28-03-2024 - Physics - Thermodynamics of closed systems (4/13) [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
28-03-2024 - Physics - Thermodynamics of closed systems (4/13) [EN]-[IT]
Thermodynamics of closed systems
Carnot's engine
The Carnot engine is a theoretical heat engine, which operates with the Carnot cycle, a reversible thermodynamic cycle. Designed by Carnot.
Thermodynamic efficiency
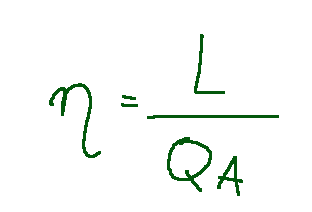
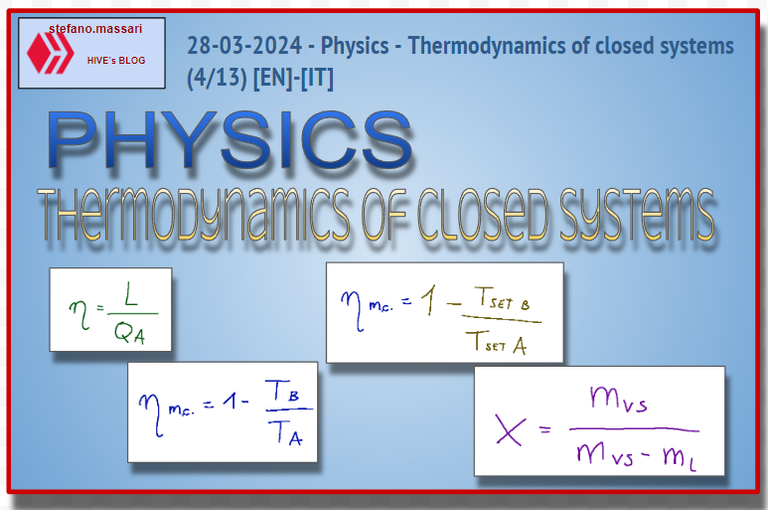
The thermodynamic efficiency is equal to the ratio between converted energy (mechanical energy) and energy to be converted (thermal energy supplied to the system)
We can summarize the thermodynamic efficiency as the ratio between the converted energy and the energy to be converted.
Mating term
By coupling term we mean the term of entropy production associated with heat production.
System production
By internal production of the system we mean the end of the entropy production due to the production of single S of each system.
performance of the Carnot engine
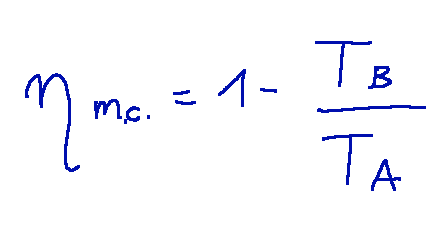
Where TB and TB we can sometimes see them written as Tf/Tc.
These are the temperatures of the cold source and the hot source respectively measured in Kelvin.
Cyclic machines
direct cycle
A direct cycle is an hourly cycle that represents a continuous conversion of heat to work.
Upper limit
The following formula represents the upper limit of the efficiency obtainable from thermal machines operating between different temperatures TA and TB
refrigerators and heat pumps
Difference between refrigerator and heat pump
The refrigerator is a system in which the SET A temperature is controlled, the heat pump is a system in which the SET B temperature is controlled.
Effect coefficient
The useful effect coefficient of the refrigerator is usually identified by the letters cf.
cf is the thermal energy removed from the SET at lower temperature with the work L on the mechanical energy supplied.
The states
State diagram
The state or phase diagram is a Cartesian diagram referring to a pure substance or a mixture which represents the state of the thermodynamic system and therefore the phase. The phase can be gas, liquid or solid.
Critical point
The critical point of a substance on the phase diagram is the set of particular conditions of maximum temperature and maximum pressure (called critical temperature and critical pressure) at which a substance can exist as a two-phase gas-liquid mixture.
The title in the blends
Below is the formula for the title in the mixtures.
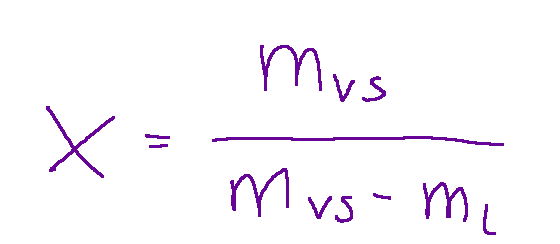
Where:
mvs = mass of dry vapor found in the phase under consideration
ml = mass of liquid+vapour (mixture) found in the phase under consideration.
In certain cases it is convenient to describe the system using the x content of the dry steam.
Conclusions
As regards the refrigeration machine we can say that its operation is identical to that of the heat pump, with the difference that the useful result sought is that of the heat extracted from the cold body.
Request
Have you installed heat pumps in your homes? or air conditioners?

28-03-2024 - Fisica - Termodinamica dei sistemi chiusi (4/13) [EN]-[IT]
Termodinamica dei sistemi chiusi
Macchina di Carnot
La macchina di Carnot è una macchina termica teorica, che opera con il ciclo di Carnot, un ciclo termodinamico reversibile. Ideata da Carnot.
Rendimento termodinamico
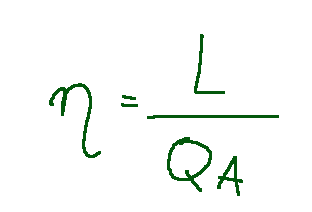
Il rendimento termodinamico è uguale al rapporto tra energia convertita (energia meccanica) e energia da convertire (energia termica fornita al sistema)
Possiamo sintetizzare il rendimento termodinamico come il rapporto tra l'energia convertita e l'energia da convertire.
Termine di accoppiamento
Per termine di accoppiamento si intende il termine della produzione di entropia associata alla produzione di calore.
Produzione del sistema
Per produzione interna del sistema si intende il termine della produzione di entropia dovuto alla produzione di S singola di ogni sistema.
rendimento della macchina di Carnot
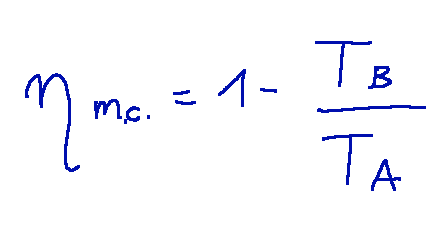
Dove TB e TB possiamo a volte vederli scritti come Tf/Tc.
Queste sono rispettivamente le temperature della sorgente fredda e di quella calda misurate in Kelvin.
Macchine cicliche
ciclo diretto
Un ciclo diretto è un ciclo orario che rappresenta una conversione continua di calore in lavoro.
Limite superiore
La seguente formula rappresenta il limite superiore dei rendimenti ottenibili da macchine termiche che operano tra temperature diverse TA e TB
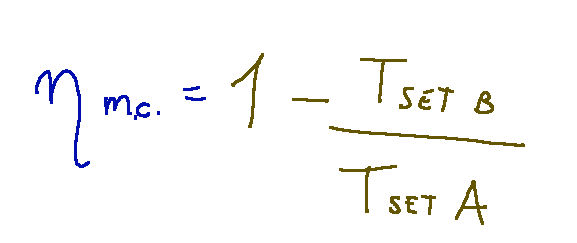
frigoriferi e pompe di calore
Differenza tra frigorifero e pompa di calore
Il frigorifero è un sistema in cui viene controllata la temperatura SET A, la pompa di calore è un sistema in cui è controllata la temperatura SET B.
Coefficiente d'effetto
Il coefficiente d'effetto utile del frigorifero viene solitamente identificato dalle lettere cf.
cf è l'energia termica sottratta al SET a temperatura inferiore con il lavoro L sull'energia meccanica fornita.
Gli stati
Diagramma di stato
Il diagramma di stato o di fase è un diagramma cartesiano riferito ad una sostanza pura o ad una miscela che rappresenta lo stato del sistema termodinamico e quindi la fase. La fase può essere, gas, liquido o solido.
Punto critico
Il punto critico di una sostanza sul diagramma di fase è l'insieme di particolari condizioni di massima temperatura e massima pressione (denominate temperatura critica e pressione critica) in corrispondenza delle quali una sostanza può esistere come miscela bifase gas-liquido.
Il titolo nelle miscele
Qui di seguito è rappresentata la formula del titolo nelle miscele.
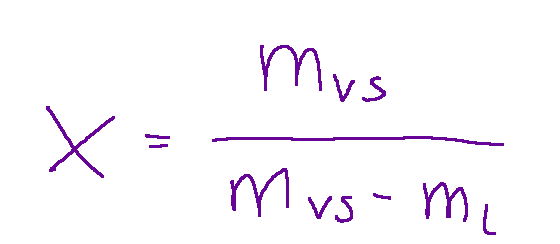
dove:
mvs = massa del vapore secco che si trova nella fase in considerazione
ml = massa di liquido+vapore (miscela) che si trova nella fase in considerazione.
In certi casi conviene descrivere il sistema utilizzando il titolo x del vapore secco.
Conclusioni
Per quanto riguarda la macchina frigorifera possiamo dire che il suo funzionamento è identico a quello della pompa di calore, con la differenza che il risultato utile che si ricerca è quello del calore estratto al corpo freddo.
Domanda
Nelle vostre abitazioni avete installato delle pompe di calore? oppure dei condizionatori?
THE END
Ciao @stefano.massari, rimetti la delega, ti dirò dopo, ma vado con molta motivazione e perseveranza, la prossima settimana fermerò power down.
Un abbraccio, ti apprezzo moltissimo e ti sono molto grato, benedizioni a te e alla tua famiglia.
Ricevuto caro @lupega
The close and open system seem similar or somewhat similar to me
In this article I talk about various things and I also make some mention of Canot's machine, who was a very important physicist for thermodynamics. Meanwhile he introduces the concept of thermodynamic efficiency which is the ratio between the converted energy and the energy to be converted.
Then the concept of the coupling term is introduced which is the entropy production term associated with heat production. Another concept introduced is that of the internal production of the system which is the term of the entropy production due to the single production of each system.
Finally, the main concept which is the performance of the Carnot machine:
It actually takes me a long time to differentiate between the close system and the open system
I confirm that it is not easy but the distinction between closed and open systems must be made and is quite important. In this article another important thing is that of the forward and reverse cycle. By direct cycle we mean a thermodynamic cycle that represents a continuous conversion of heat into work. Below is a graph that represents an hourly cycle, i.e. a direct cycle.