12-07-2024 - Energy systems - The 4T Diesel cycle [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
12-07-2024 - Energy systems - The 4T Diesel cycle [EN]-[IT]
The 4-stroke Diesel cycle
The four-stroke (4T) Diesel cycle is a thermodynamic cycle used in Diesel engines, which is known for its thermal efficiency and ability to operate on a variety of fuels. The Diesel engine was patented in 1892 by Rudolf Diesel.
Below is a list of the phases:
Aspiration (Intake Stroke)
Compression (Compression Stroke)
Combustion and Expansion (Power Stroke)
Exhaust Stroke
The phases of the diesel time cycle
The phases of the 4-stroke Diesel cycle are listed below.
0-1: intake (during this phase, the intake valve opens and the piston moves downward from Top Dead Center (TDC) to Bottom Dead Center, BDC)
1-2: Adiabatic compression (intake valve closes and piston moves up from BDC to TDC, compressing the air in the cylinder)
2-3: isobaric combustion (just before the piston reaches TDC, Diesel fuel is injected at high pressure directly into the cylinder, where the air is highly compressed and hot)
3-4: adiabatic expansion
4-1 : Spontaneous exhaust (The exhaust valve opens and the piston moves upward from BDC to TDC, expelling exhaust gases from the cylinder)
1-0: forced exhaust at constant pressure
Below is the graph of the ideal Diesel cycle
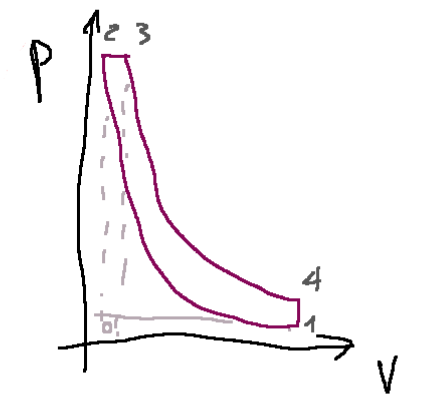
Ideal and real Diesel cycle
Below is the diagram of the indicated cycle (real cycle) of a Diesel engine
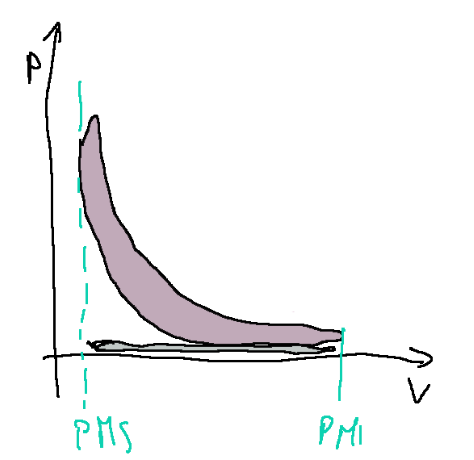
Compared to the ideal cycle, the real cycle differs due to:
-heat losses
-non-isobaric combustion
-exhaust valve opening time
-pumping work
In the case of diesel engines, since the fuel needs an incubation period to start combustion, it is necessary to introduce the injection advance.
Conclusions
We can say that the ideal Diesel cycle provides a theoretical model useful for understanding the fundamental principles of the operation of Diesel engines, while the real cycle takes into account the various losses and inefficiencies that occur in practice
Request
Have you driven more cars with petrol engines or diesel engines in your life?

ITALIAN
12-07-2024 - Sistemi energetici - Il ciclo Diesel a 4T [EN]-[IT]
Il ciclo Diesel a 4T
Il ciclo Diesel a quattro tempi (4T) è un ciclo termodinamico utilizzato nei motori Diesel, che è noto per la sua efficienza termica e la capacità di operare con una varietà di combustibili. Il motore Diesel fu brevettato nel 1892 da Rudolf Diesel.
Qui di seguito un elenco delle fasi:
Aspirazione (Intake Stroke)
Compressione (Compression Stroke)
Combustione ed Espansione (Power Stroke)
Scarico (Exhaust Stroke)
Le fasi del ciclo Diesel a tempi
Le fasi del ciclo Diesel a 4 tempi sono elencate qui sotto.
0-1 : aspirazione (durante questa fase, la valvola di aspirazione si apre e il pistone si muove verso il basso dal Punto Morto Superiore (PMS) al Punto Morto Inferiore, PMI)
1-2 : compressione adiabatica (la valvola di aspirazione si chiude e il pistone si muove verso l'alto dal PMI al PMS, comprimendo l'aria nel cilindro)
2-3 : combustione isobara (poco prima che il pistone raggiunga il PMS, il carburante Diesel viene iniettato ad alta pressione direttamente nel cilindro, dove l'aria è altamente compressa e calda)
3-4 : espansione adiabatica
4-1 : scarico spontaneo (La valvola di scarico si apre e il pistone si muove verso l'alto dal PMI al PMS, espellendo i gas di scarico dal cilindro)
1-0 : scarico forzato a pressione costante
Qui di seguito il grafico del ciclo ideale Diesel

Ciclo Diesel ideale e reale
Qui di seguito il diagramma del ciclo indicato (ciclo reale) di un motore Diesel

Rispetto al ciclo ideale il ciclo reale differisce per:
-perdite di calore
-combustione non isobara
-tempo di apertura della valvola di scarico
-lavoro di pompaggio
Nel caso dei motori diesel poiché il combustibile ha bisogno di un periodo di incubazione per avviare la combustione, è necessario introdurre l’anticipo di iniezione.
Conclusioni
Possiamo dire che il ciclo Diesel ideale fornisce un modello teorico utile per comprendere i principi fondamentali del funzionamento dei motori Diesel, mentre il ciclo reale tiene conto delle varie perdite e inefficienze che si verificano nella pratica
Domanda
Nella vostra vita avete guidato più auto con motori benzina o con motori Diesel?
THE END
I know absolutely nothing about this but thank you for the course
I’ve driven more cars with petrol engine
I haven’t driven anyone with diesel engine before
The real Diesel cycle differences from the ideal one are very interesting. I’ve driven diesel so I appreciate this hehehehe thanks brother
At first the equation really looks so hard and difficult to really understand