27-07-2024 - energy systems - gas turbines [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
27-07-2024 - energy systems - gas turbines [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction regarding the technical topic mentioned in question
(code notes: X60-_)
Gas Turbines
A gas turbine is a thermal machine that converts the chemical energy of the fuel into mechanical energy and this process occurs through a series of thermodynamic transformations.
The ideal reference for the operation of gas turbines is the gas turbine cycle or the Brayton-Joule thermodynamic cycle
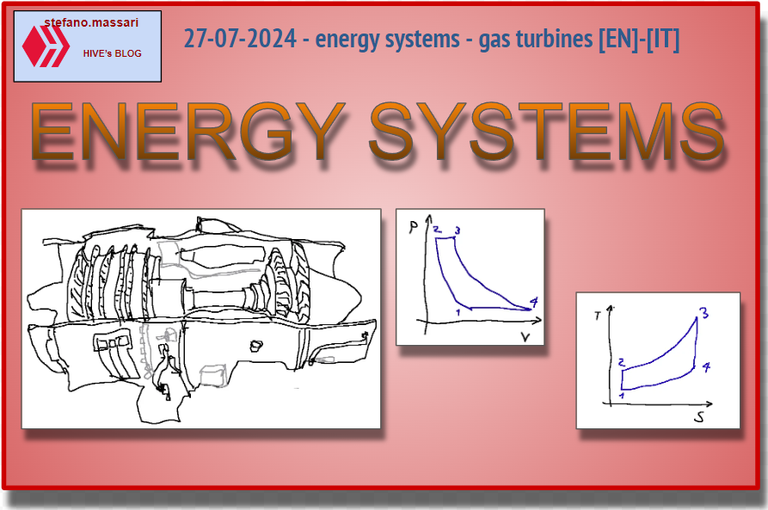
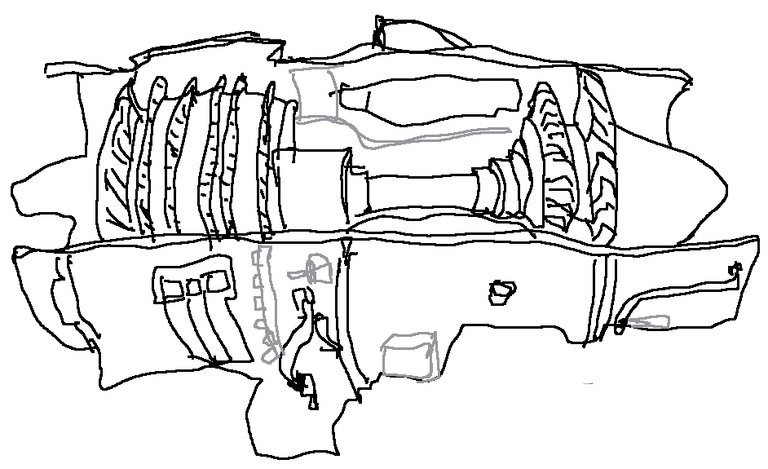
Below is a sketch of a gas turbine
Gas turbine cycle
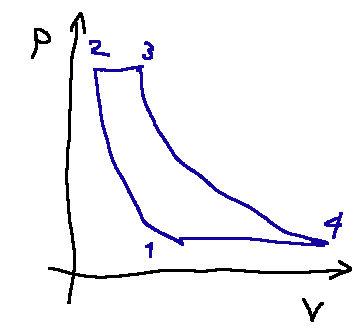
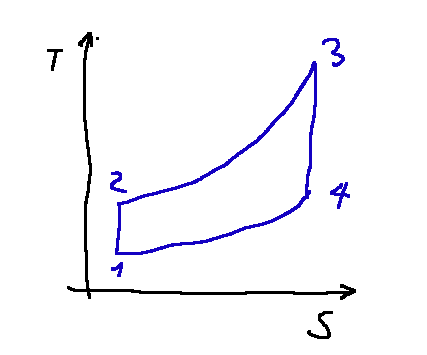
The gas turbine cycle or Brayton-Joule cycle is composed of 4 phases, below are the p-v (pressure-volume) and T-s (temperature-entropy) diagrams
p-V diagram
T-s diagram
Phases
The Brayton-Joule cycle is divided into 4 phases in which the 4 thermodynamic transformations relating to this cycle take place. The 4 transformations are listed and explained below:
1-Isentropic compression
In the first phase the compressor performs work and isentropic compression occurs.
The air sucked in from the external environment is compressed and this increase in pressure leads to a rise in the air temperature.
2-Heat exchange.
In this phase the compressed air is sent into the combustion chamber. In this phase the air is mixed with the fuel so that the air-fuel mixture is ignited. In this way gas is produced at high temperature and high pressure.
In this phase, isobaric heating occurs (at constant pressure)
3-Isentropic expansion
In this phase characterized by expansion, the gas at high temperature and pressure passes through the turbine. The gases expand and transfer their kinetic energy to the turbine blades. This action rotates the shaft connected to the turbine and mechanical energy is thus produced. This mechanical energy can then be used for different purposes in different applications.
4-Heat exchange
In this phase, isobaric cooling (at constant pressure) occurs.
The exhaust gases are released into the external environment or pass through a heat exchanger.
Synthesis of the Brayton-Joule cycle
1-2 Isentropic compression
2-3 Isobaric heat addition (combustion)
3-4 Isentropic expansion
4-1 Isobaric heat removal (cooling)
Conclusions
The Brayton-Joule cycle is the ideal thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of gas turbines and is composed of 4 main phases.
Request
Have you ever seen a gas turbine somewhere?

[ITALIAN]
27-07-2024 - sistemi energetici - turbine a gas [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento tecnico citato in oggetto
(code notes: X60-_)
Turbine a gas
Una turbina a gas è una macchina termica che converte l’energia chimica del combustibile in energia meccanica e questo processo avviene tramite una serie di trasformazioni termodinamiche.
Il riferimento ideale per il funzionamento delle turbine a gas è il ciclo turbogas ovvero il ciclo termodinamico di Brayton-Joule
Qui di seguito uno schizzo di una turbina a gas

Ciclo turbogas
Il ciclo turbogas o ciclo Brayton-Joule è composto da 4 fasi, qui di seguito i diagrammi p-v (pressione-volume) e T-s (temperatura-entropia)
Diagramma p-V

Diagramma T-s

Le fasi
Il ciclo Brayton-Joule si divide in 4 fasi in cui avvengono le 4 trasformazioni termodinamiche relative a questo ciclo. Qui di seguito sono elencate e spiegate le 4 trasformazioni:
1-Compressione isoentropica
Nella prima fase il compressore compie un lavoro ed avviene una compressione isoentropica.
L’aria aspirata dall’ambiente esterno viene compressa e questo aumento di pressione comporta un innalzamento della temperatura dell’aria.
2-Scambio di calore.
In questa fase l’aria compressa viene inviata nella camera di combustione. In questa fase l’aria viene miscelata con il combustibile in modo che la miscela aria-combustibile venga accesa. In questo modo si produce gas ad alta temperatura e ad alta pressione.
In questa fase avviene un riscaldamento isobaro (a pressione costante)
3-Espansione isoentropica
In questa fase caratterizzata da un’espansione il gas ad alta temperatura e ad alta pressione passano attraverso la turbina. I gas si espandono e trasferiscono la loro energia cinetica alle pale della turbina. Questa azione fa ruotare l’albero collegato alla turbina e viene così prodotta energia meccanica. Questa energia meccanica potrà poi essere utilizzata per diversi scopi in diverse applicazioni.
4-Scambio di calore
In questa fase avviene il raffreddamento isobaro (a pressione costante).
I gas esausti vengono rilasciati nell’ambiente esterno o passano attraverso uno scambiatore di calore.
Sintesi del ciclo Brayton-Joule
1-2 Compressione isoentropica
2-3 Aggiunta di calore isobara (combustione)
3-4 Espansione isoentropica
4-1 Rimozione di calore isobara (raffreddamento)
Conclusioni
Il ciclo Brayton-Joule è il ciclo termodinamico ideale che descrive il funzionamento delle turbine a gas ed è composto da 4 fasi principali.
Domanda
Avete mai visto una turbina a gas da qualche parte?
THE END
I’ve never seen a gas turbine somewhere but I can be in search of it
You mentioned that a gas turbine can convert the chemical energy of fuel to mechanical
Does it mean that a gas turbine can as well be a refinery?