HERBALIST SPACE // Healing properties of Terminalia catappa secondary metabolites

The specimens of Terminalia catappa, in the Asian countries are designated in a vernacular way as Indian almond tree, or simply almond tree as it is known in most of the South American and Caribbean countries, however, beyond the name that this prodigious ethnobotanical resource receives, the facility of this manuscript consists of socializing the biological potentialities, that have the secondary metabolites present in the leaves and fruits of T. catappa, and the positive effects that they have to cure certain pathologies in the human beings.

Fig. 2 Leaves with oblanceolated morphology Terminalia catappa. Public domain image, Author: Prenn, 2012 / CC BY-SA 3.0 Observation: The photograph was edited by the user @lupafilotaxia, by means of size adjustments and incorporation of texts.
Friends and members of the community of @NaturalMedicine, perhaps of the specimen I have mentioned, only know its link of ornamental use, due to the shade generated by the exuberant foliage branching system of Terminalia catappa however, it is important to mention that this plant resource, is extensively cultivated in Asian countries essentially in the Malayan region where it is believed to originate, and where, besides the ornamental use, its fruits are destined to the consumption, basically because its almonds are rich in proteins, calcium, fats and carbohydrates, whereas the leaves are considered vegetative structures of phytopharmacological importance, fundamentally because they have secondary metabolites able to generate positive answers to certain pathological pictures, among these the ones of greater effect are; Chebulagic acid, Corilagina, 1-degaloil eugenina, Geranina, Granatina, Punicalagina, Punicalina, Tercataina, Terflavina, and Tergalagina.
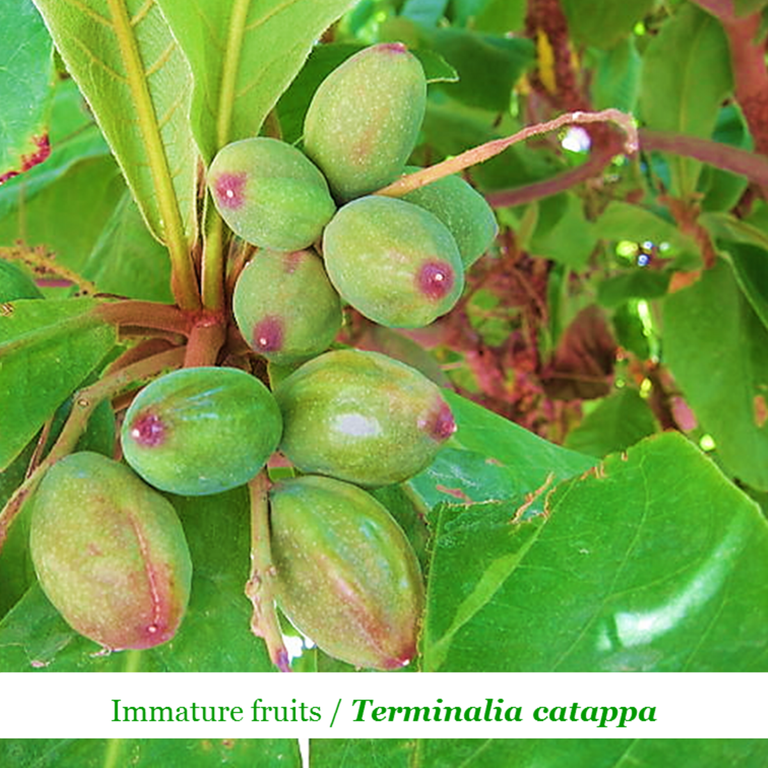

Fig. 3 Immature fruits of Terminalia catappa. Public domain image, Author: Own W, 2012 / CC BY-SA 3.0 Observation: The photograph was edited by the user @lupafilotaxia, by means of size adjustments and incorporation of texts.
Antioxidant activity
Terminalia catappa has variable concentrations of organic substances, among them; water-soluble tannins, whose chemical structures act as an antioxidant, preventing the oxidation of molecules, a reaction that prevents the progressive deterioration of the metabolic system at the cellular level, a crucial element for health.
Phytoanalgesic effect
The analgesic effect of aqueous extracts of Terminalia catappa leaves, induced by high concentrations of substances such as punicaline and punicalagine, has been demonstrated.

Fig. 4 Dried fruits and almonds from Terminalia catappa. Author: @lupafilotaxia.
Anti-inflammatory property
Phyto-molecules, such as the polyphenols present in the organographic structures of Terminalia catappa, possess anti-inflammatory activity.
Anti-diarrheal responses
The consumption of extracts based on Terminalia catappa leaves has shown astringent and therefore antidiarrheal action, this because, because its secondary metabolites tend to precipitate with the proteins present in the stomach secretions.
In summary, the vegetative structures of Terminalia catappa specimens possess multiple biological potentialities favorable to the treatment of conditions that afflict our health. Therefore, it is advisable to consider this plant material among the plants to be used to elaborate extracts to cure certain infectious conditions.
BIBLIOGRAPHICAL REFERENCES CONSULTED:
[1] Ángel M., Bacallao L., Domínguez, D., y Padilla D. Almendro de la India: potencial biológico valioso. Revista Cubana Investigación Biomédica, Las Habana. 2003; 22: 1: 41 - 7. Article: Online access
[2] Chen P., Li J., Liu T., and Lin T. Folk medicine Terminalia catappa and its major tannin component, punicalagin, are effective against bleomycin-induced genotoxicity in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Lett. 2000; 152; 2: 115 - 22. Article: Online access
 Join The Best Natural Health Community on Hive
Join The Best Natural Health Community on Hive
0
0
0.000
#Posh Twitter:
https://twitter.com/lupafilotaxia/status/1300535059259195399
Oh, an almond is SUCH a good tree to plant, though I'm not sure if it's the same one as the oone I planted last week. A good source of protein - can't wait til mine fruits.
@riverflows in my mother's house we had a leafy almond tree, I tell you, that in my childhood I used to spend long hours hitting the nuts with a stone, to be able to extract the almonds that I accumulated to eat later in quantity, and without a doubt to eat these almonds are very flavorful and generate an exquisite sensation to the palate. Thanks for visiting the blog.
Hola @lupafilotaxia. Conozco el almendro desde mi infancia, son gratos los recuerdos, también solía buscar este fruto para sacarle su almendra, además jugábamos con su pepa. Pero hasta ahorita que leo tu publicación es que estoy conociendo sus propiedades curativas. Muchas gracias por compartir tan valiosa información.
Saludos @pnessy, así es de mi infancia el almendro es el árbol del que más recuerdos guardo, correcto prescribe múltiples beneficios fitofarmacológicos. Gracias por dejar tu comentario.