When the earth parted. (EN - CAST) Cuando la tierra se separó.
When the earth parted. (EN - CAST) Cuando la tierra se separó.

Souce
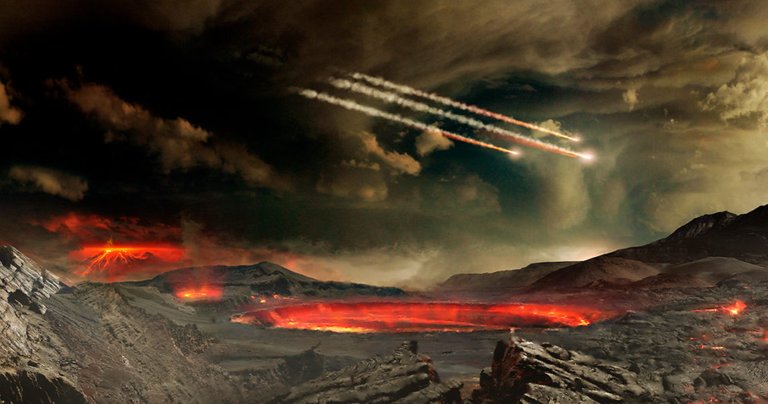
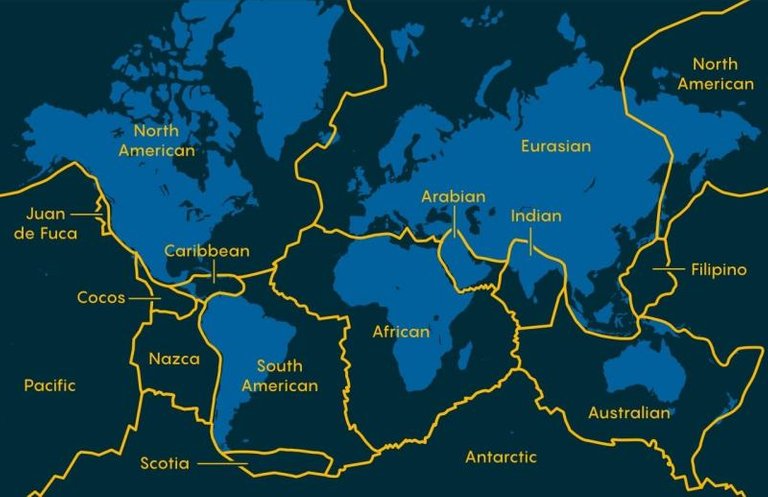
Two researchers have managed to establish the precise moment in which the crust of the earth cracked, forming the tectonic plates and beginning in movement that was giving rise to the continents and oceans.
Dos investigadores han conseguido establecer el momento preciso en que la corteza de la tierra se resquebrajó, formando las placas tectónicas y comenzando en movimiento que fue dando origen a los continentes y océanos.
Souce
According to scientists, radioactive decay made the interior of the earth in its early days much hotter than it is today, there was a crust, yes, but it was very thin and loose, it took a while to cool down enough to thicken and form plates that will float on the mantle, scientists have long debated when that moment happened and this finding has provided the date, that event in which the crust broke into plates happened 3.2 billion years ago and is a very important event as it helped the development of life forms.
Según los científicos la desintegración radioactiva hacía que el interior de la tierra fuese en sus primeros tiempos mucho más caliente que en la actualidad, existía una corteza, sí, pero era muy delgada y flojita, tardó un tiempo en enfriarse lo suficiente, como para engrosar y formar placas que flotarán sobre el manto, los científicos debatían desde hace tiempo cuando sucedió ese momento y este hallazgo ha proporcionado la fecha, ese evento en el que la corteza se rompió en placas sucedió hace 3200 millones de años y es un evento muy importante, ya que ayudó al desarrollo de las formas de vida.

Souce
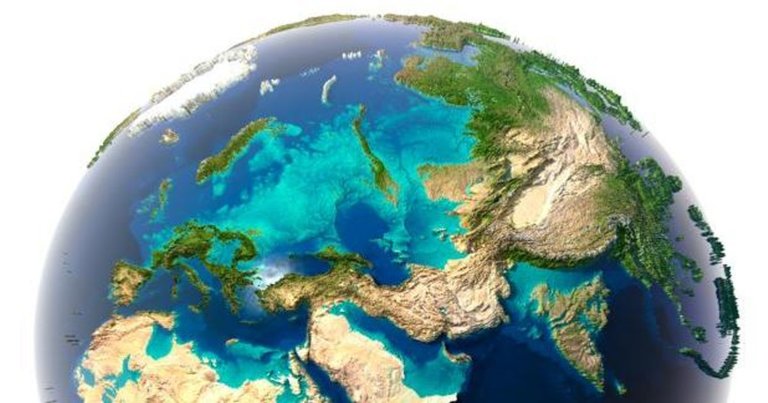
Thanks to the formation of tectonic plates, the earth has maintained a habitable climate for billions of years, although the brightness of the sun is increasing little by little, our climate is largely the result of chemical reactions between the carbon dioxide from the air and silicate minerals, this reaction slowly reduces the level of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, burying them in sediments and preventing us from becoming a planet like Venus, most of these reactions between silicates and Carbon dioxide is produced on the slopes of the mountains, which are created when tectonic plates collide and all this must be added the recycling of materials, between the mantle, the crust, the oceans and the atmosphere, guaranteeing a continuous supply of elements crucial to life.
Gracias a la formación de las placas tectónicas, la tierra ha mantenido un clima habitable durante miles de millones de años, pese a que el brillo del sol va aumentando poco a poco, nuestro clima es en gran medida el resultado de las reacciones químicas entre el dióxido de carbono del aire y los minerales silicatados, esta reacción reduce lentamente el nivel de los gases de invernadero en la atmósfera, enterrando los en los sedimentos y evitando que nos convirtamos en un planeta como venus, la mayor parte de estas reacciones entre silicatos y dióxido de carbono se produce en las laderas de las montañas, que se crean a chocar las placas tectónicas y a todo esto hay que sumar el reciclado de los materiales, entre el manto, la corteza, los océanos y la atmósfera garantizando un suministro continuo de elementos cruciales para la vida.

Thank you for visiting my blog. If you like posts about #science, #planet, #politics, #rights
#crypto, #traveling and discovering secrets and beauties of the #universe, feel free to
Follow me as these are the topics I write about the most. Have a wonderful day
and stay on this great platform :) :)
Gracias por visitar mi blog. Si te gustan las publicaciones sobre #ciencia, #planeta, #politica, #derechos
#crypto, #traveling y descubriendo secretos y bellezas del #universo, siéntete libre de
seguirme, ya que estos son los temas sobre los que más escribo. ¡Tenga un día maravilloso
y siga en esta gran plataforma :) :)
0
0
0.000
0 comments