17-06-2024 - Energy systems - Cavitation[EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
17-06-2024 - Energy systems - Cavitation[EN]-[IT]
Cavitation
When we talk about cavitation we mean to identify the phenomenon of the appearance of vapor bubbles within a liquid mass. This occurs due to the reduction in pressure that goes below a critical pressure.
We can also describe cavitation as follows.
Some conditions can act on the fluid and then cause cavitation to arise
a pressure higher than the vapor pressure of the liquid and therefore the pmin is equal to:
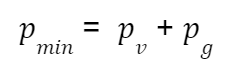
Where:
-pv indicates saturated vapor pressure
-pg the partial one of the dissolved gas.
Cavitation within a circuit with a turbomachine will cause a drop in the performance of the machine in terms of efficiency, head and flow rate.
The main causes of cavitation can be:
-Reduction of pressure
-Increased speed
-Inadequate design
Inconveniences caused by cavitation
Cavitation can cause the following damage:
-Surface Damage: Cavitation bubbles implode violently when they return to a high pressure area, causing damage to material surfaces.
-Reduced Performance: Cavitation can reduce the efficiency of pumps and turbines and can compromise their operation.
-Noise and Vibrations: The implosion of cavitation bubbles generates noise and vibrations which can be harmful to mechanical structures, furthermore noise and vibrations can cause unstable operation.
When cavitation does not occur
Cavitation can be avoided by reducing the installation height of the pump.
It can also be avoided by reducing fluid dynamic losses along the intake duct.
To avoid cavitation we must check the presence of the following condition:
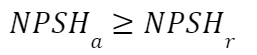
Where:
NPSHa = net positive suction head available
NPSHr = net positive suction head required
As the flow rate processed by the pump varies, the NPSHr varies
maximum height h0_max
If we refer to the suction height, the maximum height h0_max at which the pump can be installed is calculated as follows:
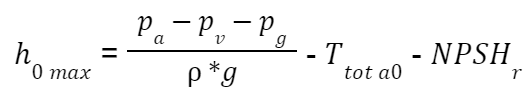
Therefore if it turns out that h0_max<0 the pump must be installed under head.
Conclusions
Cavitation is defined as the formation of vapor zones within a fluid.
Request
Have you seen the formation of bubbles inside a fluid? Or have you ever seen a pump go into cavitation?

ITALIAN
17-06-2024 - Sistemi energetici - La cavitazione[EN]-[IT]
La cavitazione
Quando parliamo di cavitazione intendiamo identificare il fenomeno dell’apparizione di bolle di vapore in seno ad una massa liquida. Questo avviene a causa della riduzione di pressione che va al di sotto di una pressione critica.
Possiamo anche descrivere la cavitazione come segue.
Alcune condizioni possono agire sul fluido per poi far scaturire la cavitazione ad
una pressione superiore a quella di tensione del vapore del liquido e pertanto la pmin risulta pari a:
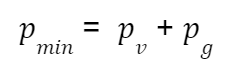
dove:
-pv indica la pressione di vapore saturo
-pg quella parziale del gas disciolto.
La cavitazione all’interno di un circuito con una turbomacchina sarà causa di caduta delle prestazioni della macchina in termini di rendimento, prevalenza e portata.
Le principali cause della cavitazione possono essere:
-Riduzione della pressione
-Aumento della velocità
-Desgin inadeguato
Inconvenienti provocati dalla cavitazione
La cavitazione può provocare i seguenti danni:
-Danni alle Superfici: Le bolle di cavitazione implodono violentemente quando ritornano in una zona di alta pressione, causando danni alle superfici dei materiali.
-Riduzione delle Prestazioni: La cavitazione può ridurre l'efficienza di pompe e turbine e possono compromettere il loro funzionamento.
-Rumore e Vibrazioni: L'implosione delle bolle di cavitazione genera rumore e vibrazioni che possono essere dannosi per le strutture meccaniche, inoltre rumore e vibrazioni possono determinare un funzionamento instabile.
Quando non avviene la cavitazione
La cavitazione può essere evitata riducendo l’altezza di installazione della pompa.
Può essere evitata anche riducendo le perdite fluidodinamiche lungo il condotto di aspirazione.
Per evitare la cavitazione dobbiamo verificare la presenza della seguente condizione:
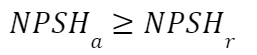
Dove:
NPSHa = net positive suction head disponibile
NPSHr = net positive suction head richiesto
Al variare della portata elaborata dalla pompa varia il NPSHr
massima altezza h0_max
Se facciamo riferimento all’altezza di aspirazione, la massima altezza h0_max alla quale può essere installata la pompa risulta essere calcolata come segue:
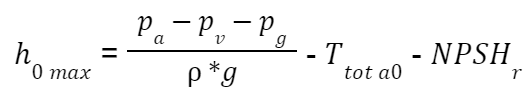
Quindi se dovesse risultare che h0_max<0 la pompa deve essere installata sotto battente.
Conclusioni
Viene definita cavitazione la formazione di zone di vapore all'interno di un fluido.
Domanda
Avete ai visto la formazione di bolle all'interno di un fluido? Oppure avete mai visto una pompa andare in cavitazione?
THE END
Wasn't too knowledgeable about this until reading your article. It's interesting how cavitation can damage pumps and turbines. Have you noticed cavitation issues often in your work though?
If I have seen bubbles, in champagne, here I am smiling, Ignore me.
A hug and I wish you a happy start to the week
!hiqvote
!discovery 35
@libertycrypto27, the HiQ Smart Bot has recognized your request (1/2) and will start the voting trail.
In addition, @stefano.massari gets !LOL from @hiq.redaktion.
For further questions, check out https://hiq-hive.com or join our Discord. And don't forget to vote HiQs fucking Witness! 😻
lolztoken.com
To the dock
Credit: reddit
@stefano.massari, I sent you an $LOLZ on behalf of hiq.smartbot
(8/8)
Farm LOLZ tokens when you Delegate Hive or Hive Tokens.
Click to delegate: 10 - 20 - 50 - 100 HP
Thank you so much dear friend for taking your quality time to explain this in details to us
I’ve only seen bubbles inside a fluid but don’t know how hat works
Thanks for the topic
Good one!