Basic Trigonometry Ratios For Right Angled Triangles
Hi there. In this post I cover the topic of basic trigonometry ratios.
I use witeboard.com and Windows snipping tool for the math screenshots.
Topics
- Right Angle Triangle Properties
- Sine, Cosine & Tangent Ratios
- Finding An Unknown Angle With Inverse Trigonometry Functions
Right Angle Triangle Properties
A right angle triangle is a special case of a triangle where one of the angles is 90 degrees. This 90 degree angle is called a right angle which is indicated with a square symbol at the corner. The other two angles are both acute angles where each of the two angles is less than 90 degrees. In addition, the longest side of the right angle triangle is called the hypotenuse. This hypotenuse is always opposite to the 90 degree angle.
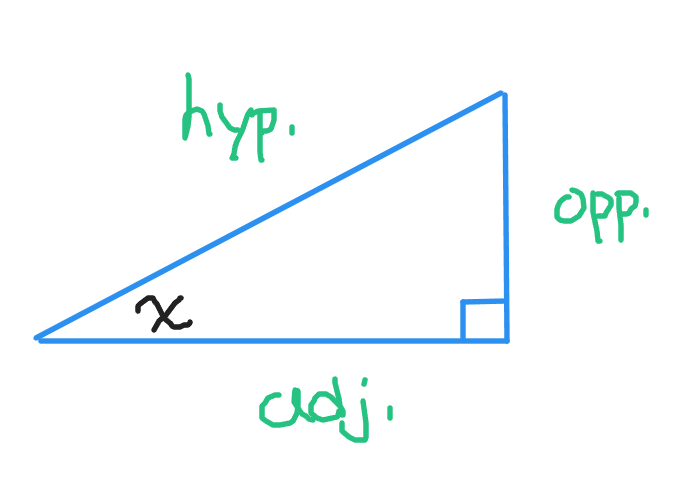
Sine, Cosine & Tangent Ratios
Given an acute angle in a right angle triangle we have three sides based on the positioning of the angle. We have three sides relative to the angle. These are the opposite side to the angle, the hypotenuse opposite to the right angle and the adjacent angle that is next to the angle. Note that the adjacent angle is never the hypotenuse. I use x for the angle.
The sine of an angle is the opposite side length divided by the hypotenuse length.
The cosine of an angle is the adjacent side length divided by the hypotenuse length.
The tangent of an angle is the opposite side length divided by the adjacent side length.
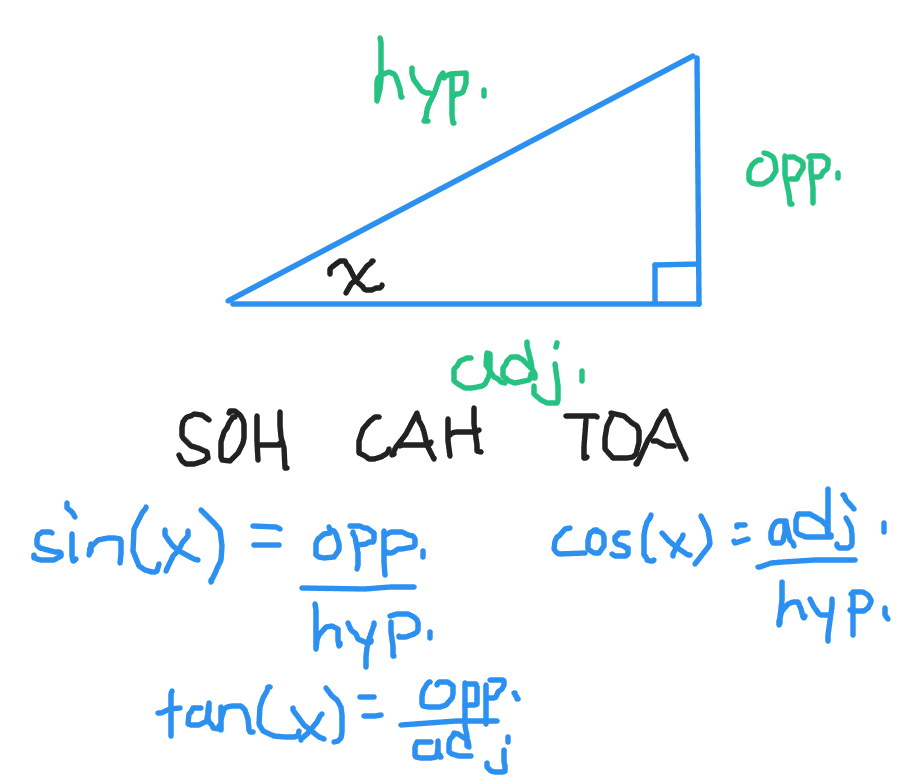
SOH CAH TOA Memory Aid
In mathematical notation, sine is abbreviated by sin, cosine by cos and tangent by tan. There is a neat memory aid that helps a lot with memorizing the three basic trigonometric ratios. It is called SOH CAH TOA.
Sine is opposite over hypotenuse. S is from sine, O is from opposite and H is from hypotenuse.
Cosine is adjacent over hypotenuse. C is from cosine, A is from adjacent and H is from hypotenuse.
Tangent is opposite over adjacent. T is from tangent, O is from opposite and A is from adjacent.
Example One
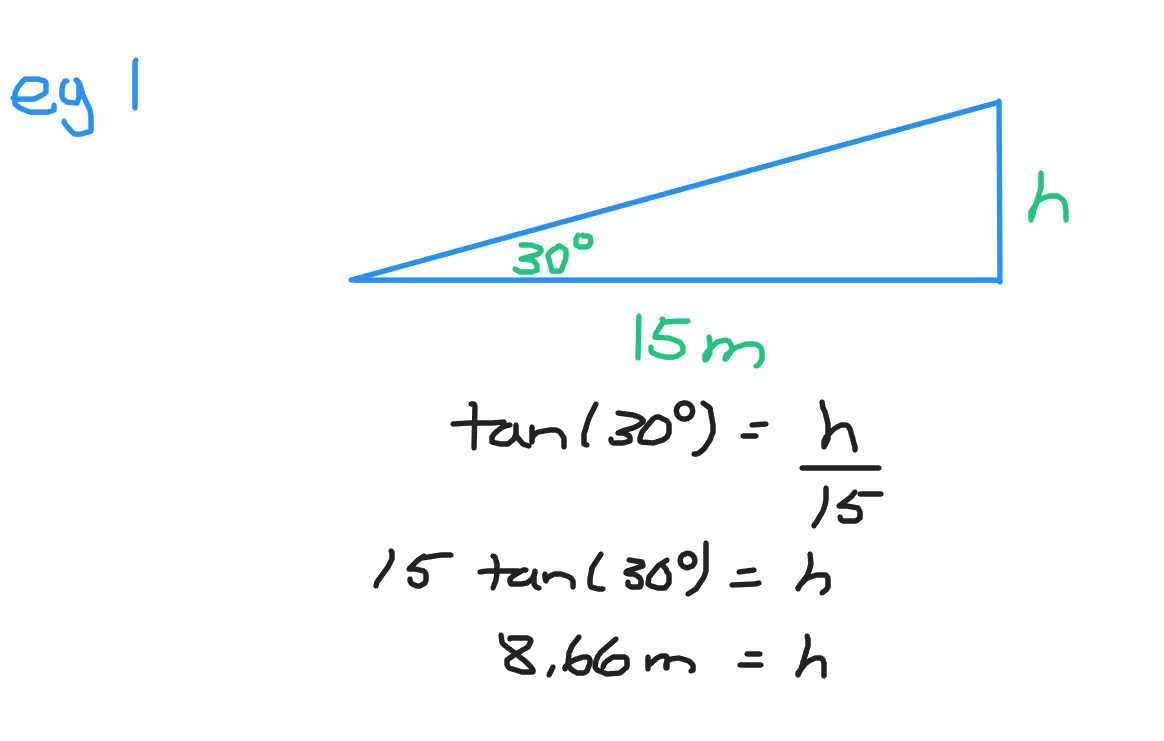
The bottom of a ramp is 15 metres with an incline of 30 degrees. What is the height of the ramp?
Start with deciding which trigonometric ratio to use. The bottom of the ramp is adjacent to the 30 degrees and the height of the ramp is opposite to 30 degrees. Use the tangent ratio and solve for the height of the ramp.
Example Two
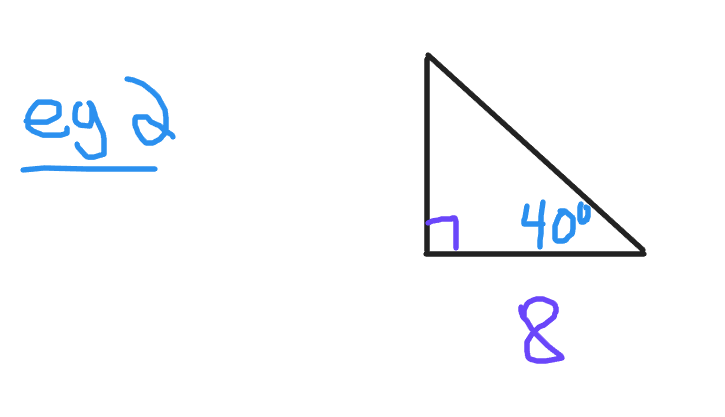
In this second picture there is a 40 degree angle. The side length of 8 is adjacent or next to the given angle. Remember that the adjacent side is never the hypotenuse. Use the cosine trigonometric function to find the length of the hypotenuse.
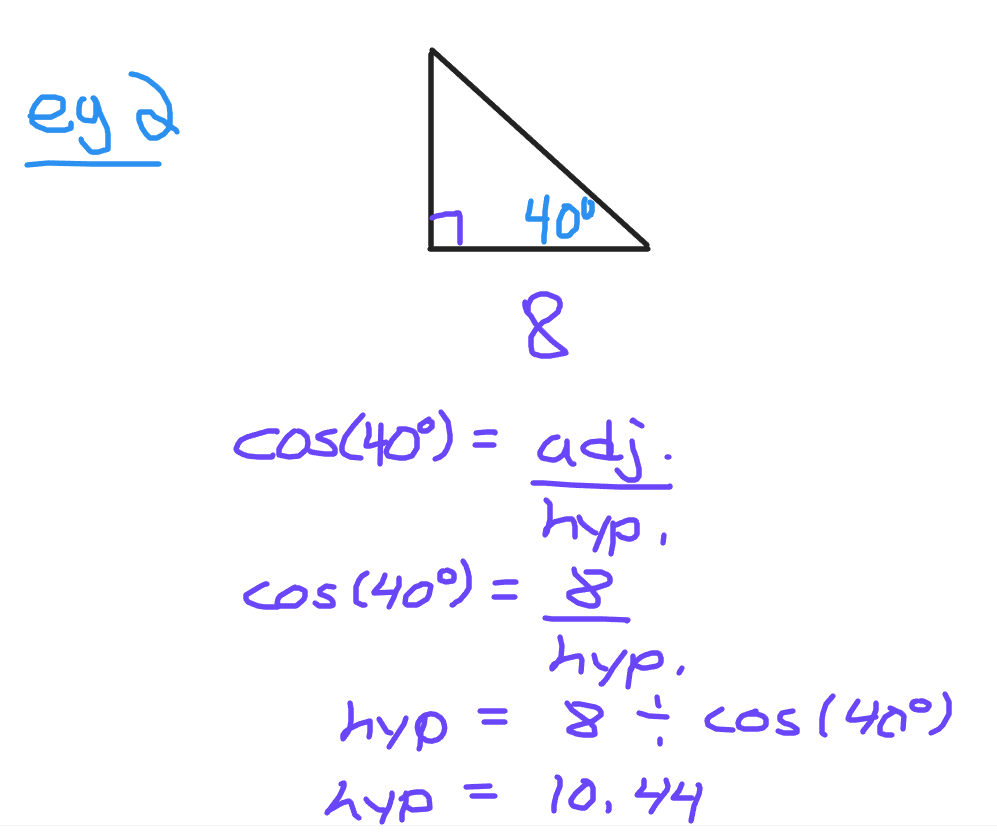
Example Three
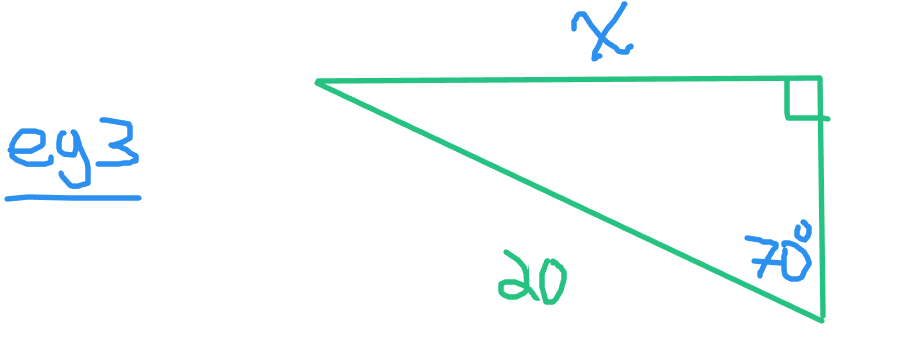
In example three there is the given angle of 70 degrees and a hypotenuse of 20 units.
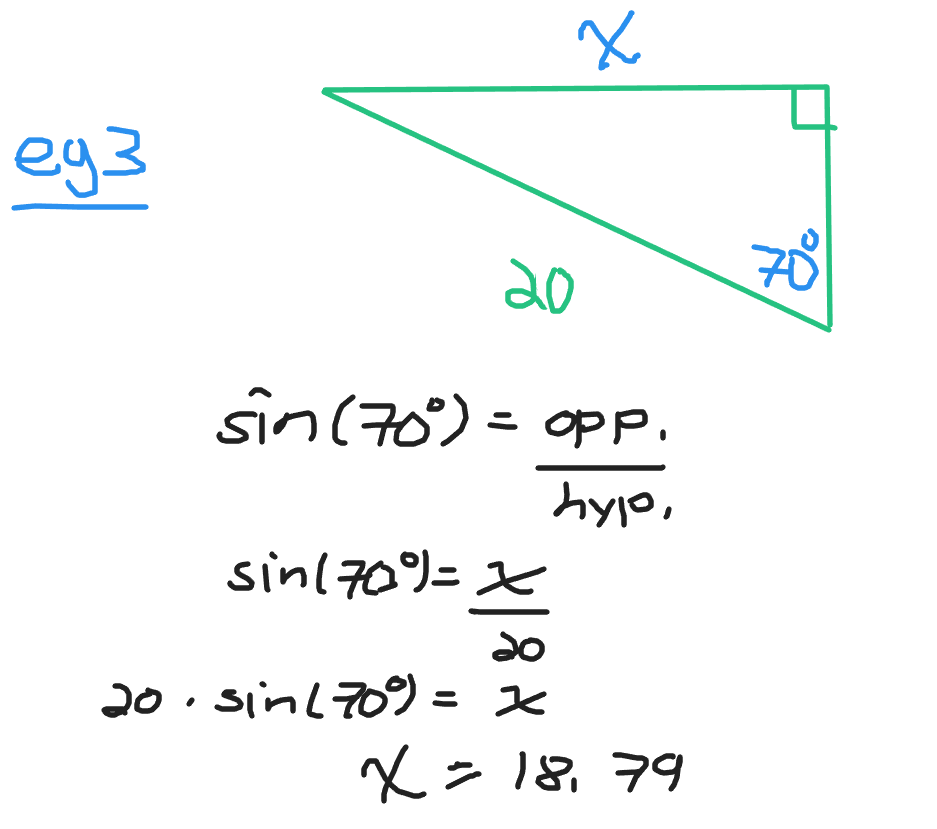
Finding An Unknown Angle With Inverse Trigonometry Functions
What if you have the side lengths and need to find an unknown angle? A new concept or method is needed in this case. When it comes to finding an unknown angle we need to use an appropriate inverse trigonometric function to solve for an unknown angle.
Example One - Ramp Example
A ramp has a base of 20 metres and a height of 3 metres. What is the angle of inclination?
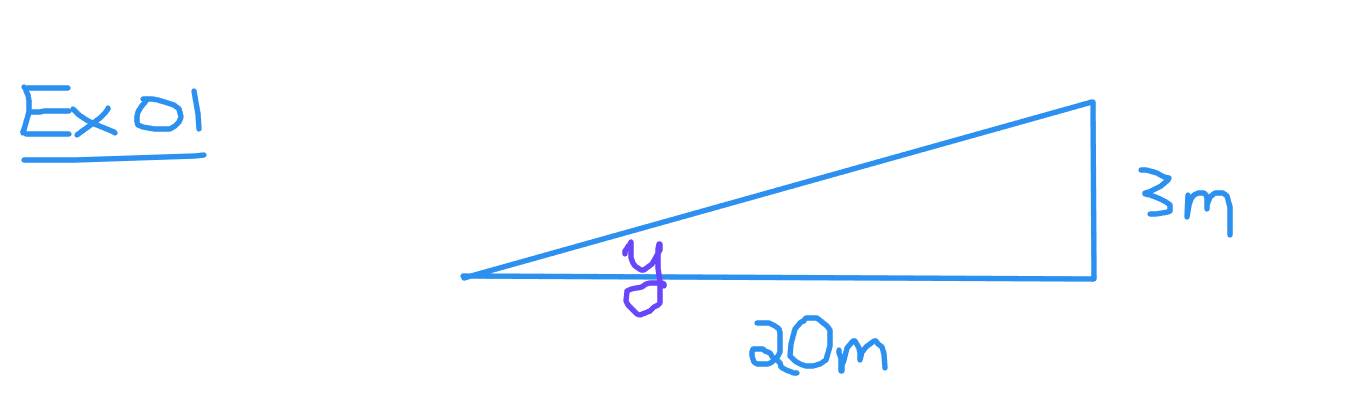
The angle of inclination is given by y. The height of three metres is opposite to y and the twenty metres is adjacent to the angle y. Use the tangent ratio to set up the equation.
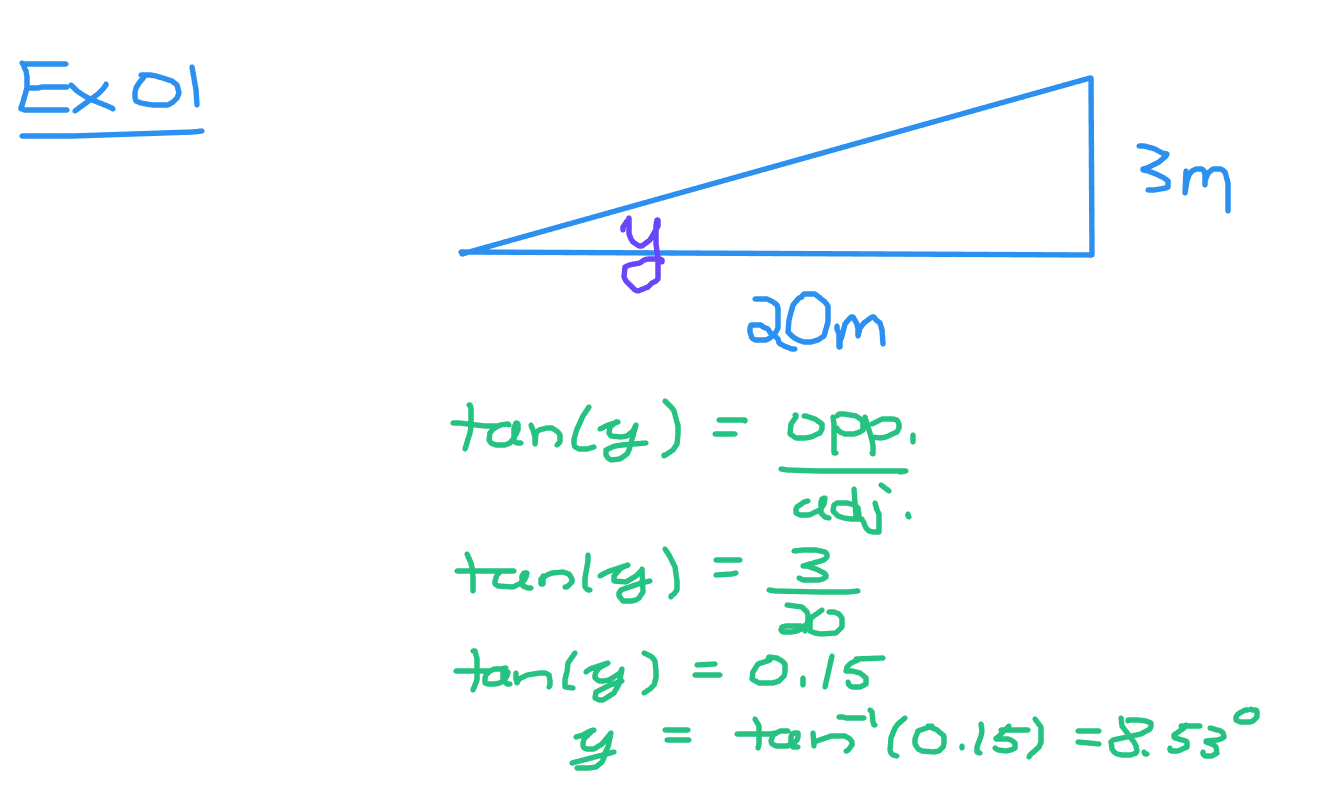
The tangent of the angle y is three out of twenty or 0.15. Obtaining the angle y requires using the inverse tangent function. Anytime an angle is an unknown value you need to use the appropriate inverse trigonometric function. This is the second function button on a scientific calculator. My Casio calculator has a SHIFT button which is like second function.
Use tan^(-1)(0.15) to obtain an angle of inclination of about 8.53 degrees.
Example Two
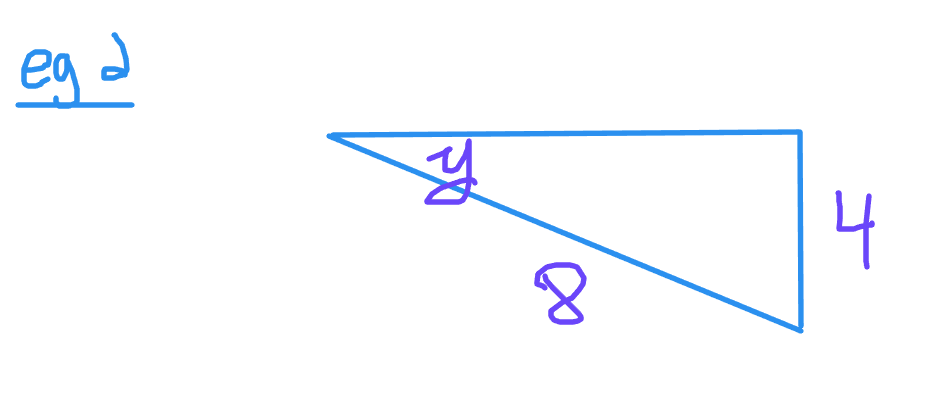
The unknown angle here is y. The given sides are the opposite and hypotenuse lengths. Use the sine ratio to set up the equation.
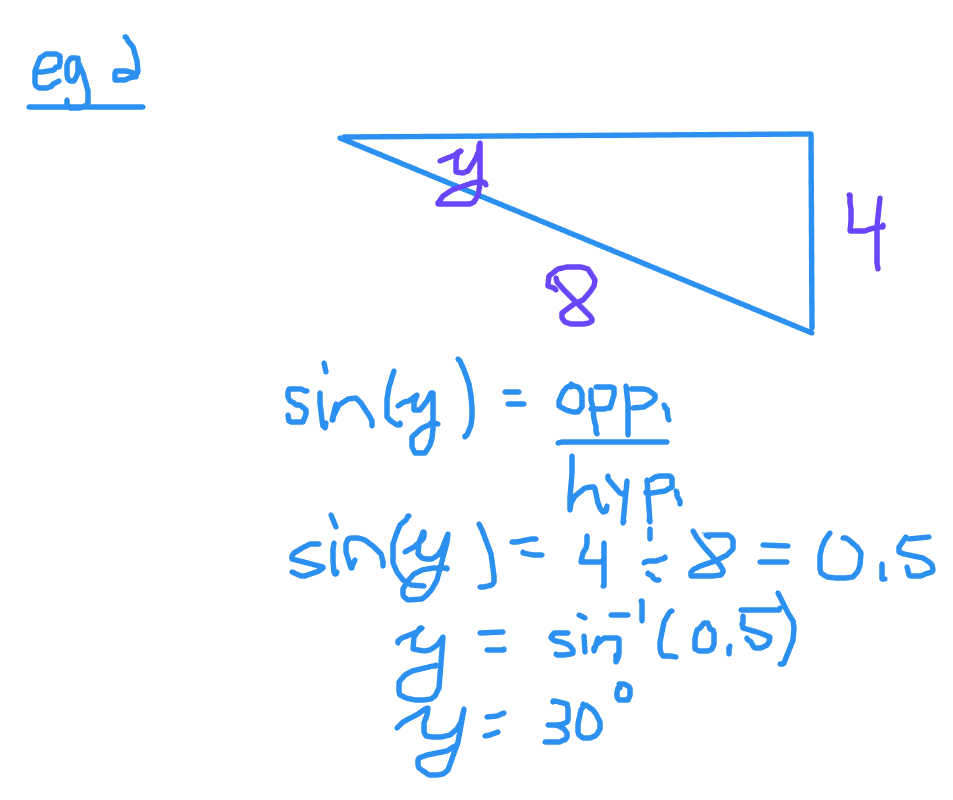
Sine is opposite divided by hypotenuse. It is 4 divided by 8 to give 0.5. Take the sine inverse function of 0.5 to obtain an angle of 30 degrees.
Posted with STEMGeeks
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.
That is a nice class
!1UP
You have received a 1UP from @gwajnberg!
@stem-curator
And they will bring !PIZZA 🍕.
Learn more about our delegation service to earn daily rewards. Join the Cartel on Discord.
I gifted $PIZZA slices here:
@curation-cartel(10/20) tipped @dkmathstats (x1)
Please vote for pizza.witness!