CYMOTHOA EXIGUA: THE MARINE PARASITE THAT DEVOURS THE TONGUES OF ITS GUESTS
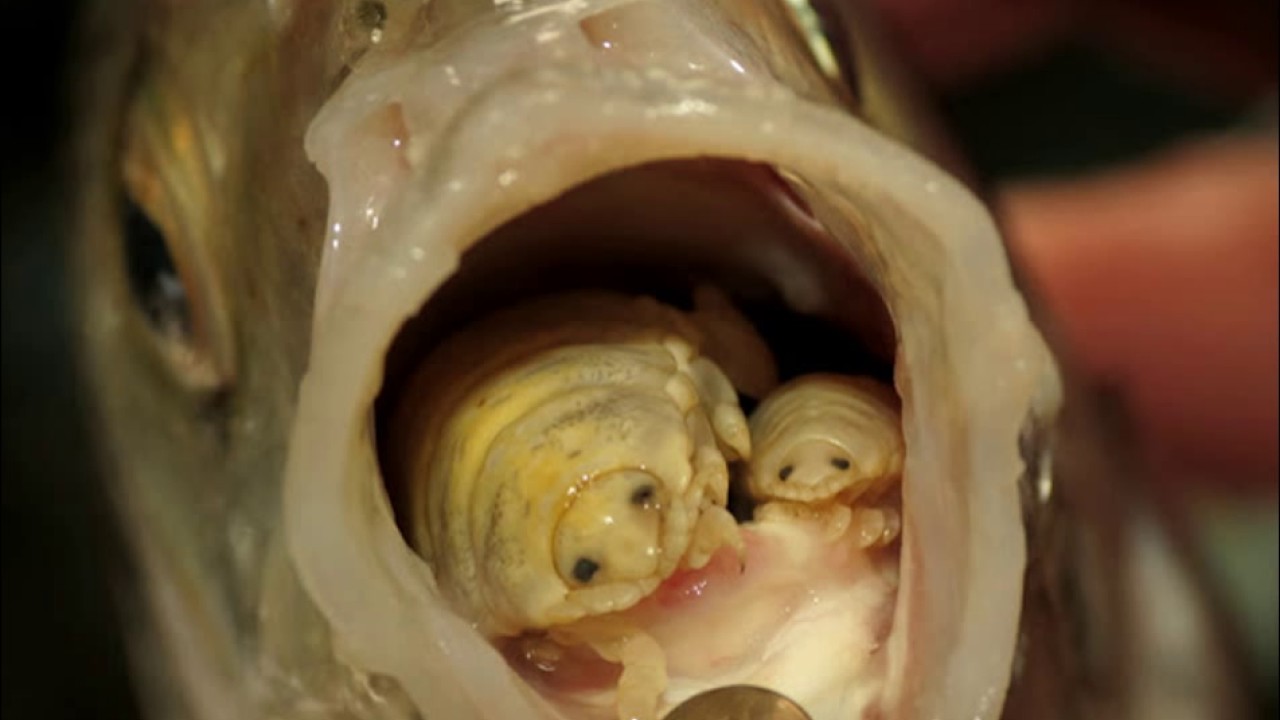
The Cymothoa Exigua is an isopod crustacean of the cymotoid family, which can grow up to 10 mm (millimeters) in length. It is a parasite that attaches itself to the tongue of its host fish through its three pairs of front legs, and then drinks from the artery that supplies blood to this organ. Over time, the tongue atrophies until it disintegrates completely, and the crustacean replaces the function of the organ with its own body and relieves the blood pressure of the host's circulatory system there. The fish can use the parasite as if it were a tongue. normal, and does not receive much damage, since the Cymothoa Exigua feeds on the mucous membranes of the fish, so it does not seem to show much interest in the food that its host eats.
Their distribution is quite extensive, since they can be found from the southern Gulf of California to the northern Gulf of Guayaquil in Ecuador, and sightings have even been reported in Greece and the United Kingdom. Although few studies document in more detail the biology and reproduction of these crustaceans, it is believed that the Cymothoa Exigua parasites are all born as males and have the ability to change sex depending on the circumstances. That is, if there is not a female present, but only two males, one of them can become a female in order to reproduce.
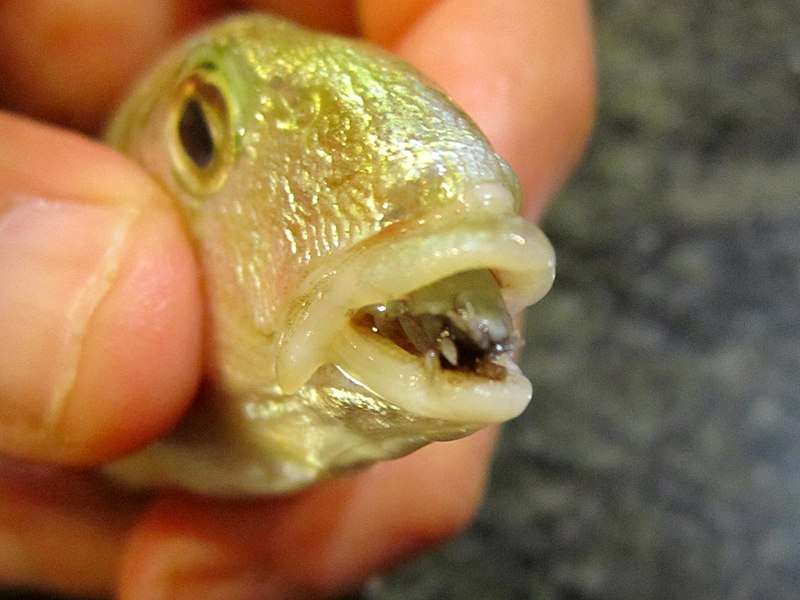
This crustacean parasitizes eight different species of fish, including some commercial ones, and it is the only known parasite that successfully replaces an organ of its host.
** This post was researched and written 100% by me, and the images used are cited to their respective sources. Thank you very much for reading, and see you in the next post.
Posted with STEMGeeks