Self-Purification Of streams
SELF PURIFICATION OF STREAMS
When sewage is discharged into natural steam or river, the organic matter is converted to ammonia, nitrates, sulphates, carbon dioxide etc. by bacteria. In this process of oxidation, the dissolved oxygen content of natural water is utilized and deficiency of oxygen is created in stream water which is filled up by the absorption of atmospheric oxygen. Stable bio-products (ammonia, nitrates, sulphates, carbon dioxide etc.) are nutrients for microbes and algae and supply oxygen to maintain aerobic conditions. The bacteria are eaten by protozoa which is further the food of fish and aquatic life.
Thus, the stream water becomes free from organic matter, microorganism and DO contains reaches to its original stage. This phenomenon, of automatic purification of polluted water bodies is called self-purification of stream or river.
FACTORS AFFECTING SELF PURIFICATION
The following are the factors which affect the self-purification of steam/river;
1.DILUTION
Wastewater disposal practices are based on the premise ‘the solution to pollution is dilution.’ When sewage is discharged into receiving water, it is dispersed and dilution takes place due to which the concentration of organic matter is reduced and the potential nuisance of sewage is also reduced. When the dilution ratio is quite high, large quantities of DO is available which will accelerate the chance of purification and reduce pollution effects. Aerobic condition will always exist because of higher dilution. The dilution capacity of a stream can be calculated by using the principle of mass balance.
CsQS+CrQr=C(Qs+Qr)
C=(CsQs+CrQr)/(Qs+Qr)
Where,
C = resulting mixture concentration (mass/volume)
Cs = Sewage concentration (mass/volume)
Cr = Concentration in river or stream (mass/volume)
Qs, Qr = Flow rate of sewage and river respectively (volume/time)
2.Current
Self-purification of stream largely depends upon currents, (as rapids, whirlpools, waterfalls and turbulent flow) which will readily disperse the wastewater in the stream, preventing local accumulation of pollutants. High velocity accelerates reaeration and reduces the time of recovery, though the length of stream affected by the wastewater is increased. On the other hand, slow current cause sedimentation and growth of algae increases resulting production of oxygen.
- Sunlight
Sunlight acts as a disinfectant and stimulates the growth of the algae which produce oxygen. Sunlight helps photosynthesis of certain aquatic plants (as algae) to absorb carbon dioxide and give out oxygen, thus accelerating self-purification. - Temperature
At low temperature, the microbial activities is low and hence rate of decomposition will also be slow, though DO will be more because of increased solubility of oxygen in water. At higher temperatures, the self-purification takes lesser time, though the quantity of DO will be less. - Sedimentation
Solid liquid separation by the action of gravity is called sedimentation. Sedimentation or settling out is natural’s method of removing suspended particles from a watercourse, and most large solids will settle out readily in quiescent water. Particles in colloidal size can stay in suspension for the longer period of time, though eventually most of these will also settle out. Thus, settled organic matter undergoes decomposition an-aerobically and the byproduct again mixed or dispersed up with water by current. If the dilution factor is sufficient, no anaerobic condition will occur.
If the stream velocity is lesser than the scouring velocity of particle, sedimentation will take place, which will have two effects. (i) The suspended solids, which contribute largely the oxygen demand, will be removed by settling and hence water quality of the downstream is improved. (ii) Due to settled solids, anaerobic condition may take place. - Oxidation
Organic matter is acted upon by the aerobic bacteria utilizing dissolved oxygen present in water bodies. The deficiency of oxygen so created is filled up by absorbing from atmosphere. The process of oxidation continues till the oxygen demand is fully satisfied. - Reduction
Organic matter settled in the bottom of the stream or river is reduced to liquid and gases due to hydrolysis either chemically or biologically. Anaerobic bacteria are responsible for splitting the complex organic matter to liquid and gas thus make a way for their stabilization by oxidation. Hence reduction assists the self-purification of stream or river.
OXYGEN SAG CURVE
As sewage is discharged in the river or stream depletion of DO starts in order to meet the BOD of the sewage. This is termed as deoxygenation and closely follows the progress of BOD of polluted water. The variation of the rate of deoxygenation respect to time is shown in figure (curve 2) of deoxygenation curve. The rate of deoxygenation depends on amount of organic matter remaining to be oxidized at any time ‘t’, time available for decomposition and temperature of diluting water.
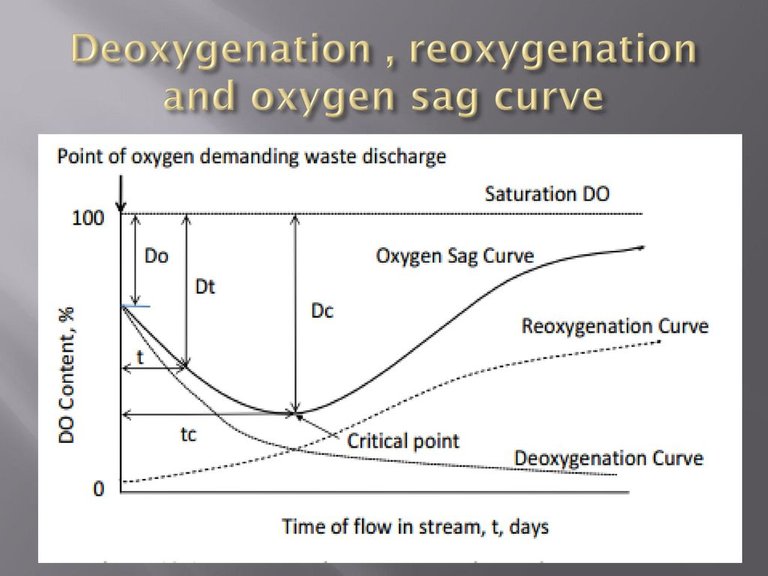
Due to deoxygenation, the DO of the water decreases and also oxygen is absorbed from the atmosphere when DO falls below saturation level. Oxygen is also contributed by green plants (plankton, algae) by photosynthesis process. This adsorption of the oxygen by the river or stream is termed as reoxygenation or reaeration. The variation rate of reoxygenation with respect to time is shown in figure (curve 3) and reoxygenation curve. The rate of deoxygenation depends upon depth, velocity, temperature of receiving water and DO saturation level.
Reoxygenation and deoxygenation occur simultaneously in any polluted stream or river exposed to atmosphere. The ordinate below deoxygenation curve indicates the Do content remaining in the stream water after satisfy of BOD. The ordinate below reoxygenation curve indicate the oxygen absorbed by the stream or river. The algebraic sum of these two curves gives a curve (curve 1) is called oxygen sag curve. This represents the DO deficit at different time.
The oxygen sag curve shows increase in Do deficit at the beginning and when oxygenation and deoxygenation are equal, the maximum deficit is obtained and after this point oxygen deficit decreases till it becomes zero.
ZONES OF POLLUTION IN STREAMS:
The self-purification process of a stream polluted by the wastewater or effluent discharged into it can be divided into following four zones.
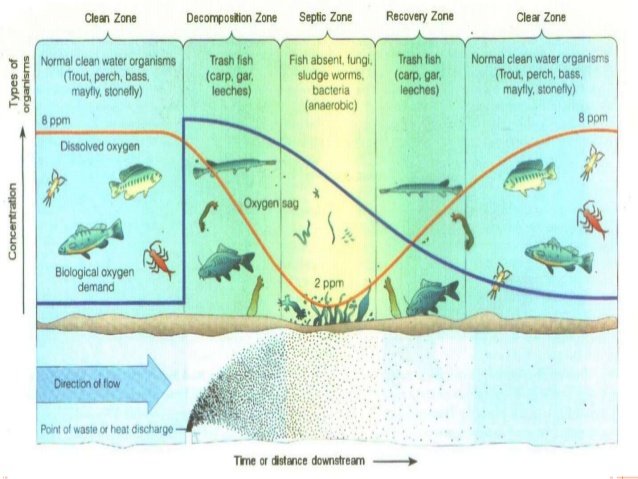
Decomposition zone
This zone is situated just below the outfall sewer while discharging its content into the stream. In this zone, water is rendered dark and turbid, having the formation of sludge deposits at the bottom. The DO is reduced to 40% of the saturation values. There is an increase in CO2 content, and reaeration is much slower than deoxygenation, (though condition is unfavorable for aquatic life, fungi at shallow depth and bacteria at greater depth breed along with the small worms, which ‘work over’ and stabilize the sewage and sludge). The decomposition of solid matter takes place in this zone and anaerobic decomposition prevails over aerobic decomposition.Septic zone
This zone is just the continuation of degradation zone and is marked by heavy pollution. Water in this zone becomes grayish and dark than in previous zone. The DO concentration in this zone falls down to zero. Active anaerobic organic decomposition takes place, with the evolution of Methane, hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide and nitrogen bubbling to the surface with masses of sludge forming black scum. Fish life is absent in this zone but bacterial flora will flourish with the presence of anaerobic bacteria at the upper end and aerobic bacteria at the lower end. However, near the end of this zone, as the decomposition slackens, reaeration sets in and DO again rises to original level of 40% (of saturation value).Recovery zone
In this zone, the process of recovery starts from its degraded conditions to its former purer conditions. The stabilization of organic matter takes place in this zone. Due to this most of the stabilized organic matter settles as sludge, BOD falls and DO content rises over 90% value. Near the end of the zone, fungi wave out and algae reappear.Clear zone
In this zone, the natural water condition of stream is restored with the result that (i) water becomes clearer and attractive in appearance. (ii) DO rises to the saturation level, and BOD drops to the lowest value. (iii) oxygen balance is attained.
Please follow @amit.pangeni
This post was originally posted to https://steemit.com/hive-148441/@amit.pangeni/self-purification-of-streams
Please share the source of your information. Plagiarism is not treated nicely here and this is basically copy and paste. If you post things like this you have to include where you got the information from. If you don’t you will get down voted at some point.
I don’t want that to happen or to do that so please include the sources, thanks!
You should also include the sources for your images. That’s just as important.
Thank you so much !! Will include surely from next time.
Thank you! I appreciate that you understand it and don’t suffer negative consequences from a mistake. Cheers!
Congratulations @amit.pangeni! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s) :
You can view your badges on your board And compare to others on the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPSupport the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!