18-12-2024 - Computer Basics - Calculator, memories [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
18-12-2024 - Computer Basics - Calculator, memories [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction on the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_89)
Calculator, memories
The memories of a calculator are used for data storage and management.
They are mainly divided into 4 categories:
1-Volatile memory (such as RAM):
Characteristics: Data is lost when the power is interrupted.
Function: It temporarily stores the data and instructions necessary for the execution of programs in progress. It is very fast, but of limited capacity.
2-Non-volatile memory (such as ROM and mass storage devices such as HDD or SSD):
Characteristics: Data is retained even without power.
Function: It stores permanent information, such as firmware (ROM) or user data (HDD/SSD). ROM is read-only, while mass storage devices are slower but offer very high storage capacity.
3-Cache: Small and fast, used to store data that is frequently used by the CPU, thus improving system performance.
4-CPU Registers: Ultra-fast memories located inside the CPU, used to store temporary data and intermediate results of operations.
There are also magnetic disk memories.
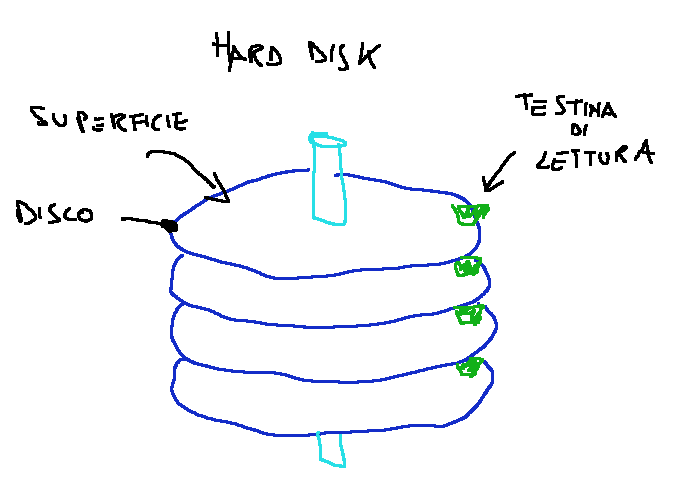
There are mainly two magnetic disk memories: the hard disk (HD) and the floppy disk.
The hard disk is a mass storage device that uses one or more magnetic disks to store data and represents the main secondary memory of a computer since it contains all the system software programs, applications and documents created. The hard disk is essentially made up of one or more plates made of aluminum or glass and coated with ferromagnetic material. The set of tracks at equal distance from the center and on different surfaces is called a cylinder.
Here are some information pills about the subject in question
1-capacity of a memory
The capacity of a memory is understood as the number of bits that can be stored
The capacity of a memory refers to the total amount of data that can be stored inside it. This quantity is measured in bits, although more commonly it is expressed in bytes, kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB) or terabytes (TB), where:
1 byte = 8 bits
2-The access time
The access time of a memory is the time that elapses between the instant in which an address is presented to the memory and the instant in which the data is stored or made available.
The access time of a memory represents the interval of time necessary for a system to access a stored data.
3-access to locations
In RAM memory, access to memory locations is uniform.
In RAM (Random Access Memory), access to memory locations is uniform, which means that all memory cells can be reached directly and with the same access time, regardless of their physical location.
4-access speed
The access speed of RAM memory is 10-20 nanoseconds
This speed is crucial to ensure that the CPU can access data without significant delays, thus improving the overall performance of the system.
5-memory order
If we put memories in order from the fastest to the slowest we would have the following list: CPU registers - cache - RAM - mass storage.
The order of speed of memories in a computer system is determined by their position with respect to the CPU and the technology used:
6-Associative mode
Associative mode is a memory access mode
Associative mode is a memory access technique used mainly in cache memories and in some specialized memories (such as associative memories or CAM - Content Addressable Memory).
7-transfer speed
The transfer speed of a memory is the amount of data that can be transferred from the memory in the unit of time
The transfer speed of a memory indicates the amount of data that can be transferred in the unit of time (for example, in seconds). It is measured in bytes per second (B/s), megabytes per second (MB/s), or gigabits per second (Gbps), depending on the type of memory considered.
8-volatile memories
In volatile memories, information is maintained only in the presence of power.
Volatile memories are memories that lose the data stored when the power is interrupted. Typical examples of volatile memories include RAM (Random Access Memory), which is emptied every time the computer is turned off or restarted.
9-Cache memory
Cache memory is a small and fast memory.
Cache memory is a small but very fast memory, used to temporarily store data that the CPU accesses most frequently.
10-ROM Memory
ROM memory is read-only memory.
ROM (Read-Only Memory) is a type of memory that only allows reading of stored data. The data is written only once, during the manufacturing process, and cannot be modified (or can be modified only with difficulty, as in the case of programmable ROMs).
Conclusions
The memories of a computer are essential components for storing and managing data.
Question
When you buy a PC, do you give importance to the capacity of the memories?

[ITALIAN]
18-12-2024 - Basi di informatica - Calcolatore, le memorie [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_89)

Calcolatore, le memorie
Le memorie di un calcolatore vengono usate per l'archiviazione e la gestione dei dati.
Si suddividono principalmente in 4 categorie:
1-Memoria volatile (come la RAM):
Caratteristiche: I dati sono persi quando l'alimentazione viene interrotta.
Funzione: Memorizza temporaneamente i dati e le istruzioni necessari per l'esecuzione dei programmi in corso. È molto veloce, ma di capacità limitata.
2-Memoria non volatile (come la ROM e le memorie di massa come HDD o SSD):
Caratteristiche: I dati sono conservati anche senza alimentazione.
Funzione: Memorizza informazioni permanenti, come il firmware (ROM) o i dati utente (HDD/SSD). La ROM è di sola lettura, mentre le memorie di massa sono più lente ma offrono capacità di archiviazione molto elevate.
3-Cache: Piccola e veloce, usata per memorizzare i dati che vengono frequentemente utilizzati dalla CPU, migliorando così le prestazioni del sistema.
4-Registri della CPU: Memorie ultra-veloci situate all'interno della CPU, utilizzate per memorizzare dati temporanei e risultati intermedi delle operazioni.
Ci sono anche le memorie disco magnetico.
Le memorie a disco magnetico sono principalmente due: l’hard disk (HD) e il floppy disk.
L’hard disk è un dispositivo di massa che usa uno o più dischi magnetici per l’archiviazione dei dati e rappresenta la principale memoria secondaria di un calcolatore poiché contiene tutti i programmi del software di sistema, gli applicativi e i documenti creati. L’hard disk è formato essenzialmente da uno o più piatti realizzati in alluminio o vetro e rivestiti di materiale ferromagnetico. L’insieme delle tracce ad uguale distanza dal centro e su superfici diverse è detto cilindro.
Qui di seguito alcune pillole di informazioni a riguardo dell’argomento in oggetto
1-capacità di una memoria
La capacità di una memoria è intesa come il numero di bit che possono essere memorizzati
La capacità di una memoria si riferisce alla quantità totale di dati che può essere memorizzata al suo interno. Questa quantità è misurata in bit, anche se più comunemente viene espressa in byte, kilobyte (KB), megabyte (MB), gigabyte (GB) o terabyte (TB), dove:
1 byte = 8 bit
2-Il tempo di accesso
Il tempo di accesso di una memoria è il tempo che intercorre tra l’istante in cui un indirizzo è presentato alla memoria e l’istante in cui il dato viene memorizzato o reso disponibile.
Il tempo di accesso di una memoria rappresenta l'intervallo di tempo necessario affinché un sistema acceda a un dato memorizzato.
3-accesso alle locazioni
Nella memoria RAM, l'accesso alle locazioni di memoria è uniforme.
Nella memoria RAM (Random Access Memory), l'accesso alle locazioni di memoria è uniforme, il che significa che tutte le celle di memoria possono essere raggiunte in modo diretto e con lo stesso tempo di accesso, indipendentemente dalla loro posizione fisica.
4-velocità di accesso
La velocità di accesso della memoria RAM è 10-20 nanosecondi
Questa velocità è cruciale per garantire che la CPU possa accedere ai dati senza significativi ritardi, migliorando così le prestazioni complessive del sistema.
5-ordine le memorie
Se mettessimo in ordine le memorie dalle più veloci alle più lente avremo il seguente elenco: registri CPU - cache - RAM - memoria di massa.
L'ordine di velocità delle memorie in un sistema informatico è determinato dalla loro posizione rispetto alla CPU e dalla tecnologia utilizzata:
6-La modalità associativa
La modalità associativa è una modalità di accesso alla memoria
La modalità associativa è una tecnica di accesso alla memoria utilizzata principalmente nelle memorie cache e in alcune memorie specializzate (come le memorie associative o CAM - Content Addressable Memory).
7-velocità di trasferimento
La velocità di trasferimento di una memoria è la quantità di dati trasferibili dalla memoria nell’unità di tempo
La velocità di trasferimento di una memoria indica la quantità di dati che può essere trasferita nell'unità di tempo (ad esempio, in secondi). Viene misurata in byte per secondo (B/s), megabyte per secondo (MB/s), o gigabit per secondo (Gbps), a seconda del tipo di memoria considerata.
8-memorie volatili
Nelle memorie volatili l'informazione è mantenuta solo in presenza di alimentazione.
Le memorie volatili sono memorie che perdono i dati immagazzinati quando l'alimentazione elettrica viene interrotta. Esempi tipici di memorie volatili includono la RAM (Random Access Memory), che viene svuotata ogni volta che il computer viene spento o riavviato.
9-La memoria cache
La memoria cache è una memoria piccola e veloce.
La memoria cache è una memoria piccola ma molto veloce, utilizzata per memorizzare temporaneamente i dati a cui la CPU accede più frequentemente.
10-La memoria ROM
La memoria ROM è memoria di sola lettura.
La memoria ROM (Read-Only Memory) è una tipologia di memoria che consente solo la lettura dei dati immagazzinati. I dati vengono scritti una sola volta, durante il processo di fabbricazione, e non possono essere modificati (o possono esserlo solo con difficoltà, come nel caso delle ROM programmabili).
Conclusioni
Le memorie di un calcolatore sono componenti essenziali per l'archiviazione e la gestione dei dati.
Domanda
Quando acquistate un PC date importanza alla capacità delle memorie?
THE END
!PIZZA
!LOL
!INDEED
lolztoken.com
She really hit the roof!
Credit: reddit
@stefano.massari, I sent you an $LOLZ on behalf of cryptoyzzy
(1/10)
NEW: Join LOLZ's Daily Earn and Burn Contest and win $LOLZ
$PIZZA slices delivered:
@cryptoyzzy(1/5) tipped @stefano.massari
(1/25)
@stefano.massari! @cryptoyzzy Totally agrees with your content! so I just sent 1 IDD to your account on behalf of @cryptoyzzy.
But how do we even know that calculators have memories?
https://x.com/lee19389/status/1869498807924441090
#hive #posh
Fantastico!
Mi ricorda l'esami di informatica all'università :p