25-07-2024-Operation-Useful power for a compressor [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
25-07-2024-Operation-Useful power for a compressor [EN]-[IT]
Useful power for one compressor
Below is an exercise regarding what was written in question. I will try to provide the necessary information to understand and carry out this exercise even without profound knowledge of the topic.
Brief description about the topic
The power of an ideal compressor can be obtained through the value of the isentropic compression power.
Exercise
A compressor compresses an air flow rate of 1000 m3/h from a pressure of 2 bar and a temperature of 288 K to a pressure of 6 bar. Assuming ideal compression, how much power is needed? Assume cp=1.005 kj/kgk, k=1.4 and R=0.287 kj/kgK
Procedure
Below we will see all the steps that need to be considered in order to calculate the necessary power assuming ideal compression with the exercise data.
I would like to point out that in this exercise the calculations will not be shown in detail, but the main objective is to show the sequence of reasoning to be done to arrive at the power calculation.
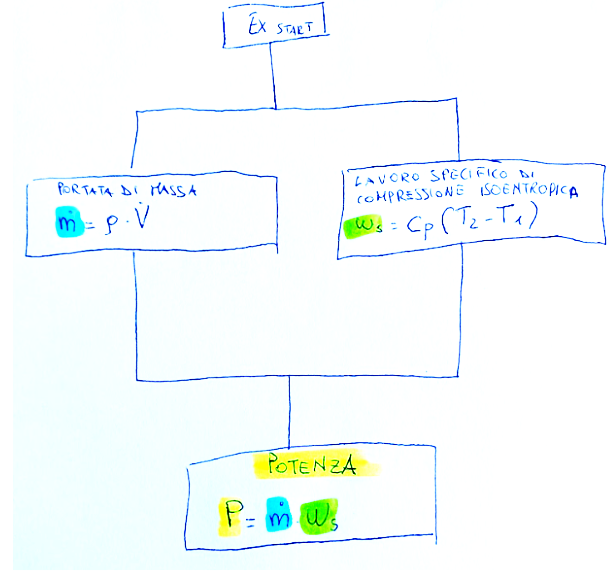
First of all we need to establish what we need and what we need is the mass flow rate and the specific work of isentropic compression
So our goal will be to have the data to satisfy the following account
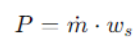
Where:
m = mass flow rate
ωs = Specific work of isentropic compression
We must divide the exercise into two channels to arrive at the result and below I propose a scheme:
Mass flow rate
The mass gate, or mass flow rate, can be obtained by multiplying the density of the air in initial conditions by the mass flow rate of air.
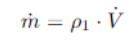
If we analyze the situation we see that the flow rate data is provided by the operation, but we do not have the value of the air density.
To obtain the air density data one must rely on the equation of state of ideal gases.
Below is an example of the formula to apply:
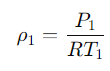
Specific work of isentropic compression
To calculate the power we need to multiply the mass flow rate by the specific work of isentropic compression.
At this point we therefore need to know the value of the specific work of isentropic compression.
To obtain this data you need to multiply the specific heat at constant pressure (cp) by the difference between T2 and T1, the formula below.
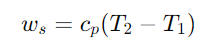
At this point we will have all the data available
Result
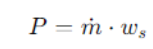
Conclusion
The power of a compressor, assuming ideal compression, is calculated by multiplying the mass flow rate by the specific work of isentropic compression

Request
Have you ever tried to calculate the power of a compressor?

ITALIAN
25-07-2024-Esercizio-Potenza utile ad un compressore [EN]-[IT]
Potenza utile ad un compressore
Qui di seguito un esercizio a riguardo di quanto scritto in oggetto. Cercherò di fornire le indicazioni necessarie per comprendere e svolgere questo esercizio anche senza una profonda conoscenza dell’argomento.
Breve descrizione a riguardo dell’argomento
La potenza di un compressore ideale si può ricavare tramite il valore della potenza di compressione isoentropica.
Esercizio
Un compressore comprime una portata di aria pari a 1000 m3/h dalla pressione di 2 bar e temperatura di 288 K alla pressione di 6 bar. Ipotizzando la compressione ideale a quanto ammonta la potenza necessaria? Si assuma cp=1,005 kj/kgk, k=1,4 e R=0,287 kj/kgK
Svolgimento
Qui di seguito vedremo tutti i passaggi che sono da considerare per riuscire a calcolare la potenza necessaria ipotizzando una compressione ideale con i dati dell'esercizio.
Preciso che in questo esercizio non verranno mostrati i calcoli nel dettaglio, ma l'obiettivo principale è mostrare la sequenza dei ragionamento da fare per arrivare al calcolo della potenza.
Prima di tutto dobbiamo fissare cosa ci serve e quello che ci serva è la portata di massa ed il lavoro specifico di compressione isentropica
Quindi il nostro obietti sarà avere i dati per soddisfare il seguente conto
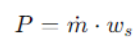
Dove:
m = portata di massa
ωs = Lavoro specifico di compressione isoentropica
Dobbiamo dividere l'esercizio in due canali per arrivare al risultato e qui di seguito propongo uno schema:

Portata di massa
La porta di massa, o portata massica, la possiamo ottenere moltiplicando la densità dell'aria in condizioni iniziali per la portata di massa d'aria.
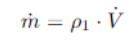
Se analizziamo la situazione vediamo che il dato della portata ce lo fornisce l'esercizio, ma non abbiamo il valore della densità dell'aria.
Per ricavare il dato della densità dell'aria bisogna appoggiarsi all'equazione di stato dei gas perfetti.
Qui di seguito un esempio della formula da applicare:
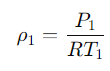
Lavoro specifico di compressione isoentropica
Per calcolarci la potenza abbiamo bisogno di moltiplicare la portata massica al lavoro specifico di compressione isoentropica.
A questo punto quindi abbiamo bisogno di sapere il valore del lavoro specifico di compressione isoentropica.
Per avere questo dato bisogna moltiplicare il calore specifico a pressione costante (cp) alla differenza tra T2 e T1, qui di seguito la formula.
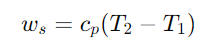
A questo punto avremo tutti i dati a disposizione
Risultato
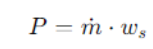
Conclusione
La potenza di un compressore, ipotizzando la compressione ideale, si calcola moltiplicando la portata massica al lavoro specifico di compressione isoentropica

Domanda
Avete mai provato a calcolare la potenza di un compressore?
THE END
I have tried to calculate the power of the compressor, but I got tired of it because I am not really familiar with mathematical or science questions
This course is really simple because I’ve done something very familiar to this and it was an interesting course
Calculating compressor power can be challenging but pretty useful. Your step-by-step guide makes it clearer for beginners. It's not easy explaining these stuff but you keep doing it well brother well done !WEED
@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 0/48) Liquid rewards.