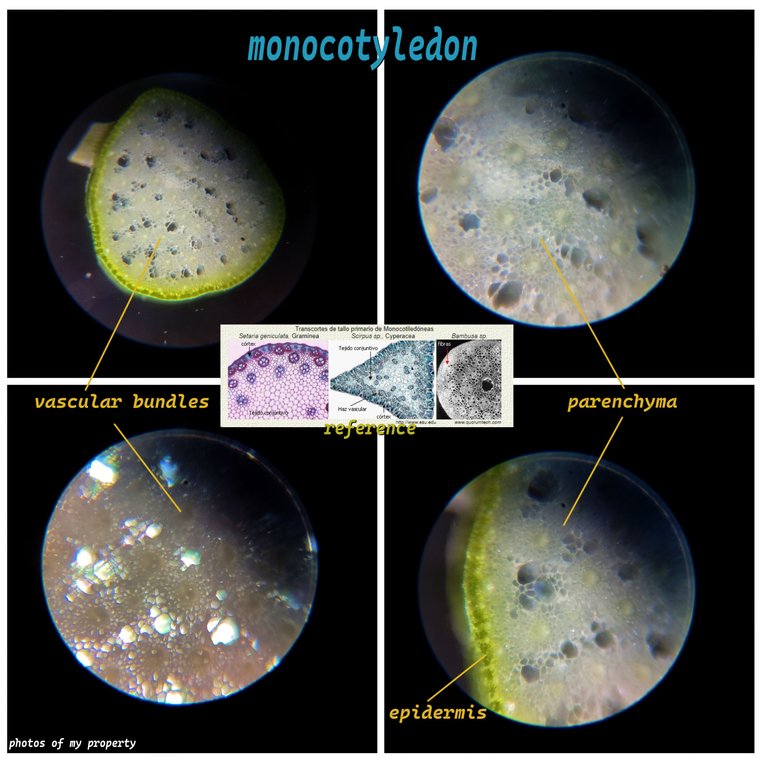
What a beautiful section of a monocotyledonous herbaceous plant, everything is different inside the medulla, as you can see there is no defined center, on the contrary there is a parenchyma that is dispersed throughout the stem, and another difference is how the vascular bundles are arranged, do you remember that the previous sections were around the medulla? Not here, they are dispersed everywhere! We see a beautiful defined epidermis that has chloroplasts, however here we notice that the parenchyma does not have plastids, that is why it appears "transparent".
https://www.ugr.es/~mcasares/Organografia/Tallo/Estructura%20tallo.htm

The variety of stems🧫🔬🫛🌷🌻
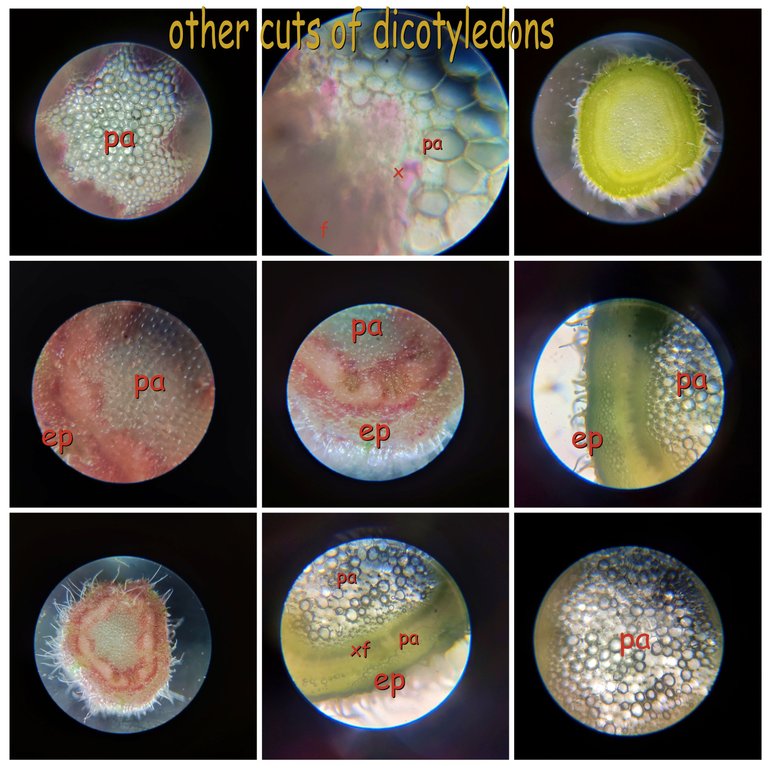
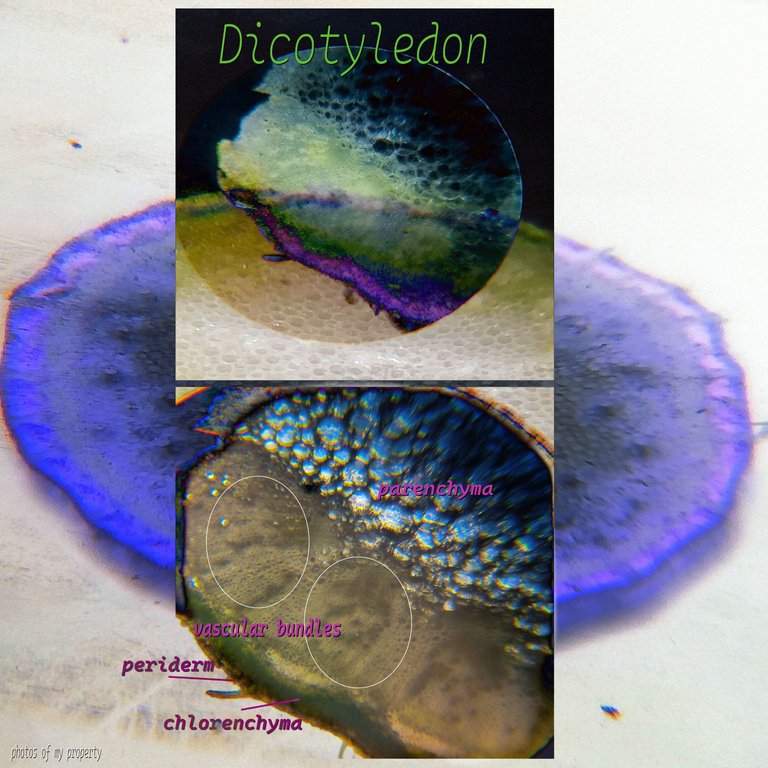
Finally, to close the post we have some other examples of the stem tissue and the arrangement of its structures, we see from the parenchyma to the vascular bundles, as you can see some plants in the epidermis have structures that serve as a means of propagation or protection, they are evagiations of the dermis layer, other plants have substances that make them look another color like red. Place the abbreviated terms so you can differentiate each thing you see in the photos: (pa parenchyma), (e epidermis), (x xylem, f phloem).🫛🌎

Special features in Amazing Nature
Thank you for being with us and see you next time with more amazing posts!
Make sure you post directly in our community.
Our curation team will be happy to review and upvote your work.
To be eligible for curation:
Join and post through the community and you can earn curation rewards.
Contents must be posted into the Amazing Nature Community feed or use as first tag if posting from Ecency.
Photographs must be your own or properly sourced with a description of at least a few sentences.
Entries for the Amazing Nature Contest are separate. They will be highlighted in the competition evaluation.
unfortunately we publish with peakd because eency gives us bug errors.😔

All photos shown in the post were taken by me.🧫🔬🚩🧑🏻🎓



















Congratulations @hive-174680! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next payout target is 50 HP.
The unit is Hive Power equivalent because post and comment rewards can be split into HP and HBD
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPGood morning dear friends @hive-174680
What an entertaining and interesting post to read
I appreciate all the work you have done to share all this excellent information
Interesting project.
Nice microscope images of plants! That reminds me plant physiology classes that I had in school hehe