Formación de geles // Gel formation (ESP--ENG)
Una disolución diluida de albumina (ovoalbúmina por ejemplo) por ebullición en medio débilmente alcalino (disminuya la viscosidad y aumentar la tensión superficial) se transforma en suspensión. Al hervir la disolución las moléculas hidrófilas de albumina se deshidratan y desnaturalizan pero como están en medio alcalino las moléculas siguen ionizadas con carga negativa y el coloide no precipita. En cambio, hirviendo en medio ligeramente acido el coloide coagula, porque además de la acción deshidratante el acido ha modificado la reacción del medio hasta un pH que corresponde al punto isoeléctrico de la molécula proteica, y a este pH la proteína es eléctricamente neutra. Por eso en estas condiciones precipita con solo deshidratar debido a que la partícula ya no tenía cargas eléctricas que pudieran mantener la disolución en estado de suspensión.
A dilute solution of albumin (ovalbumin for example) by boiling in a weakly alkaline medium (decrease the viscosity and increase the surface tension) becomes a suspension. When the solution boils, the hydrophilic molecules of albumin dehydrate and denature, but as they are in an alkaline medium, the molecules remain ionized with a negative charge and the colloid does not precipitate. On the other hand, boiling the colloid in a slightly acidic medium coagulates, because in addition to the dehydrating action, the acid has modified the reaction of the medium to a pH that corresponds to the isoelectric point of the protein molecule, and at this pH the protein is electrically neutral. That is why under these conditions it precipitates with only dehydration because the particle no longer had electrical charges that could keep the solution in a suspended state.
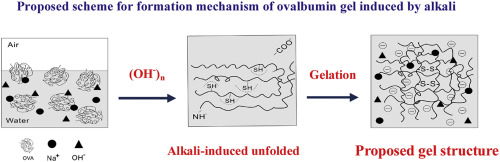
En análoga experiencia, pero con disolución más concentrada se llega a obtener un gel y se puede demostrar que la coacervación de un emulsor y la gelificacion son fenómenos esencialmente diferentes. Si una disolución concentrada de ovoalbúmina se calienta a 100° C al enfriarse adquiere una consistencia semirrígida (gelificacion) pero no coagula ni tampoco hay coacervación. En la albumina que hemos tomado como ejemplo el proceso es irreversible pero en otros casos la gelificacion es un fenómeno reversible.
In analogous experience, but with more concentrated dissolution, a gel is obtained and it can be demonstrated that the coacervation of an emulsifier and gelation are essentially different phenomena. If a concentrated solution of ovalbumin is heated to 100 ° C upon cooling, it acquires a semi-rigid consistency (gelling) but does not coagulate and there is no coacervation. In the albumin that we have taken as an example, the process is irreversible but in other cases, gelation is a reversible phenomenon.

Al geleficacion se caracteriza por la inversión de las fases del coloide: el agua pasa constituir la fase dispersa que se mantiene retenida dentro de las mallas del gel y la trama formada por las partículas coloidales viene a resultar así el medio de dispersión de las pequeñas gotas de agua.
Gelefication is characterized by the inversion of the colloid phases: the water becomes the dispersed phase that remains retained within the gel meshes and the web formed by the colloidal particles thus becomes the dispersion medium of small drops of water.