25-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Thermodynamics (part 5), entropy [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
25-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Thermodynamics (part 5), entropy [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a short instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_69)

Image generated with artificial intelligence (Microsoft Copilot)
Thermodynamics (part 5), entropy
Concept of Entropy
In thermodynamics entropy is considered as a main concept. In thermodynamics entropy measures the degree of disorder of a system.
We can also see entropy as a data that tells us the amount of energy of a system that cannot be used to do work.
The symbol for entropy is "S", below is the mathematical formula:
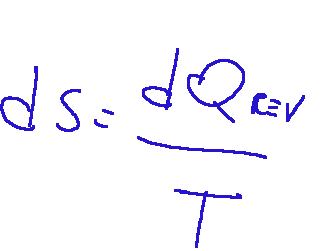
Where:
dS = entropy change
dQrev = amount of heat exchanged
T = absolute temperature of the system
One of the things we can consider is that the total entropy of a system in a reversible process remains constant. Another thing we must consider is that entropy is not an absolute quantity but a relative quantity. This means that entropy is a quantity that changes depending on the processes to which the system is subjected.
Entropy and chemical reactions
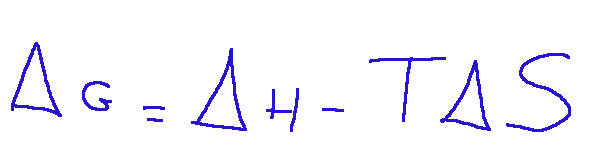
Where:
ΔG = change in Gibbs free energy,
ΔH = change in enthalpy (i.e. the heat absorbed or released by the reaction)
T = absolute temperature,
ΔS = change in entropy
When we talk about chemical reactions it is also important to introduce the concept of spontaneity of chemical reactions. The spontaneity of a chemical reaction is linked to the change in entropy and the change in enthalpy of the system. From the form we see written above, without going into technical details, we can say that if ΔG is negative the reaction is spontaneous and from the written relationship we understand that if the entropy variation is greater than zero, this will favor the spontaneity of the reaction.
What is the spontaneity of a chemical reaction?
It refers to the ability of a reaction to occur without the contribution of external energy
The expansion of a gas
We said that entropy measures disorder. It is natural to think that in a gas the disorder is greater than in a solid and it is so. In essence, the expansion of a gas occurs spontaneously from a state of higher order (lower probability of occurrence) to a state of lower order (higher probability of occurrence). It is more likely to find the 4 gas molecules uniformly distributed between the two compartments (lower order) rather than all confined in just one of the two (higher order). Based on considerations of this type, the Austrian physicist L. Boltzmann introduced the state entropy function (indicated by the capital letter S) defined as follows:
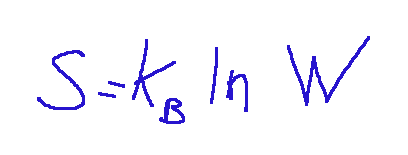
This is a mathematical expression that describes entropy in a microscopic context.
Where:
S = the entropy of the system
Kb = the Boltzmann constant
W = number of possible microscopic configurations that the system can assume while maintaining constant its macroscopic conditions such as energy, volume and number of particles.
ln = natural logarithm.
Conclusions
Entropy is a very important concept because it explains that a system is linked to the fact that energy tends to disperse and become less usable to do work.
Since entropy is fundamental to determine the spontaneity of chemical reactions and in describing chemical equilibrium, it is easy to deduce that entropy is not only a fundamental concept for thermodynamics, but it is also an important concept for chemistry.
Question
The most classic example of a chemical reaction in which entropy and spontaneity play an important role is the melting of ice that melts in water at room temperature. The passage of ice into water involves significant changes in entropy and depends on the temperature to be spontaneous. Is it true that even without knowing the technical details it is something we have all learned from life?
THE END

[ITALIAN]
25-03-2025 - Basi di chimica - Termodinamica (part 5), entropia [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_69)
Termodinamica (part 5), entropia
Concetto di Entropia
Nella termodinamica l'entropia è considerato come un concetto principale. In termodinamica l'entropia misura il grado di disordine di un sistema.
Possiamo anche vedere l'entropia come un dato che ci indica la quantità di energia di un sistema che non può essere utilizzata per compiere lavoro.
Il simbolo dell'entropia è la "S", qui di seguito la formula matematica:
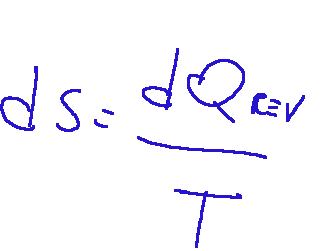
Dove:
dS = variazione di entropia
dQrev = quantità di calore scambiata
T = temperatura assoluta del sistema
Una delle cose che possiamo considerare è che l’entropia totale di un sistema in un processo reversibile rimane costante. Un’altra cosa che invece dobbiamo considerare è che l’entropia non è una grandezza assoluta ma è una grandezza relativa. Questo significa che l’entropia è una grandezza che cambia in funzione dei processi a cui è sottoposto il sistema.
Entropia e reazioni chimiche
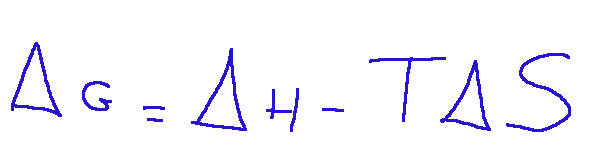
Dove:
ΔG = cambiamento nell'energia libera di Gibbs,
ΔH = cambiamento di entalpia (ovvero il calore assorbito o ceduto dalla reazione)
T = temperatura assoluta,
ΔS = cambiamento di entropia
Quando parliamo di reazioni chimiche è importante anche introdurre il concetto di spontaneità delle reazioni chimiche. La spontaneità di una reazione chimica è legata alla variazione di entropia e alla variazione di entalpia del sistema. Dalla forma che vediamo scritta qui sopra, senza entrare in dettagli tecnici, possiamo affermare che se ΔG è negativo la reazione è spontanea e dalla relazione scritta comprendiamo che se la variazione di entropia è maggiore di zero, questa favorirà la spontaneità della reazione.
Cosa è la spontaneità di una reazione chimica?
Essa si riferisce alla capacità di una reazione di avvenire senza l'apporto di energia esterna
L’espansione di un gas
Abbiamo detto che l'entropia misura il disordine. Viene spontaneo pensare che in un gas il disordine sia maggiore che in un solido ed è così. In sostanza, l’espansione di un gas avviene spontaneamente da uno stato di più alto ordine (più bassa probabilità che si verifichi) aduno stato di più basso ordine (più alta proabilità che si verifichi). È più probabile trovare le 4 molecole di gas uniformementedistribuite tra i due compartimenti (più basso ordine) piuttosto che tutte confinate in uno solo dei due (più alto ordine). Sulla base di considerazioni di questo tipo, il fisico austriaco L. Boltzmann, introdusse la funzione di stato entropia (indicata con la lettera maiuscola S) definita nel modo seguente:
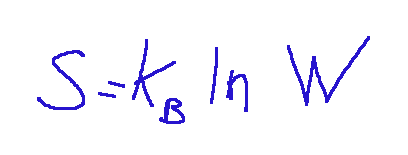
Questa è un'espressione matematica che descrive l'entropia in un contesto microscopico.
Dove:
S = l'entropia del sistema
Kb = la costante di Boltzmann
W = numero di configurazioni microscopiche possibili che il sistema può assumere mantenendo costanti le sue condizioni macroscopiche come energia, volume e numero di particelle.
ln = logaritmo naturale.
Conclusioni
L’entropia è un concetto molto importante perché spiega che un sistema è legato al fatto che l’energia tende a disperdersi e a diventare meno utilizzabile per compiere lavoro.
Siccome l’entropia è fondamentale per determinare la spontaneità delle reazioni chimiche e nel descrivere l’equilibrio chimico, si deduce facilmente che l’entropia non solo è un concetto fondamentale per la termodinamica, ma è un concetto importante anche per la chimica.
Domanda
L'esempio più classico di una reazione chimica in cui l'entropia e la spontaneità giocano un ruolo importante è lo scioglimento del ghiaccio che si scioglie in acqua a temperatura ambiente. Il passaggio del ghiaccio in acqua coinvolge cambiamenti significativi in entropia e dipende dalla temperatura per essere spontanea. E' vero che pur non conoscendo i dettagli tecnici è una cosa che abbiamo imparato tutti dalla vita?
THE END
Entropy: the universe’s way of saying "let chaos reign"!
Fascinating how disorder drives spontaneity in chemistry. 🧪
Thank you for leaving a comment. The concept of entropy is fundamental in chemistry, especially when studying thermodynamic processes, chemical reactions and changes of state. Initially, entropy might be a topic that is not paid attention to when we are in the chemical field, but this is not the case. Entropy in chemistry explains the direction of spontaneous processes, in fact many natural processes occur in the direction of increasing entropy, such as when ice becomes water
This is one of the topic that for years I am trying to actually understand but today I understand it much more better
Thank you for your kind comment. In this article in particular I wanted to talk about the importance of understanding entropy. It is essential to predict the behavior of chemical reactions. I believe that the most well-known equation in this topic and perhaps also the most important is the Gibbs free energy equation. I repost it below.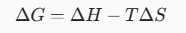
From this equation we understand how enthalpy, entropy and temperature are important in chemical reactions.
@stefano.massari, I paid out 0.581 HIVE and 0.000 HBD to reward 1 comments in this discussion thread.