23-07-2024-Physics-Mass flow [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
23-07-2024-Physics-Mass flow [EN]-[IT]
Mass flow rate
Below is an exercise regarding what was written in question. I will try to provide the necessary information to understand and carry out this exercise even without profound knowledge of the topic.
Brief description about the topic
Mass flow rate is a physical quantity that indicates the mass of a fluid flowing through a section per unit time. This physical quantity is also called mass flow rate.
If we refer to the International System, the unit of measurement of mass flow is kg/s
Exercise
A compressor compresses an air flow rate of 1000 m3/h from a pressure of 2 bar and a temperature of 288 K to a pressure of 6 bar. Assuming ideal compression, how much power is needed? Assume cp=1.005 kj/kgk, k=1.4 and R=0.287 kj/kgK
Procedure
In this exercise we have various data that will help us discover other things, for now let's identify what exactly we need.
Regarding the mass flow rate we need the volumetric flow rate and to know the density of the air in initial conditions.
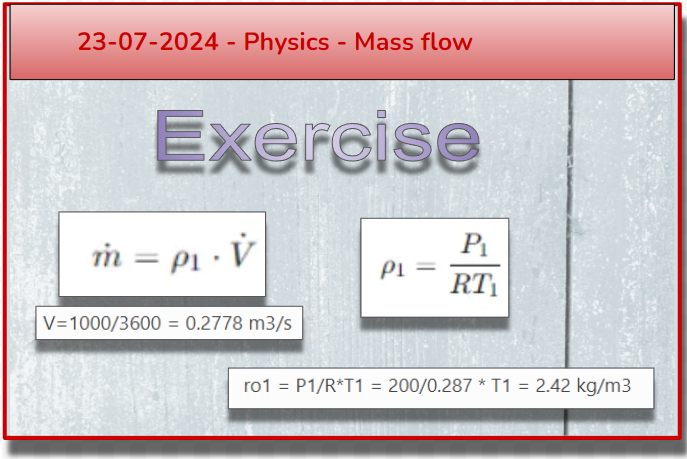
Below is the mass flow formula:
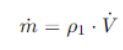
The volumetric flow rate is an operating data

while we will have to calculate the density of the air.
We therefore divide the exercise into two parts to then reach the final step:
1-Calculation of the volumetric flow rate in m3/s
2-Calculation of air density at initial conditions
-1-
Let's transform the volumetric flow data that the exercise gives us into m3/s
V=1000/3600 = 0.2778 m3/s
-2-
Now let's calculate the density of air (ro1)

In this case the density of the air is the initial pressure (P1) divided by the specific gas constant (R) multiplied by the initial temperature.
Below is the formula:
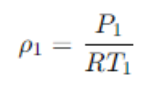
So we will have that:
ro1 = P1/R*T1 = 200/0.287 * T1 = 2.42 kg/m3
-Final Step-
Now we have the two pieces of data we need. Recall that the mass flow rate in this case is the density of the air multiplied by the volumetric flow rate.
Below is the formula:
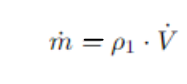
so we will have that:
m = ro1 * V = 2.42 * 0.2778 = 0.672 kg/s
Result
m = 0.672 kg/s
*Conclusion
The data needed to calculate the mass flow rate were, the volumetric flow rate, the initial pressure, the initial temperature and the specific gas constant.
Request
Have you ever tried to calculate mass flow rate? Have you ever done mass flow exercises at school?

ITALIAN
23-07-2024-Fisica-Portata di massa [EN]-[IT]
Portata di massa
Qui di seguito un esercizio a riguardo di quanto scritto in oggetto. Cercherò di fornire le indicazioni necessarie per comprendere e svolgere questo esercizio anche senza una profonda conoscenza dell’argomento.
Breve descrizione a riguardo dell’argomento
La portata di massa è una grandezza fisica che indica la massa di un fluido che scorre attraverso una sezione nell'unità di tempo. Questa grandezza fisica è chiamata anche portata massica.
Se ci riferiamo al Sistema Internazionale l'unità di misura della portata massica è kg/s
Esercizio
Un compressore comprime una portata di aria pari a 1000 m3/h dalla pressione di 2 bar e temperatura di 288 K alla pressione di 6 bar. Ipotizzando la compressione ideale a quanto ammonta la potenza necessaria? Si assuma cp=1,005 kj/kgk, k=1,4 e R=0,287 kj/kgK
Svolgimento
In questo esercizio abbiamo diversi dati che ci aiuteranno a scoprire altre cose, per ora andiamo ad identificare cosa esattamente ci serve.
Per quanto riguarda la portata massica abbiamo bisogno della portata volumetrica e di sapere la densità dell'aria in condizioni iniziali.
Qui di seguito la formula della portata massica:
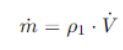
La portata volumetrica è un dato dell'esercizio

mentre la densità dell'aria dovremo calcolarcela.
Dividiamo l'esercizio quindi in due parti per giungere poi allo step finale:
1-Calcolo della portata volumetrica in m3/s
2-Calcolo della densità dell'aria a condizioni iniziali
-1-
Trasformiamo il dato della portata volumetrica che ci da l'esercizio in m3/s
V=1000/3600 = 0,2778 m3/s
-2-
Ora calcoliamo la densità dell'aria (ro1)

In questo caso la densità dell'aria è la pressione iniziale (P1) fratto la costante specifica del gas (R) moltiplicato per la temperatura iniziale.
Qui di seguito la formula:
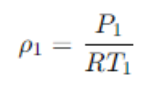
Quindi avremo che:
ro1 = P1/R*T1 = 200/0,287 * T1 = 2,42 kg/m3
-Passo Finale-
Ora abbiamo i due dati che ci servono. Ricordiamo che la portata massica in questo caso è la densità dell'aria moltiplicato per la portata volumetrica.
Qui di seguito riporto la formula:
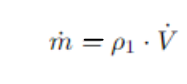
quindi avremo che:
m = ro1 * V = 2,42 * 0,2778 = 0,672 kg/s
Risultato
m = 0,672 kg/s
*Conclusione
I dati necessari per calcolare la portata massica sono stati, la portata volumetrica, la pressione iniziale, la temperatura iniziale e la costante specifica del gas.
Domanda
Avete mai provato a calcolare la portata massica? A scuola avete mai fatto esercizi riguardo la portata massica?
THE END
This topic made me reminisce my high school days about how I ran away from this particular topic
I could remember how I used to solve problems on mass flow rate in our Process Engineering back then😂
But honestly, I might have forgotten a lot about it. Thank you for this reminder.
Congratulations, you received an ecency upvote through the curator @ahmedhayat. Keep spreading love through ecency
This topic is really simple but getting the formula is the problem
It’s quite difficult
!discovery 30
@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 18/48) Liquid rewards.
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program