What is blockchain? How does it work?
The term blockchain has become a part of our modern dictionary, yet many people still ask: What is blockchain? How does it work?
In addition to many other questions that show the extent of confusion experienced by users about what this new technology is and what it does.
What is blockchain? Simple definition and explanation:
In its most basic sense, a blockchain is a publicly managed record with which transaction data is verified.
All data blocks are arranged in chronological order and connected to each other, forming a chain of blocks or what is known as a blockchain.
Meaning that the transactions are written in a block and this block is connected with another block and closely linked with it if any defect in one of them makes Bitcoin invalid at the invalid block.
Meaning that all old data blocks in the network are permanent, that is, they cannot be modified or changed retrospectively.
Blockchain is an alternative to traditional centralized systems like the traditional financial banking system, which is why blockchain is an integral part of many cryptocurrencies.
However, blockchain technology is not only beneficial for cryptocurrencies, but there are also other applications of blockchain in other industries and sectors, many of which we touched upon in previous articles on Bitcoin Arabs.
Blockchain, by simple definition, is a decentralized public ledger built on the P2P system. This system can be publicly shared among users to form an immutable record.
All blockchain transactions are time stamped and connected to one another.
Each time a new transaction is added, it joins the collection of previous transactions into a new block that is produced at the end of the chain.
Here it gets smart and it becomes more difficult for cybercriminals to manipulate the data.
A blockchain can only be updated by consensus.
That is, blockchain participants must agree on additions and changes to the chain itself, which becomes important when it is kept in mind that nothing can be removed or entered into the blockchain.
Verifiable and auditable blockchains allow for accurate and transparent record keeping.
Blockchain is similar to "Google Sheets":
If you do not understand well what has been mentioned above, we would like to clarify more and liken the blockchain to Google Sheets.
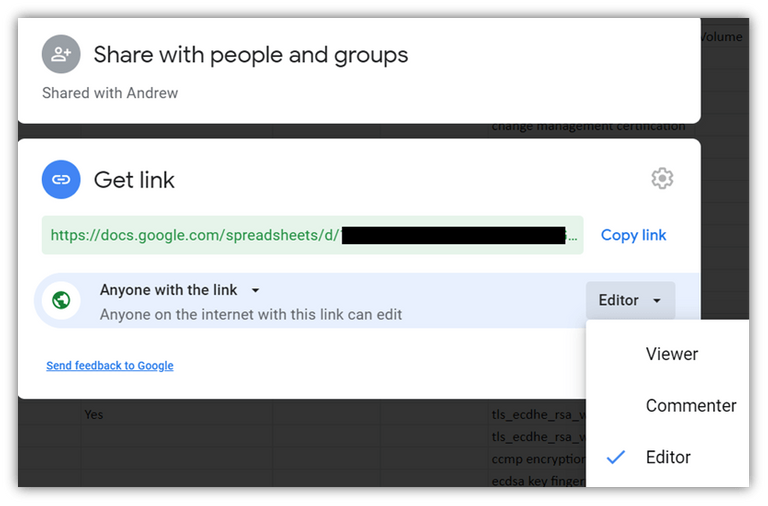
Google spreadsheets, as shown in the image above, are very similar to the blockchain, except for the difference in the inability to modify except with the consent of 51% of the callers to the network and the decentralization of data storage.
The Google spreadsheet is a file that resembles an "Excel" file from "Microsoft" that allows users connected to it to add data and information with the ability to change the data on the part of those calling the file.
Imagine, if you will, an "Excel" spreadsheet that is repeated 10,000 times across a vast network of computers.
Now, imagine that this network was designed to update this spreadsheet in real time.
Traditionally, spreadsheet documents shared for collaborative purposes must undergo a certain process in order to achieve this.
Where you must create an "Excel" document, save it and e-mail it to the recipient, who will then be asked to make modifications, save it again and e-mail it again.
There are clear benefits to "closing" the other party while the release is taking place. For example, in the world of banking, there cannot be two owners manipulating or changing the same record at the same time.
However, for many users, it was not the most efficient way to do such tasks.
There had to be an easier way for everyone to access without having to have 10,000 copies of the file with different duplicates.
Here, Google has introduced the document editor (Google Sheets), as it allows sharing a single file with everyone with the ability for everyone to access and modify it.
Therein lie a whole number of benefits, which cannot be separated from how blockchain actually works.
Since all the data on Bitcoin exists as a compatible and constantly shared database, it is very easy to see the additional points that arise from this system, and by no means only in the field of document sharing.
We mentioned earlier that blockchain differs from “Google Sheets” documents, as the blockchain does not depend on a single location in the data storage process, but rather is distributed in a decentralized manner.
How does blockchain work?
Now that we understand what a blockchain is, we proceed to explore the components of the process and answer the question:
How does blockchain work?
A graphic showing how the blockchain works.
A blockchain simply works through a sealed series of data records, run by a group of computers that are not owned by any entity, individual, or company.
Data blocks (referred to as “blocks”) are linked together using cryptographic principles, and together they form a “block chain” or what is called a blockchain.
A graphic showing how the blockchain works.
The blockchain is independently managed and used in peer-to-peer networks between groups of connected parties.
The nature of the blockchain eliminates centralization and the existence of an official.
Users work together as a group administrator.
There is another form of blockchain, generally known as private blockchain, that allows an organization to create and manage transaction networks that can be used with partners, either internally or from company to company.
Every blockchain transaction goes through the same steps regardless of whether it is used in financial transactions or to track products.
The basic principle of making any blockchain can be divided into four steps:
Recording the transaction.
Then this recording, which contains certain details of the people who conducted the transaction, is authenticated using the digital signature for each of them.
Every transaction is validated for authenticity.
Then this verification process is completed by the computers connected to the network, each independently verifying to ensure that the transaction is legitimate.
Since this process is decentralized, this means that every node in the network must agree before the process can be completed.
Once verified, every transaction is added to the block that is hashed.
“Blocks” are basically collections of transaction records, each of which is unique.
Each block also carries a symbol known as the hash value (or hash summary), which is uniquely identified and calls for its location within the blockchain.
Hashing also guarantees the integrity of the data to show that it has not been modified since it was recorded in the block.
Once completed, the block is added to the end of the blockchain.
This brings us to the end of the blockchain creation and verification process.
Once one block is complete, another block will follow which usually only takes a matter of minutes.
The three pillars of blockchain technology:
Another important aspect of understanding a blockchain involves the so-called pillars, or the three pillars.
There is some real disagreement in the online cryptocurrency community over the number and features of the blockchain.
Some say it's seven, others say it's nine.
For the sake of simplicity and convenience, we will stick to three which are:
Decentralization
Transparency
Persistence
Decentralization:
Before the arrival of blockchain, we were accustomed to services that were completely centralized.
Banks, for example.
Your money is collected by your main bank, and it cannot be accessed online or accessed personally with the need to go directly through the central systems of the bank.
While these central systems, like traditional spreadsheets, have served us well for many years, they are far from what is currently possible.
When a central system is upgraded or changed, everything stops.
If it is turned off, anyone who needs to use it will be closed automatically.
However, since the blockchain is, by nature, a decentralized system, the information is owned by every node in the network (the node is the computer connected to the network).
As such, you do not need to go through third parties to interact with your data.
It can be said that this is one of the most important forces behind the rise of Bitcoin, meaning and simply you are the only one responsible for your money, and there is no need for any bank to participate or any third party.
This does not mean that the blockchain is not vulnerable to fraud, as a 51% attack can be done.
However, the decentralized nature of blockchain in general means that blockchain is more difficult to penetrate than traditional infrastructures.
Transparency:
Interestingly, the concept of transparency is often misunderstood, and the question is usually asked:
How can absolute privacy and absolute transparency be achieved at the same time?
Well the answer to that lies in the use of complex encryption and public addresses.
For example, an individual's transaction record will be represented by an encrypted code.
It is true that the transactions of any address or digital wallet can be tracked, but it is difficult to know who is behind the address and the wallet.
Most blockchains are anonymous in this way, but this does not mean that they are completely anonymous.
However, in this system, real identities can be kept essentially secure, as long as users are careful to do so.
According to Bitcoin.org :
QuoteSince users usually have to reveal their identity in order to receive services or goods, Bitcoin addresses cannot remain completely anonymous.
Since blockchain is permanent, it is important to note that something that cannot be tracked currently may become trivial to track in the future.
For these reasons, Bitcoin addresses should only be used once and users should be careful not to reveal their addresses.
Stability:
Resilience and the inability to alter and manipulate data is the vital nerve of the blockchain, as the blockchain cannot be altered or tampered with.
This pillar helps blockchain technology to become more transparent by preventing double spending, as well as preventing money manipulation and data alteration.
What industries can benefit from blockchain?
Blockchain is creating a new era of reliability.
Although it is still a relatively new technology, it is proving useful and effective across a number of vital industries.
The potential of blockchain is being demonstrated day after day, and its uses have manifested themselves in surprising ways.
What's next for blockchain technology?
The blockchain revolution, while already impressive in terms of its scope and transformative potential, is only just getting started.
In fact, there is still a certain amount of resistance to blockchain technology among some organizations and companies, although the technology brings with it many opportunities, and blockchain offers stability, transparency and decentralization.
However, traditional systems will not easily exaggerate their mechanisms and means for the sake of a modern technology that appeared only 10 years ago.
In other words, there are a plethora of challenges that must be addressed before blockchain technologies become mainstream.
There are real concerns that must be addressed first, and companies need to weigh the options that are best for them.
Posted Using LeoFinance Beta