Grafting must remove cambium and phloem
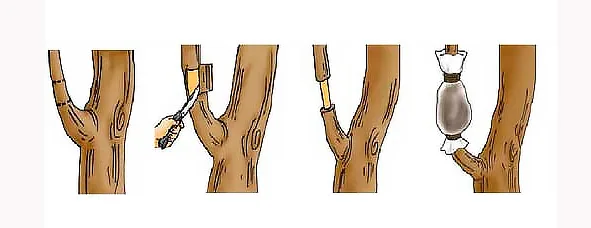
Grafting must remove cambium and phloem
Hello Steemian.
Sunday is a day that can be used with family. I went with the eldest to the garden and saw a longan tree that was nauseous with nausea. One tree bearing fruit. This tree has sweet and thick fruit. I feel the need to reproduce this longan by grafting. I hope to get plants with the same fruit as the parent. Sweet longan and thick fruit flesh.
I bring a sharp knife and then choose a stem that has the opportunity to become a sturdy and fast stem root. Then I started scraping the bark until it was no longer slippery. When scraping the stem clean suddenly the eldest is more caring.
"Why does it have to be scraped off like this. Dad?"
I'm happy to hear the eldest's question.
"Later, when I finish, I explain. Now help me to coat this stem with soil," I replied.
After wrapping the layer of soil with coconut fiber I explain the eldest's question.
Cambium and Floem
Grafting is a method of vegetative propagation that has been chosen to obtain superior plant seeds. Grafted plants have exactly the same characteristics as their parent plants.
The easy way and low cost is the reason people choose grafting as a plant multiplication. Grafting does not require special skills and equipment, so it is quite cheap and easy to do.
Kit can choose the tree trunk to be grafted. A stem the size of a pinky finger can usually be grafted — most importantly a cambium stem. Cambium is a layer of meristematic tissue in plants whose cells actively divide and cause the secondary growth of plants.
Good stem characteristics to graft are brown stems with young green branches. In stems like this, the process of cell division is still very active, so it will easily grow roots.
We need to peel the bark 2 cm - 10 cm (depending on the size of the stem) until the cambium is completely gone. How to get rid of cambium can be by wiping or scraping parts of wood sticks that have been peeled with a knife. But there are also those who leave the wood chips open for several days.
In biology, it is explained that in the dicotyledonous trees there are transport networks called xylem and phloem. Xylem has the ability to carry water and nutrients to the leaves while the phloem functions to produce photosynthesis from the leaves to all parts of the plant. When we scramble cambium we are removing phloem. When transplanting, cambium on branches or twigs must be removed so that the skin does not re-form. When the skin is re-formed, the roots cannot be formed. Conversely, if the cambium layer is clean, photosynthesis results will accumulate in the cambium that has been cleaned and root growth can be stimulated properly. Once the root is pretty much ready to be separated from its parent by cutting it.
Thus all my writing this time may useful for all of us.
Thank you for reading my post. I hope you enjoy it.
0
0
0.000
0 comments