[ESP/ENG] ¿Qué es la diabetes y cómo podemos evitarla? / ¿What is diabetes and how can we avoid it?


En esta oportunidad quiero hablarles sobre una patología bastante delicada, peligrosa, y, sobre todo, silenciosa: la diabetes.

A cordial greeting to the entire community, a pleasure to greet you, here is your server: @galejandrovv.
On this occasion I want to talk to you about a rather delicate, dangerous, and, above all, silent pathology: diabetes.

¿QUÉ ES LA DIABETES?
¿WHAT IS THE DIABETES?

Fuente / Source
Esto puede presentarse por dos razones:
- El páncreas (órgano productor de insulina) no produce insulina para contrarrestar los niveles elevados de glucosa o lo hace de manera deficiente.
- El páncreas produce insulina, pero, el organismo no la utiliza de manera adecuada.
This can occur for two reasons:
- The pancreas (insulin-producing organ) does not produce insulin to counteract high glucose levels or does so poorly.
- The pancreas produces insulin, but the body does not use it properly.

¿QUÉ ES LA INSULINA?
¿WHAT IS INSULIN?
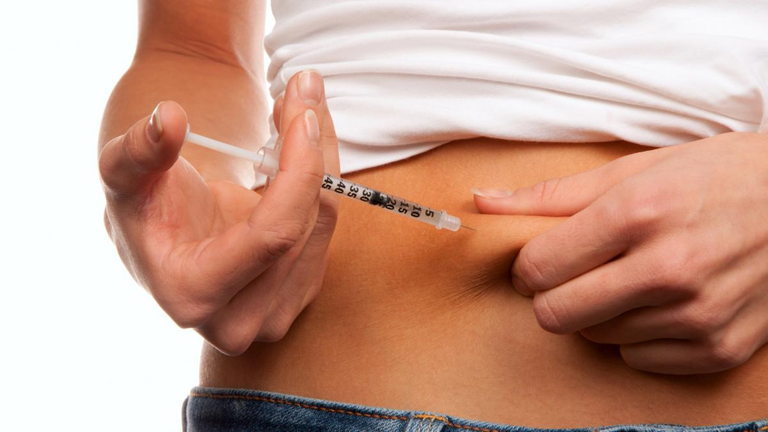
Fuente / Source

¿QUÉ ES LA GLUCOSA?
¿WHAT IS GLUCOSE?
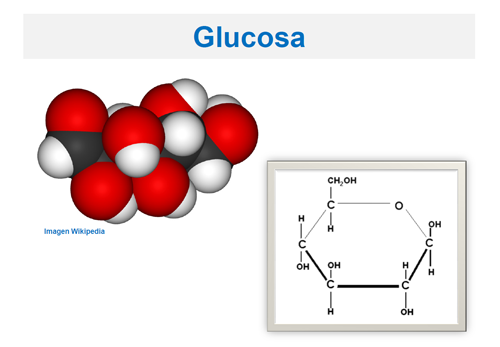
Fuente / Source

¿CUÁNTOS TIPOS DE DIABETES EXISTEN?
¿HOW MANY TYPES OF DIABETES ARE THERE?
- Diabetes tipo 1: es la llamada "insulinodependiente", aparece a edades muy temprana y es debida a que el páncreas no produce insulina, de tal manera que, hay que administrarla de manera exogena.
Diabetes tipo 2: es aquella que aparece en la adultez y está estrechamente enlazada a los hábitos de la persona; aquí, la producción de insulina es adecuada, pero, el cuerpo no la utiliza de manera idónea.
Diabetes gestacional: es aquella que aparece durante la gestación, producto de los cambios que se producen durante el embarazo; suele desaparecer luego de extraer el producto de la gestación.
Type 1 diabetes: it is called "insulin-dependent", it appears at a very early age and is due to the fact that the pancreas does not produce insulin, in such a way that it must be administered exogenously.
Type 2 diabetes: is one that appears in adulthood and is closely linked to the person's habits; here, insulin production is adequate, but the body does not use it properly.
Gestational diabetes: is one that appears during pregnancy, product of the changes that occur during pregnancy; It usually disappears after extracting the product of gestation.

Fuente / Source

¿CUÁLES SON LOS FACTORES DE RIESGO PARA DESAROLLAR DIABETES TIPO 2?
¿WHAT ARE THE RISK FACTORS FOR DEVELOPING TYPE 2 DIABETES?

¿CUÁLES SON LOS SIGNOS Y SÍNTOMAS DE LA DIABETES?
¿WHAT ARE THE SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS OF DIABETES?
- Polidipsia (sed excesiva)
- Polifagia (hambre excesiva)
- Poliuria (deseo excesivo de orinar)
- Perdida de peso.
Esos son los signos y síntomas principales de la enfermedad, no obstante, hay otros como: debilidad, náuseas, vómitos, visión borrosa, etc.
- Polydipsia (excessive thirst)
- Polyphagia (excessive hunger)
- Polyuria (excessive desire to urinate)
- Weightloss.
These are the main signs and symptoms of the disease, however, there are others such as: weakness, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, etc.
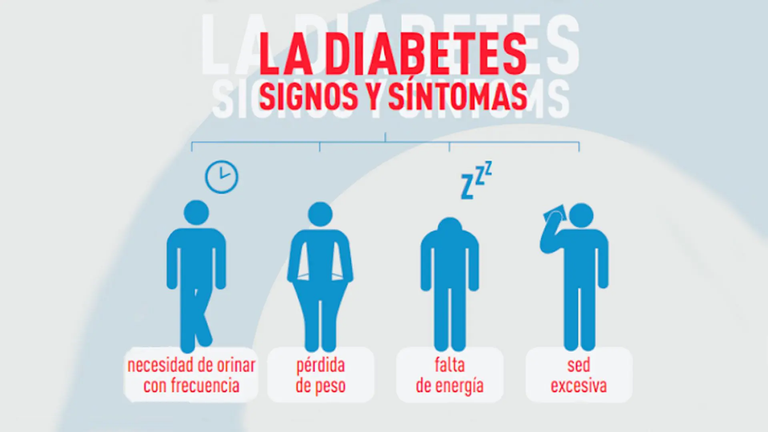
Fuente / Source

¿CÓMO PUEDO PREVENIR LA DIABETES?
¿HOW CAN I PREVENT DIABETES?

Fuente / Source

¿CUÁLES SON LAS COMPLICACIONES DE LA DIABETES?
¿WHAT ARE THE COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES?
La más temida es la pérdida de la sensibilidad, ya que, los niveles altos de glucosa tienden a dañar los nervios y eso produce serias complicaciones como: pie diabético, pérdida de la visión, etc.
The most feared is the loss of sensitivity, since high glucose levels tend to damage the nerves and this produces serious complications such as: diabetic foot, vision loss, etc.
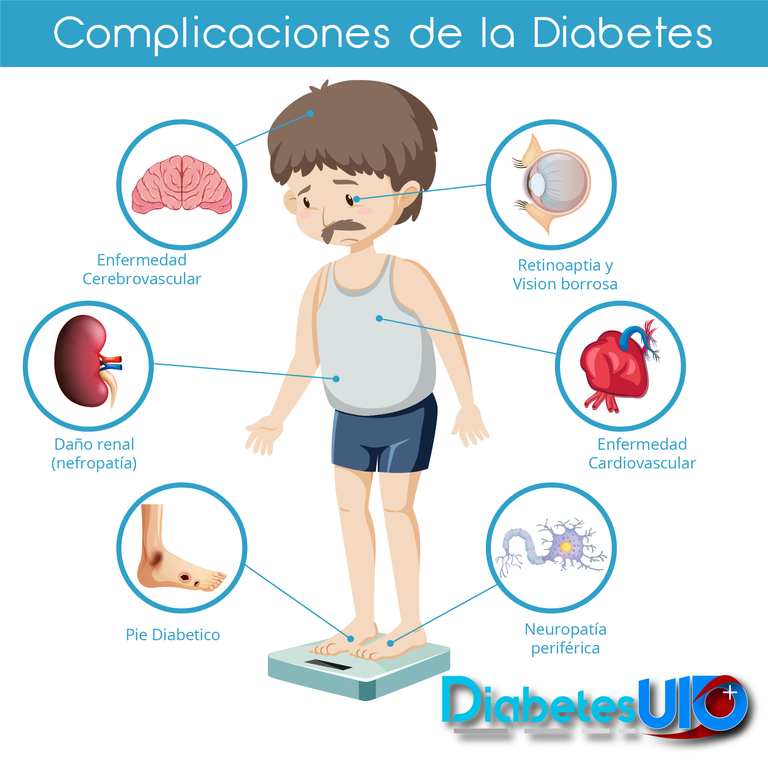
Fuente / Source

 |  |  |  |
 |  |  |  |
Texto traducido en XTranslate
Separadores creados en Gravit Designer
Vectores descargados de Flaticon
Banner's creados en Canva
Translated text with the extension XTranslate
Separators created in Gravit Designer
Vectors downloaded from Flaticon
Banner's created in Canva

PRIMUM NON NOCERE

https://twitter.com/gablejandrovv/status/1488936238702813192
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the person sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.