18-07-2024 - basic concepts of energy systems - Turbogas [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
18-07-2024 - basic concepts of energy systems - Turbogas [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction regarding the technical topic mentioned in question
(code notes: 260-xxx)
turbogas
Turbogas plants are mainly used for the generation of electricity. To produce energy they use a gas turbine. Operational efficiency and flexibility are among the main characteristics of a gas turbine plant.
gas turbine plant - organic efficiency
The product of auxiliary efficiency and mechanical efficiency gives the so-called
organic efficiency, i.e. the efficiency evaluated through the mechanical power available to the shaft, therefore with only the internal losses of the turbine:
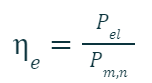
Regarding the mechanical efficiency we can also say the following.
The organic efficiency of a gas turbine plant is a fundamental parameter for evaluating the efficiency of the process of converting the chemical energy of the fuel into mechanical energy.
Gas turbine units - characteristics
It is not correct to think that gas turbine units have low operating temperatures; on the contrary, they operate at very high temperatures to maximize efficiency.
NOTE: The characteristics of the gas turbine groups are: low weight/power value, reduced installation dimensions, rapid commissioning times.
Gas turbine units - electrical efficiency
Electrical efficiency is not a characteristic of gas turbine systems.
NOTE: Gas turbine systems, although very flexible and quick to start, typically do not have the highest electrical efficiencies compared to other power generation technologies.
Brayton cycle - real open
In the case of a real open Brayton cycle, the compression and expansion transformations are considered adiabatic but not reversible.
Important note: The Brayton cycle is the thermodynamic principle underlying the operation of gas turbine systems.
Note 2: The main irreversibilities of a real Brayton-Joule cycle are related to the compression and expansion transformations, which are considered adiabatic non-reversible.
Brayton cycle - closed ideal
In the case of a closed ideal Brayton cycle the efficiency does not depend on the specific heat of the gas.
NOTE: The performance of the ideal Brayton cycle does not depend on the maximum and minimum temperatures, but exclusively on the compression ratio.
NOTE 2: Saying that the efficiency depends on the maximum cycle temperature is incorrect. In the ideal cycle, the efficiency does not directly depend on the maximum temperature of the cycle, but rather on the compression ratio.
NOTE 3: It is not correct to say that in the case of an ideal closed Brayton cycle the efficiency depends solely on the isentropic temperature rise provided by the compressor, indeed we could say that it depends solely on the compression ratio.
NOTE 4: It is not correct to state that in the case of a closed ideal Brayton cycle, as the end compression temperature increases, the average heat introduction temperature decreases. The average heat introduction temperature is influenced by various factors, but is not directly related to the end-of-compression temperature in a way that affects performance in the ideal context considered here.
Conclusions
Gas turbine plants are based on the Brayton cycle and are one of the main technologies for generating electricity.
Request
Have you ever visited or studied a gas turbine plant?

[ITALIAN]
18-07-2024 - basic concepts of energy systems - Turbogas [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento tecnico citato in oggetto
(code notes: 260-xxx)
turbogas
Gli impianti turbogas vengono utilizzati principalmente per la generazione di energia elettrica. Per produrre energia utilizzano una turbina a gas. Efficienza operativa e flessibilità sono tra le caratteristiche principali di un impianto turbogas.
impianto turbogas - rendimento organico
Il prodotto di rendimento degli ausiliari e rendimento meccanico fornisce il cosiddetto
rendimento organico, ovvero il rendimento valutato attraverso la potenza meccanica disponibile all’albero, quindi con le sole perdite interne alla turbina:
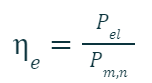
A riguardo del rendimento meccanico possiamo dire anche quanto segue.
Il rendimento organico di un impianto turbogas è un parametro fondamentale per valutare l'efficienza del processo di conversione dell'energia chimica del combustibile in energia meccanica.
Gruppi turbogas - caratteristiche
Non è corretto pensare che i gruppi turbogas abbiano basse temperature di esercizio, al contrario, operano a temperature molto elevate per massimizzare l'efficienza.
NOTA: Le caratteristiche dei gruppi turbogas sono: basso valore peso/potenza, ingombri di installazione ridotti, rapidi tempi di messa in servizio.
Gruppi turbogas - efficienza elettrica
L’efficienza elettrica non è una caratteristica degli impianti turbogas.
NOTA: Gli impianti turbogas, sebbene siano molto flessibili e rapidi nell'avviamento, tipicamente non hanno le più elevate efficienze elettriche rispetto ad altre tecnologie di generazione di energia.
Ciclo Brayton - reale aperto
Nel caso di ciclo di Brayton reale aperto le trasformazioni di compressione ed esapansione sono considerate adiabatiche ma non reversibili.
Nota importante: Il ciclo di Brayton è il principio termodinamico alla base del funzionamento degli impianti turbogas.
Nota 2: Le principali irreversibilità di un ciclo Brayton-Joule reale sono legate alle trasformazioni di compressione ed espansione, che sono considerate adiabatiche non reversibili.
Ciclo Brayton - ideale chiuso
Nel caso di ciclo Brayton ideale chiuso il rendimento non dipende dal calore specifico del gas.
NOTA: Il rendimento del ciclo Brayton ideale non dipende dalle temperature massima e minima, ma esclusivamente dal rapporto di compressione.
NOTA 2: Dire che il rendimento dipende dalla temperatura massima di ciclo non è corretto. Nel ciclo ideale, il rendimento non dipende direttamente dalla temperatura massima del ciclo, ma piuttosto dal rapporto di compressione.
NOTA 3: Non è corretto dire che nel caso di ciclo Brayton ideale chiuso il rendimento dipende unicamente dall'innalzamento di temperatura isentropico fornito dal compressore, anzi potremmo affermare che dipende unicamente dal rapporto di compressione.
NOTA 4: Non è corretto affermare che nel caso di ciclo Brayton ideale chiuso all'aumentare della temperatura di fine compressione diminuisce la temperatura media di introduzione del calore. La temperatura media di introduzione del calore è influenzata da vari fattori, ma non è direttamente correlata alla temperatura di fine compressione in modo tale da influenzare il rendimento nel contesto ideale considerato qui.
Conclusioni
Gli impianti turbogas sono basati sul ciclo di Brayton e sono una delle principali tecnologie per la generazione di energia elettrica.
Domanda
Avete mai visitato o studiato un impianto turbogas?
THE END
👏 Keep Up the good work on Hive ♦️ 👏
❤️ @reeta0119 suggested sagarkothari88 to upvote your post ❤️
🙏 Don't forget to Support Back 🙏
Energy system is really key that we need to sustain ourselves and so much to learn from this
I’ve seen a gas turbine plant before but I didn’t really take bit of so many things though
Great explanations as always brother. Keep em coming always
This is like the fullest explanation of the gas turbine course
It was a good one
Thank you!