21-03-2024 - Physics - Thermodynamic systems (1/13) [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
21-03-2024 - Physics - Thermodynamic systems (1/13) [EN]-[IT]
Thermodynamic systems
Thermodynamics
First of all, let's define what we mean by thermodynamics. Thermodynamics is the science that studies, from a macroscopic point of view, the modifications undergone by a system as a result of the transfer of energy, in the form of heat and work.
The system
One of the fundamental concepts of thermodynamics is the system. So we need to define what we mean by system. By system we mean a quantity of matter, or a defined quantity of space that we intend to study.
control surfaces
Another important concept in thermodynamics is control surfaces. These are simply the walls that border the system.
the environment
Another fundamental concept of thermodynamics is the environment. What does the environment represent? The environment is everything that is external to the system, and is able to interact with it.
Closed systems
The first systems to study to begin to understand thermodynamics are closed systems. So let's define what a closed system is. A closed system in thermodynamics is a system that does not allow mass exchange with the environment
internal energy
One of the most important concepts in thermodynamics, perhaps the fundamental one, is that of internal energy. So now we need to clarify what the internal energy of a thermodynamic system is. The internal energy of a thermodynamic system is the change in energy that occurs following a transformation in a thermodynamic system.
Every time we carry out a transformation in a thermodynamic system, there will always be a change in energy, energy which is called internal energy, identified with the letter U.
anegotic surfaces
Anergotic surfaces are surfaces that do not allow workflows.
Adiabatic surfaces
Adiabatic surfaces are surfaces that do not allow heat flow.
diathermic surfaces
Diathermic surfaces are surfaces that allow heat flows
The general report
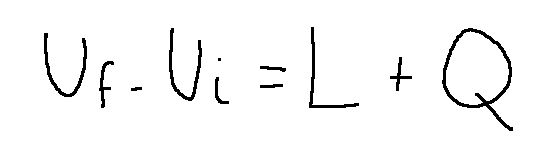
Which we can also write like this:
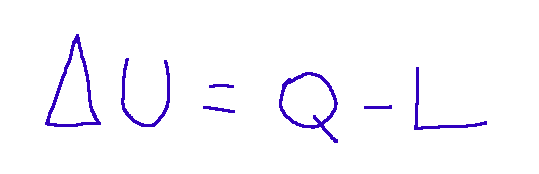
Entropy
Entropy in thermodynamics is a quantity that is interpreted as a measure of the disorder present in a system. It is generally represented by the letter S and is measured in joules divided by kelvins (J/K).
Entropy postulates
Entropy is a state function, that is:
- S = S (m,V,U)
- it is additive
- has production >= 0
- In an isolated system, the state of equilibrium that is reached by eliminating an internal constraint is such as to maximize the entropy, compatibly with other constraints of the system.
entropy, magnitude
Entropy is an extensive quantity
dU expression
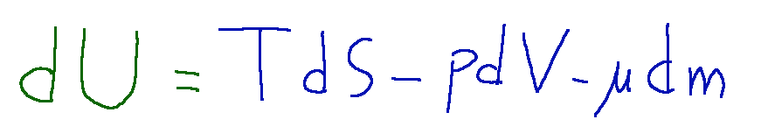
From this expression we deduce that the product between the extensive and intensive quantities, dimensionally, is equal to an energy.
Furthermore we can deduce that each intensive quantity corresponds to its extensive quantity.
Formula of an isolated system
The formula representing the second law of thermodynamics for an isolated system is the following:

Since entropy is a quantity that can vary according to flows and production, its balance will have the production term different from zero (in particular, it will be positive)
The balance of S (entropy), in an isolated system i.e. with flow = 0, is equal to a production greater than or equal to 0
Conclusions
In thermodynamics, systems, the environment and control surfaces are fundamental concepts that, if not well understood, will make the study of thermodynamics very complicated.
Request
Did you study thermodynamics in school? Does thermodynamics have anything to do with your work?
THE END

21-03-2024 - Fisica - Sistemi termodinamici (1/13) [EN]-[IT]
Sistemi termodinamici
La termodinamica
Innanzitutto definiamo che cosa si intende per termodinamica. La termodinamica è la scienza che studia, dal punto di vista macroscopico, le modificazioni subite da un sistema in conseguenza del trasferimento di energia, sotto forma di calore e lavoro.
Il sistema
Uno dei concetti fondamentali della termodinamica è il sistema. Quindi dobbiamo definire che cosa si intende per sistema. Si intende per sistema una quantità di materia, oppure una definita quantità di spazio che si intende studiare.
superfici di controllo
Un altro concetto importante in termodinamica sono le superfici di controllo. Queste sono semplicemente le pareti che delimitano il sistema.
l’ambiente
Un altro concetto fondamentale della termodinamica è l’ambiente. Che cosa rappresenta l’ambiente? L’ambiente è tutto ciò che è esterno al sistema, ed è in grado di interagire con esso.
I sistemi chiusi
I primi sistemi da studiare per iniziare a comprendere la termodinamica sono i sistemi chiusi. Andiamo quindi a definire che cos’è un sistema chiuso. Un sistema chiuso in termodinamica è un sistema che non consente scambi di massa con l’ambiente
energia interna
Uno dei concetti più importanti della termodinamica, forse il fondamentale, è quello dell’energia interna. Quindi ora bisogna chiarire che cos’è l’energia interna di un sistema termodinamico. L’energia interna di un sistema termodinamico è la variazione di energia che si verifica in seguito ad una trasformazione in un sistema termodinamico.
Ogni volta che operiamo una trasformazione in un sistema termodinamico, risulterà sempre una variazione di energia, energia che viene chiamata energia interna, identificata con la lettera U.
superfici anergotiche
Le superfici anergotiche sono superfici che non consentono flussi di lavoro.
Superfici adiabatiche
Le superfici adiabatiche sono le superfici che non consentono flussi di calore.
superfici di diatermiche
Le superfici di diatermiche sono superfici che consentono flussi di calore
La relazione generale
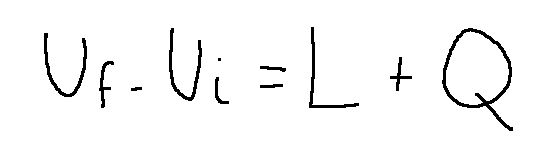
Che possiamo scrivere anche così:
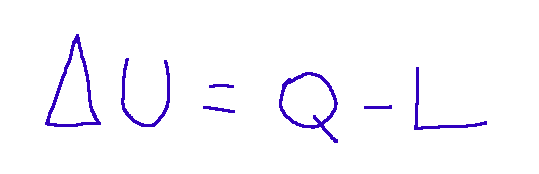
Entropia
L'entropia in termodinamica è una grandezza che viene interpretata come una misura del disordine presente in un sistema. Viene generalmente rappresentata dalla lettera S e si misura in joule fratto kelvin (J/K).
Postulati dell’entropia
L’entropia è una funzione di stato, cioè:
- S = S (m,V,U)
- è additiva
- ha produzione >= 0
- In un sistema isolato lo stato di equilibrio che si raggiunge eliminando un vincolo interno, è tale da rendere massima l'entropia, compatibilmente con altri vincoli del sistema.
entropia, grandezza
L'entropia è una grandezza estensiva
Espressione dU
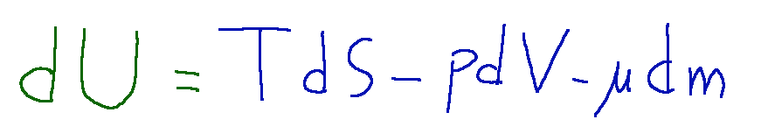
Da questa espressione deduciamo che il prodotto tra la grandezza estensiva e quella intensiva, dimensionalmente, è uguale ad un’energia.
Inoltre possiamo dedurre che ad ogni grandezza intensiva corrisponde una sua grandezza estensiva.
Formula di un sistema isolato
La formula che rappresenta la seconda legge della termodinamica per un sistema isolato è la seguente:

Essendo l’entropia una grandezza che può variare per flussi e per produzione, il suo bilancio avrà il termine produzione diverso da zero (in particolare, sarà positivo)
Il bilancio di S (entropia), in un sistema è isolato cioè con flusso = 0, è uguale ad una produzione maggiore o uguale a 0
Conclusioni
In termodinamica i sistemi, l'ambiente e le superfici di controllo sono concetti fondamentali che se non si comprendo bene, renderà lo studio della termodinamica molto complicato.
Domanda
Avete studiato termodinamica a scuola? La termodinamica ha a che fare con il vostro lavoro?
THE END
👏 Keep Up the good work on Hive ♦️ 👏
🙏 Don't forget to Support Back 🙏
There is different register word in English. In some aspect of life, they see system as a way of running things but in physics,it quite looks so different
HI @precab and thanks for being here. In this case we are talking about thermodynamic systems. So the first thing we need to do is try to understand what a thermodynamic system is. By thermodynamic system we mean a quantity of matter, or a defined quantity of space, which we intend to study.
It’s good to know that we got back to physics
I had a lovely time learning
Thanks for your kind words. In fact, I have decided to make a series of 13 articles where I summarize what I know about thermodynamics. Then you will see that I will exhaust my technical physics resources. Meanwhile, I wrote this article to remind you what thermodynamics is. Thermodynamics is the science that studies from a macroscopic point of view the modifications undergone by a system as a result of the transfer of energy. This energy transfer occurs in the form of heat or work.
!discovery 25
Grazie per la segnalazione.. e per il costante supporto.
In questo post ci sono delle definizioni base per quanto riguarda la termodinamica, come le seguenti:
-Un ambiente, in termodinamica, è tutto ciò che è esterno al sistema ed è in grado di interagire con esso.
-Un sistema chiuso è un sistema che non constente scambi di massa con l'ambiente.
-L'energia interna di un sistema termodinamico è la variazione di energia che si verifica in seguito ad una trasformazione in un sistema termodinamico.
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
grazie per l'appoggio
In questo post parlo di alcuni concetti e definizioni basilari. Ad esempio, in termodinamica, ci sono dei termini basilari, che se non sono conosciuti potrebbero portare alla non compresione dell'argomento. Ad esempio i seguenti:
-Superfici anergotiche = superfici che non consentono flussi di lavoro
-Superfici adiabatiche = superfici che non consentono flussi di calore
-Superfici diatermiche = che consente flussi di calore
!PIZZA
NO, non c'entra niente con il mio lavoro, ancora NO, che negatività ho hahaha, ma sono sincero, lo sai
Oggi la professione più toccata da questo argomento direi che è quella del termotecnico. Grazie per aver lasciato un commento !BEER
View or trade
BEER.Hey @lupega, here is a little bit of
BEERfrom @stefano.massari for you. Enjoy it!Did you know that <a href='https://dcity.io/cityyou can use BEER at dCity game to buy cards to rule the world.
$PIZZA slices delivered:
@stefano.massari(1/5) tipped @discovery-it