25-02-2024 - Physics - Radiative heat exchange in curved cavities [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
25-02-2024 - Physics - Radiative heat exchange in curved cavities [EN]-[IT]
Basic concepts
In thermodynamics there are several basic concepts, below we see one.
Usage of mixtures
It may happen that the system is in an intermediate phase and there are mainly two phases:
-saturated vapor phase
-solid and liquid phase
In these cases it is convenient to describe the system using the x content of the dry steam.
The formula for title x is as follows:
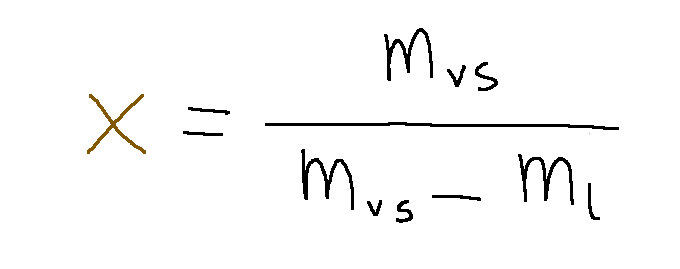
Where:
mvs = mass of dry vapor found in the phase under consideration;
ml = mass of liquid+vapour (mixture) found in the phase under consideration.
Radiative heat exchange in curved cavities
A system in which heat exchange occurs can be analyzed with its electrical analogue.
Let's consider having a gray cavity made up of a convex surface (A1) that is completely surrounded by another (A2).
Also in this case we can obtain the electrical analogue of the system and study the heat exchange.
Below is the electrical analogue of the system we talked about above.
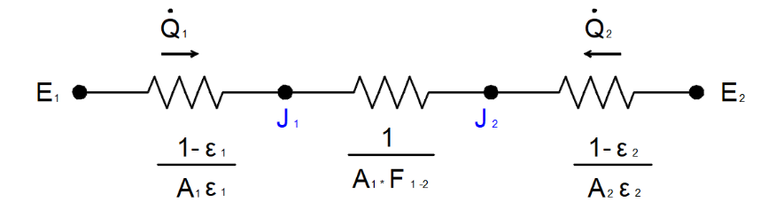
Considerations:
F1-1 = 0
F1-2 = 1
F2-1 = A1/A2
F2-2 = 1 – (A1/A2)
We will therefore have that:
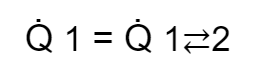
If A1 is much less than A2 the above formula would be written as follows.
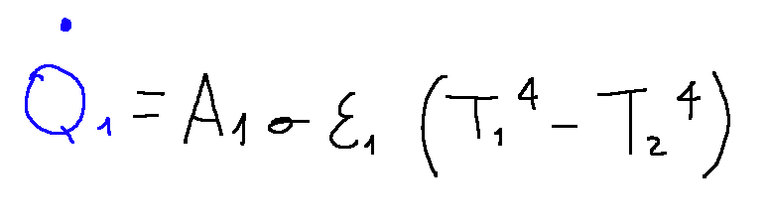
Conclusions
When analyzing radiative heat transfer we can facilitate the analysis by running and studying its electrical analogue.
Request
Have you ever tried to transform a thermodynamic system with heat exchange into its electrical analogue?

25-02-2024 - Fisica - Scambio termico radiativo in cavità curve [EN]-[IT]
Concetti base
Nella termodinamica ci diversi concetti base, qui di seguito ne vediamo uno.
Utilizzo delle miscele
Può capitare che il sistema si trovi in una fase intermedia e queste fasi sono principalmente due:
-fase di vapore saturo
-fase di solido e liquido
In questi casi conviene descrivere il sistema utilizzando il titolo x del vapore secco.
La formula del titolo x è la seguente:
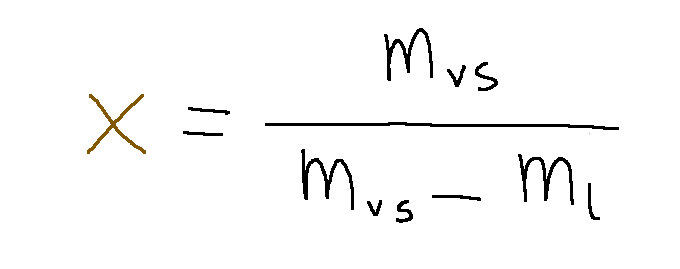
Dove:
mvs = massa del vapore secco che si trova nella fase in considerazione;
ml = massa di liquido+vapore (miscela) che si trova nella fase in considerazione.
Scambio termico radiativo in cavità curve
Un sistema in cui avviene uno scambio termico può essere analizzato con il suo analogo elettrico.
Prendiamo in considerazione di avere una cavità grigia costituita da una superficie convessa (A1) che è circondata completamente da un’altra (A2).
Anche in questo caso possiamo ricavare l’analogo elettrico del sistema e studiare lo scambio termico.
Qui di seguito l’analogo elettrico del sistema di cui abbiamo parlato sopra.

Considerazioni:
F1-1 = 0
F1-2 = 1
F2-1 = A1/A2
F2-2 = 1 – (A1/A2)
Avremo quindi che:
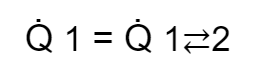
Se A1 è molto minore di A2 la formula qui sopra si scriverebbe nella seguente maniera.
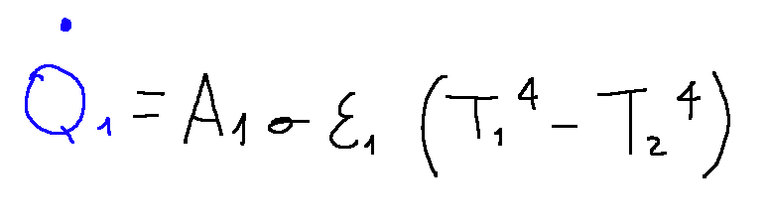
Conclusioni
Quando si analizza lo scambio termico radiativo possiamo facilitare l'analisi eseguendo e studiando il suo analogo elettrico.
Domanda
Avete mai provato a trasformare un sistema termodinamico con scambio termico in un suo analogo elettrico?
THE END
Heat to eletric not yet hehhee thanks for the class
`
Want to Know more about Hivepakistan?
Ping Us On Hive Pakistan Discord server
To support HivePakistan, delegate Hive Power to hivepakistan and earn 90% curation reward :)
Here are some handy links for delegation
A delegation of 500 or more HP makes you earn Hivepakistan supporter badge.
`
Thanks for your support
This formula is a very long one and I’m sure that I will forget it
Incase not to forget, I wrote it somewhere already
The study of radiative heat exchange in cavities with curved surfaces is complex and in my opinion many of us can agree here. Let's even see the temperature terms that have the power at 4
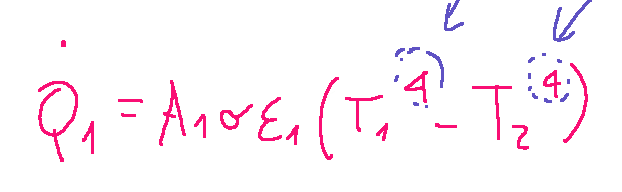
Heat exchange can really be devastating most of the time most especially when you are having a tough time to understand
I think one of the most interesting things about this article is to note how the temperature factor affects heat exchange.
Let's consider the heat exchange in cavities with curved surfaces and write its relationship. I report it below.
Note how the temperature terms are considered to the fourth mathematical power
Therefore, when the temperature is raised, the radiative heat exchange in cavities with curved surfaces could occur in greater quantities.
Non l'ho mai fatto.
Ti auguro una felice giornata
Grazie per aver risposto. In effetti trasformare un sistema termodinamico nel suo analogo elettrico è più un lavoro da termotecnici, di solito altre figure professionali non affrontano questo esercizio.
If only I have hard teachers like you in my early days in school, it will have been much more better for me to understand some subjects
HI @biyimi , Studying radiative heat exchange in cavities with curved surfaces is however a complex study. I believe that even the best can admit this. It should be noted that the heat exchange in cavities with curved surfaces is not represented by the following formula in which the temperatures are erroneously inverted.
The correct formula is as follows