Biliary Lithiasis
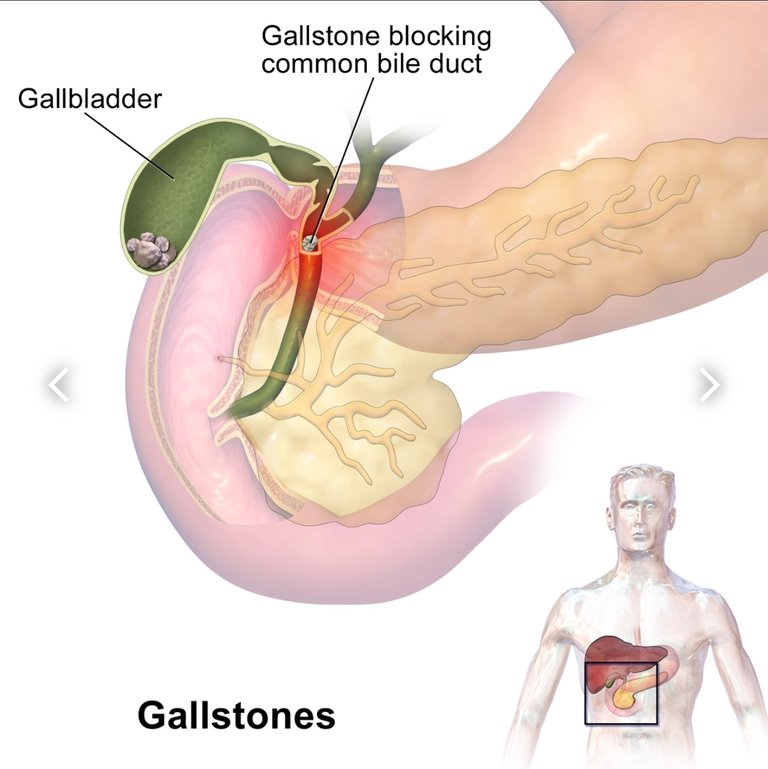
Source: wikipedia
Definition
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
Biliary lithiasis is the presence of stones in the bile ducts, although it must be clarified that there are several types of stones and that these can be located both in the gallbladder and in the intrahepatic or extrahepatic ducts.
Anatomical count
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
The biliary system extends from the canaliculi formed by the very walls of the liver cells to the vater papilla in the second portion of the duodenum. In addition, it comprises the cystic duct and the gallbladder.
The following figure shows the extrahepatic bile ducts and their termination in the second portion of the duodenum in the Vater's ampula:
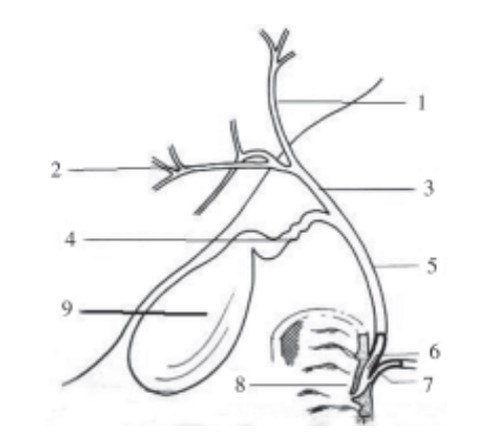
- Left hepatic duct.
- Right hepatic duct.
- Common hepatic
- Cystic duct.
- Choledochus
- Sphincter of the common bile duct.
- Sphincter of the Wirsung.
- Vater's papilla.
- Gallbladder
The intrahepatic portion of the bile ducts is made up of ducts that join each other to form thicker and thicker channels, until they reach the hepatic hilum and form the right and left hepatic ducts.
The gallbladder is a kind of piriform bag that is connected to the bile ducts through the cystic, it is located on the underside of the liver, in a depression called the vesicular fossa. The length and caliber of the different segments of the bile ducts vary from one subject to another.
During the digestive period, when acidic foods rich in fats pass into the duodenum, they cause a hormone to be released in the mucosa of this: cholecystokinin, which by blood causes the gallbladder to contract energetically and the sphincter of Oddi relaxes and then flows into the duodenum, bile from the bile ducts first and then that of the gallbladder.
When bile reaches the duodenum, it begins to perform its digestive functions, which consist in facilitating the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K), the latter very important for the phenomena of blood coagulation. Any condition that prevents the flow of bile along the entire length of the biliary tract, will cause its retention, causing the so-called icteric syndrome, which is serious, and produces the yellow coloration of the skin and mucous membranes.
Frequency
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
Biliary lithiasis is a widespread condition in the world, according to some it affects between 10 to 20% of the world's population. It is quite frequent in the countries of Europe and the Western Hemisphere; less frequent and sometimes rare in Africa. In Asia, in the Far East the presence of biliary lithiasis in its form of cholesterol stones, of intrahepatic localization is not frequent.
In Cuba this condition is very common. In general surgery services, it ranks second
as a cause of interventions in elective surgery. It is much more frequent in women than in men, in the proportion of three women to one man.
In women, it is seen that they are more frequent in those who have had several pregnancies and have a tendency to obesity. Although this has not been verified, it has been seen that there are families in which several of its members this condition is very frequent. It is associated with other entities such as: hiatal hernia, umbilical hernia, sigmoid diverticulitis, among others, without this association being explained.
Etiology
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
The cause of biliary lithiasis is currently not known; but the actions and mechanisms that in many cases cause it are. There are other factors that can facilitate these mechanisms, such as advanced age, female sex, obesity, some ethnic groups, gallbladder stasis, alteration of biliary mucus and infections.
Clinical picture
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
The disease can evolve without any symptoms and be classified as silent or asymptomatic; according to some authors the proportion of patients in this form is 20% to 30% and can become symptomatic at any time.
The symptomatic form has clinical features that make it possible to assume its diagnosis. The main symptom of this entity is pain, which occurs in two variants: first a pain of light to moderate intensity, localized in the right epigastrium or hypochondriumhypochondrium, radiating to the back in the scapular region and to the right shoulder. This pain is not constant, it can be relieved spontaneously or need some medications. It almost always appears after ingestion of copious and high-fat meals.
The other form is the intense one also called biliary, vesicular or hepatic colic, which has the same locations and irradiation. It is not frequent and almost always appears 2 h or 3 h after ingestion of high-fat meals or foods not tolerated. These pains can be accompanied by vomiting, mainly in an intense form.
Other symptoms that may appear are: belching, abdominal distension, burning, flatulence, food intolerances (foods rich in fats, for example: eggs and chocolate), heartburn, aerophagia, among others. On physical examination these patients have very few signs, sometimes only a palpable vesicle appears.
So far we have only talked about the symptoms and signs of uncomplicated vesicular lithiasis, but when it becomes complicated and evolves into another form (acute cholecystitis, choledochian lithiasis, among others), the following symptoms can be added: jaundice, which can be light or intense, fever and chills.
Supplementary examinations
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
With the advent of new techniques, the diagnosis of vesicular lithiasis has been simplified, so at present these investigations can be classified into imaging and biochemical or laboratory techniques.
Imaging techniques
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
In recent years, ultrasound replaced oral cholecystography as the first examination to be indicated. It has a very high sensitivity (about 95%) and is also non-invasive. It is not effective in the diagnosis of lithiasis of the ducts or in cases of very obese patients, the only requirement that exists to have this examination is to attend the Radiology Department fasting.

Ultrasound. Photo: medical.canon
Computed axial tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance
These are investigations that are rarely indicated in these patients and would only be used if the most frequently indicated techniques offer doubtful results.
Simple X-ray of the abdomen
Above all, of the right hypochondrium, it only allows to visualize the radiopaque stones; but since in a high percentage they are radiotransparent, this examination is of little use.
Oral cholecystography
It was the main means of diagnosis until the appearance of ultrasound, consists of the ingestion of some iopanoic acid tablets, which at 10 h to 12 h are eliminated by bile and that when concentrated in the gallbladder allow to diagnose the radiolucent and opaque stones. This examination is quite sensitive, however, it has several drawbacks, in cases of vesicles with the clogged cystic is not visualized, there is a relative number of patients who have an allergy to iodine and then the research can not be used, some small stones are also not seen in such research.
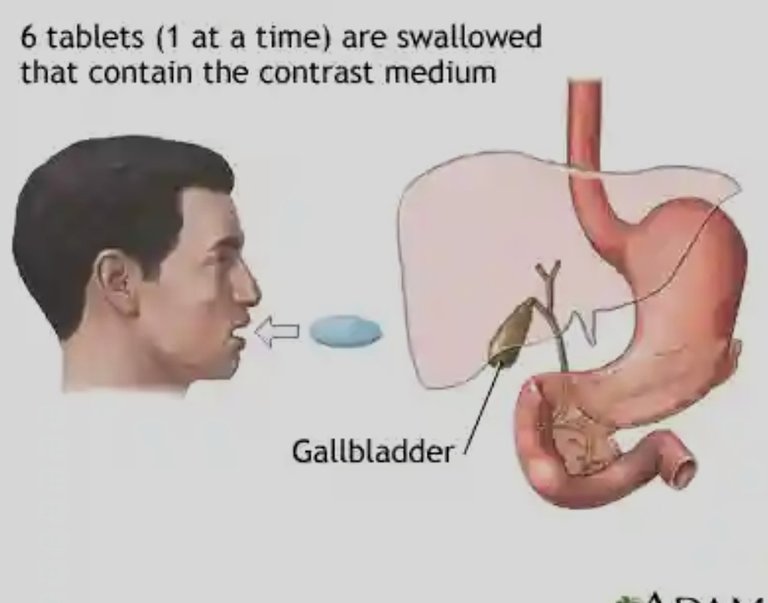
Source: medlineplus
Intravenous cholangiography
It is another radiological method of great importance for the diagnosis of these conditions, water-soluble salts of iopanoic acid are used. In this investigation the dye is injected in the early morning with the patient fasting and views are taken at 10 min, 15 min, 20 min and 30 min, 1 h and 2 h after the injection, this allows to observe the extrahepatic bile ducts well. If combined with linear tomography, more accurate views of the bile ducts could be obtained. It has the drawback that it cannot be used in patients with iodine allergy and that in addition the visualization of the gallbladder is less frequent. These two contrasted investigations cannot be used in case patients have jaundice.
For these patients (with jaundice), two investigations are used that can give the etiological and localization diagnosis of the possible obstruction:
Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography: the technique consists of percutaneously puncturing the planes of the abdominal wall, in the epigastric region or the hypochondrium, to reach the liver and channel a dilated conduction and introduce the contrast drawing the complete biliary tree is very useful for the diagnosis of cholestasis. Laparoscopic cholangiography can also be used, which has the same indications as percutaneous; but it is done with visual control through a laparoscope, so it allows to avoid some risks.

Source: wikipedia
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: this has been possible since flexible endoscopes were introduced. This technique has the advantage that it allows performing therapeutic procedures such as: sphincterotomy, stone extraction, prosthesis implantation and removal of polyps.
Biochemical or laboratory techniques
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
In patients with uncomplicated biliary lithiasis there are no specific investigations; however, it is recommended to perform the determination of two enzymes in the blood that appear when there is cell damage in these organs such as glutamic pyruvic transaminase (TGP) and glutamic oxaloaacetic transaminase (TGO) and protombin time. In addition, the laboratory examinations that are done in any ordinary preoperative period will be performed.
Finally, in cases where it was necessary when making a study of bile, drainage can be used duodenal, which when extracting the different types of bile will allow to study their specific characters and the presence or not of parasites.
Forecast
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
The vast majority of patients with vesicular lithiasis have a favorable prognosis, but when these patients become more complicated, the prognosis darkens, if they also appear in elderly patients and with associated conditions such as diabetes or cardiovascular diseases, this prognosis will become more gloomy, hence early surgical treatment of this condition is recommended, even in asymptomatic cases of the disease.
Prevention
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
There are no measures that can be taken to avoid vesicular lithiasis, since the true pathophysiology of stone formation is not known with certainty; however, because there are some factors that could favor its formation, certain preventive measures can be taken such as low-fat diets in patients who tend to have high cholesterol and lipid figures; diabetes control, avoid and treat obesity.
The true preventive measures that can be taken in this condition is to avoid complications that, when they appear, greatly raise morbidity and mortality. The fundamental thing in this case would be to indicate surgical treatment in every patient who is diagnosed with biliary lithiasis.
Treatment
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
The treatment of this condition is currently surgical, however, there is a group of patients to whom this treatment cannot be practiced and the doctor would be applied.
Medical treatment
This can be divided into:
- Hygienic: it is aimed at avoiding some of the many complications of this condition, since it cannot be curative.
- Dietary: it is essential that patients make a diet low in fats or foods that contribute to stimulate vesicular contraction and rich in residues, it is also important to keep them in a diet that prevents them from obesity.
Prohibited foods: animal fats, egg yolk, fried foods, liver, kidneys, smoked fish, bacon, butter, creams, sauces and chocolate.
Allowed foods: fruit juices, cereals, skim milk, jams, white meat (chicken or fish), beef, gelatin and vegetables. Within these foods, patients can form a dietary regimen that prevents painful episodes.
Some general dietary rules can also be given: such as eating slowly and chewing well, making your meals at regular times, if you could, make the main meal at noon, as for your lifestyle habits it is advised to do light exercises and non-violent sports sedentary lifestyle and obesity must be avoided.
Medicamentous treatment
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
Traditionally, patients who are carriers of biliary lithiasis who refuse surgery or who for some reason have it contraindicated, are administered a series of medications that, although they are not curative, contribute to relieving dyspeptic and painful symptoms, such as bile salts, in those who had late postprandrial digestive disorders, vitamins especially those that are fat-soluble, since there may be a deficit given the restriction of fatty foods, preparations with antispasmodics in those who had an irritable colon, light laxatives if they are constipated, among others, depending on the added pathologies that the patients may have.
Surgical treatment
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
Surgical treatment is the one of choice in biliary lithiasis, even in asymptomatic ones, it is only exempted to patients who refuse it in a precise way and in those who, due to their general condition or with a base disease, constitute a surgical risk.
Well friends so far today's topic I hope it has been of interest to you, have a nice week and until next time.
Bibliography
⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️⛑️🇨🇺🇨🇺🇨🇺
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21397448/
- https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-88-470-0763-5_2
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0002961081800220
- https://scielo.isciii.es/scielo.php?pid=S1130-01082004000700003&script=sci_abstract&tlng=en
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/cholecystectomy/about/pac-20384818

Congratulations @lindoro! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s):
Your next target is to reach 90 posts.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPTo support your work, I also upvoted your post!
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
Thank you so much for bringing light to an important subject. I learned a lot from the post.
Thanks for sharing.
!1UP
Click this banner to join "The Cartel" discord server to know more.
You have received a 1UP from @lipe100dedos!
@stem-curator
And they will bring !PIZZA 🍕.
Learn more about our delegation service to earn daily rewards. Join the Cartel on Discord.
PIZZA Holders sent $PIZZA tips in this post's comments:
@curation-cartel(15/20) tipped @lindoro (x1)
You can now send $PIZZA tips in Discord via tip.cc!