Antibiotics: The Double-Edged Sword
One of the most commonly used class of medications in our world is antibiotics as they have been effective tool to save lives and treat diseases but then they also have negative results which can be very dangerous. So in this post, i will be discussing antibiotics with you in full.
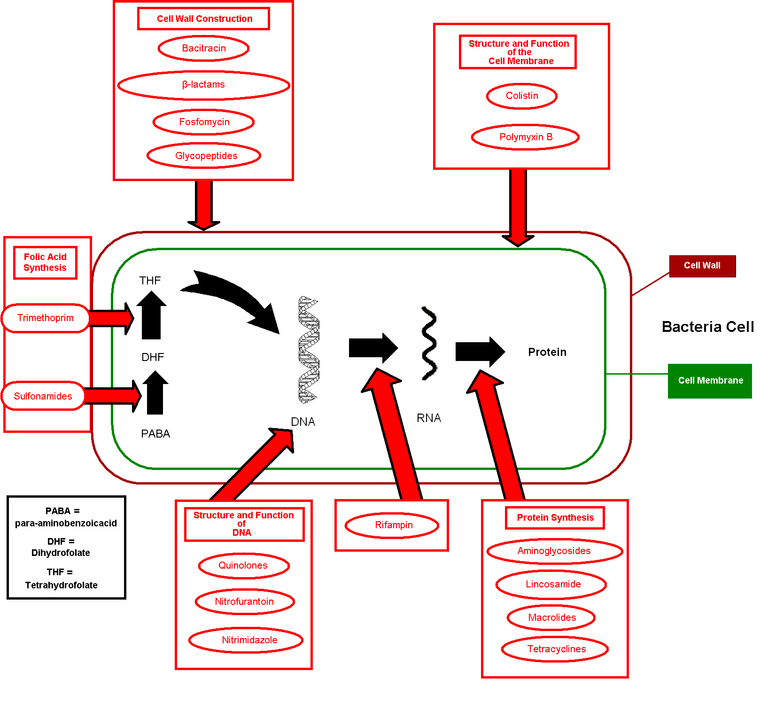
In other to get why this group of drug do both good and harm, we need to understand its meaning. Antibiotics are generally substances that kills or inhibits the growth of bacteria but while they do this, the exhibit a property know has selective toxicity where the drug has the ability to harm or kill microorganisms without causing any harm or damage to the host's cell. This is possible by allowing the drug to target the structures of the microorganism's cells through their mechanisms which is different from ours like for instance, bacteria have cell walls but our cells don't have cell walls, we also have different materials in our nucleic acids, ribosome, and cell membrane.\
While targeting these bacterial cells, the antimicrobial agents can either be bactericidal or bacteriostatic according to its definition with bactericidal killing the antibiotics, while bacteriostatic inhibits or slow the growth of the bacteria. When a person is taking a bacteriostatic antibiotics, they will require the help of their immune system to help kill the bacteria because if the drug is stopped without the bacteria being killed, the bacteria could grow again.
Most antibiotics that are known, work against the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, thereby causing water to get into the cell while preventing it from multiplying. The water then causes the cell to rupture leading to its death. These drugs are known as beta lactams which includes pennicilins (e.g Amoxicillin), cephalosporin (e.g Cephalexin) and so on. There are also some antibiotics that interfere with the Ribosome of the bacteria since they are different from that of humans, thereby preventing the synthesis of protein. With this, the bacteria growth can be slown down, and this could eventually kill the bacteria.
It is important to know that the main purpose of antibiotics is to treat infections the body couldn't fight off or would have trouble fighting off by itself, and we cannot deny that it is one of the most impressive breakthrough of the 20th century helping to increase life expectancy but then, as humans we can overuse things, and one of the most overused drugs are antibiotics.
We take antibiotics too often or for the wrong reasons, and this can change bacteria so much that they become resistant to antibiotics. This is because we use them for infections or conditions that we shouldn't thereby leading to a resistance of the bacteria known as bacterial resistance making it more difficult to treat certain infections caused by the antibiotic resistance bacteria. Although antibiotics were not designed to hurt us, they still come with potential allergic reactions, side effects, and some level of toxicity.
Allergic reactions from antibiotics would include but not limited to GI symptoms such as upset stomach, nausea, Diarrhea (antibiotic associated diarrhea), and so on. When it comes to Antibiotic Associated Diarrhea, it can be associated with broad spectrum antibiotic use. Broad Spectrum antibiotics are antibiotics that can fight against multiple different types of bacteria infection thereby killing the bacteria in your gut.
Use of antibiotics can go wrong in some people as the antibiotics suppresses their normal floral causing them to get secondary infections such as Clostridium Difficile infection. People can also have consequences such as allergies such as hypersensitivity reaction and in severe cases, anaphylaxis and there are still more side effects.
The overuse of antibiotics, particularly in cases of non-bacterial infections like viral illnesses, contributes significantly to antibiotic resistance. Bacteria possess remarkable adaptability, allowing them to evade or inactivate antibiotics effectively. One of these adaptive mechanisms includes the production of beta-lactamase enzymes, rendering antibiotics ineffective.
Antibiotics have transformed the landscape of medicine and saved countless lives. However, their overuse and misuse come at a price, fueling bacterial resistance and leading to adverse effects. A delicate balance must be struck, ensuring that antibiotics continue to be an invaluable tool in healthcare without losing their effectiveness against the ever-adapting bacterial world. Antibiotic stewardship and responsible usage are essential in safeguarding the effectiveness of these life-saving medications.
Post Reference
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/antibiotics/
https://www.nhsinform.scot/tests-and-treatments/medicines-and-medical-aids/types-of-medicine/antibiotics/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4378521/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5672523/
https://www.mdpi.com/journal/antibiotics
https://aricjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13756-022-01063-5
https://bmcpublichealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12889-019-7796-8
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/langlo/article/PIIS2214-109X(22)00510-1/fulltext
https://aacijournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13223-020-0402-x
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6563335/
https://www.mdpi.com/2079-6382/10/10/1144
Yay! 🤗
Your content has been boosted with Ecency Points, by @thomisin.
Use Ecency daily to boost your growth on platform!
Support Ecency
Vote for new Proposal
Delegate HP and earn more
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.
The Abuse of antibiotics is so rampant in Nigeria which is why many strains have developed resistance