Harmony: Next Generation of Sharding-Based Blockchain Technology

Introduction
Since the invention of bitcoin, the first ever crypto currency to be developed, in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto, time has flied and many inventions have come to play within the crypto sphere. With the idea behind the invention of the bitcoin blockchain technology clear enough and appreciated by many for its security, freedom of decentralization and is seen to disrupt the more centralized financial set up, there had been shortcomings in relation to the bitcoin blockchain mainstream adoption due to its inability to process a large amount of transactions per second compare to Visa card, a payment method for the more centralized financial institutions.
Scalability remains a main stay problem in different blockchain projects from Ethereum to Zilliqa, Stellar and rest. While the likes of Bitcoin, Ethereum uses the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus protocol, other blockchain projects EOS, IOTA, XRP, and likes have adopted different consensus protocol such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS), Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS), all in the aim of improving scalability, but non has been able to improve scalability efficiently without sacrificing other important feature such as security.
Sharding has been proposed to be the only answer of improving scalability when it comes to blockchain technology. Sharding mechanism had been adopted by Zilliqa blockchain that allows it to process 2800 transactions per second way ahead of Bitcoin and Ethereum.
Zilliqa is unable to solve the scalability problem and also maintain security due to it use of the more vulnerable PoW consensus mechanism as it randomness generation mechanism making it susceptible to one-shard attack.
A blockchain project that balances the scalability and maintain security and energy efficient is what "Harmony" is all about.
What is a Consensus Mechanism?
A consensus mechanism is an all round important feature of any blockchain project. It determines how fast and secure blockchain validators reach an agreement on the next block.
What is Sharding?
Sharding is a data fractioning technology adopted by blockchain projects to improve scalability. Sharding is an act of reducing a large data into a smaller fraction for easy and faster data processing to improve throughput. The ability of large data to be reduced into small fractions called shards, allow for efficient processing of data using a larger number of computing powers as simple as android phones to compute data. Android phones are able to serve as computing nodes as they are able to handle the more smaller data(shards).
NEXT GENERATION OF SHARDING BASED BLOCKCHAIN.
Harmony is the next generation of Sharding-based blockchain project, combining the knowledge of research from existing sharding blockchains and capitalizing on their flaws to produce the near perfect sharding-based blockchain experience with "Harmony".
The use of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) a more energy efficient consensus mechaism as its randomness generation mechanism gives it a one ahead of other sharding-based blockchain projects like Zilliqa that uses Proof-of-work (PoW) as its randomness generation mechanism that consumes more energy.
While likes of Zilliqa uses Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), a consensus protocol that has communication complexity, Harmony adopted the less complex consensus protocol called Fast Byzantine Fault Tolerance (FBFT), an improved consensus version on PBFT. PBFT selects a node to serve as leader and rest of the nodes serves as validators. The leader's node present its proposal to the validators whose in turn votes on the proposal and forward it to all validators of the block for verification. This process involves two different stages, the prepare stage and commit stage thus delay in throughput.
In contrast, FBFT is fast, capable of linear scaling with less communication complexity thus improving throughput on Harmony.
Projects trying to utilize the benefit of blockchain and decentralization, should look to build their project on Harmony network and experience the joy of scalability.
Build your project on Harmony and enjoy:
Inherent security with harmony multi nodes sharding and randomness generation mechanism.
Scalability with Harmony improved consensus protocol (FBFT).
Efficiency with Harmony PoS mechanism
Projects such as gaming, small and large scale enterprenuer can look to capitalize on Harmony numerous sharding benefits.
The table below shows the comparison between Harmony and other sharding-based blockchains
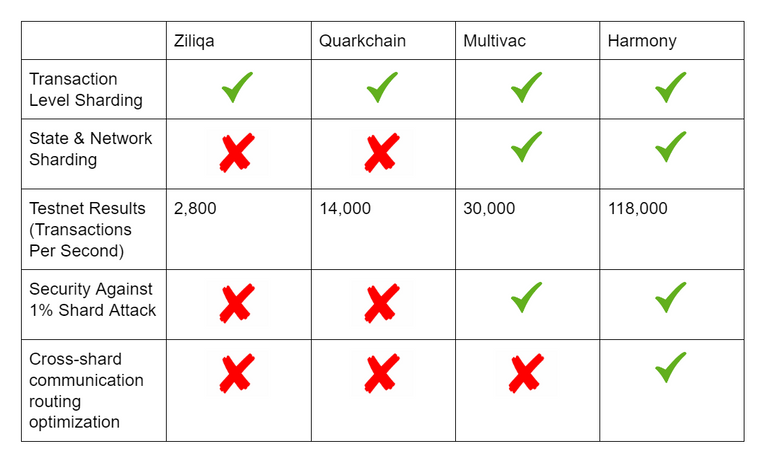 ConclusionES OF HARMONY
ConclusionES OF HARMONY
SCALABILITY: not only do Zilliqa failed due to it use of PoW consensus for it randomness generation mechanism, but it is also unable to generate state-shard: a technique that allows for blockchain data to be breakable to smaller units. Harmony on the other hand shards both transaction validation and blockchain data making it fully scalable.
EFFICIENCY: In stark contrast to PoW adopted by Zilliqa, Harmony uses the more energy efficient PoS for it randomness generation procedure.
FAST CONSENSUS: Harmony uses FBTF which is way faster than the PBTF adopted on zilliqa.
CROSS SHARDING: The atomic locking mechanism allow cross shards transactions amongst shards on harmony.
SCALABLE: Use of many adaptive techniques such as RaptorQ fountain code to propagate block with lightning speed and Kademila routing to execute cross-shards transactions.
Harmony Chains
Harmony runs on two different chain but similar functions to enhance it sharding procedure, the shard chain and beacon chain. While shard chains focuses on sharding of transaction data, beacon serves a blockchain data sharding and for deposition of stakes by stakers to become validators.
Use Case 1
Mr Collins is the head of marketing and strategic planning of pinnacle store, an utility store with a large customer base in the western part of Africa. The MD of the store sees reason for the store to explore the payment option using cryptocurrency due to the ever growwing of cryptocurrency users in the region,but their large customer base couple with the inability of blockchain technology to process large number of transaction per second makes this a big feat to achieve. After a thorough research, Mr Collins come about Harmony, a sharding- based blockchain technology that handles large transaction with explicit efficiency. Harmony is the answer, Mr Collins says.
Use Case 2
Xiang Hun Ping is a Chinese engineer and DApp developer who just developed a gaming DApp on blockchain network. Mr Xiang sees an upturn in the number of gamers using the app, and the multi-player feature begins to lag due to low computing power of the blockchain. Mr Xiang then heard of Harmony blockchain with the scalability needed for smooth running of his gaming App.
Conclusion
Harmony being able to balance between scalability and security will provide the platform for the mainstream adoption of blockchain technology.
For more information and resources:
Harmony Website
Harmony OnePager
Harmony WhitePaper
Harmony Medium Blog
Harmony Telegram Group
Harmony Twitter